Deep Scientific Insights on eflornithine hydrochloride's R&D Progress, Mechanism of Action, and Drug Target
Eflornithine hydrochloride's R&D Progress
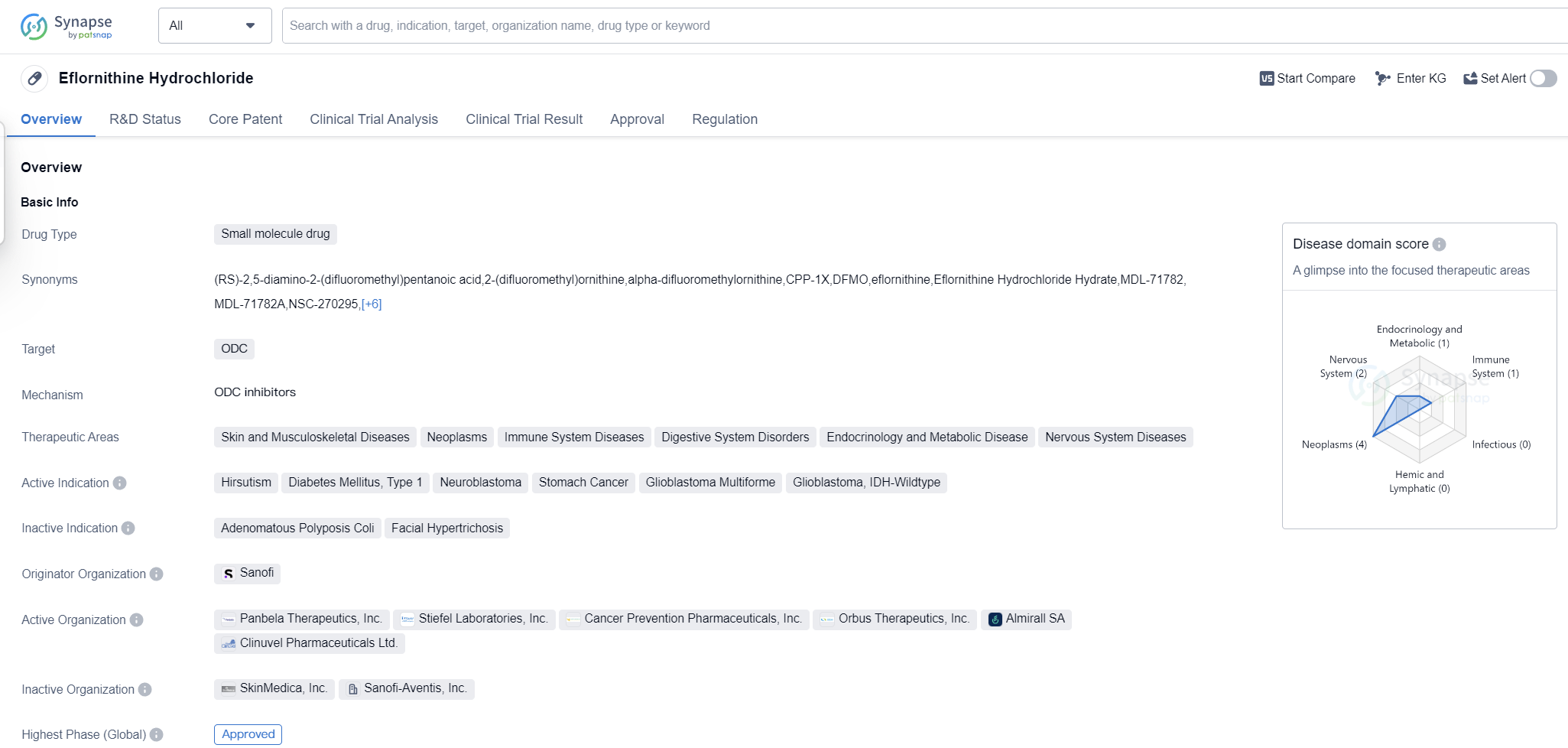
Eflornithine Hydrochloride is a small molecule drug that primarily targets the enzyme ODC (ornithine decarboxylase). It has been approved for use in various therapeutic areas, including Skin and Musculoskeletal Diseases, Neoplasms, Immune System Diseases, Digestive System Disorders, Endocrinology and Metabolic Disease, and Nervous System Diseases.
The drug has shown efficacy in treating several active indications, including Hirsutism (excessive hair growth), Diabetes Mellitus Type 1, Neuroblastoma (a type of cancer that forms in nerve tissue), Stomach Cancer, Glioblastoma Multiforme (a type of brain tumor), and Glioblastoma with IDH-Wildtype.
Eflornithine Hydrochloride was first approved in the United States in November 1990. It is worth noting that the drug has received orphan drug designation, indicating its potential to treat rare diseases or conditions.
The originator organization of Eflornithine Hydrochloride is Sanofi, a multinational pharmaceutical company. Sanofi is known for its expertise in developing innovative drugs and therapies across various therapeutic areas.
The highest R&D phase of this drug is approved. This suggests that the drug has successfully completed clinical trials and met the necessary regulatory requirements for market authorization.
👇Please click on the image below to directly access the latest data (R&D Status | Core Patent | Clinical Trial | Approval status in Global countries) of this drug.
Mechanism of Action for eflornithine hydrochloride: ODC inhibitors
ODC inhibitors are a type of drug that target and inhibit the activity of the enzyme ornithine decarboxylase (ODC). ODC is responsible for the conversion of ornithine into putrescine, which is a key step in the biosynthesis of polyamines. Polyamines play important roles in cell growth, proliferation, and differentiation.
From a biomedical perspective, ODC inhibitors are used in the field of cancer research and treatment. Cancer cells often exhibit increased ODC activity, leading to higher levels of polyamines and promoting tumor growth. By inhibiting ODC, these inhibitors can help reduce polyamine levels and potentially slow down or inhibit cancer cell growth.
ODC inhibitors have shown promise in preclinical and clinical studies, particularly in certain types of cancer such as colorectal cancer, prostate cancer, and neuroblastoma. They are being investigated as potential therapeutic agents either as standalone treatments or in combination with other anticancer drugs.
It is important to note that ODC inhibitors may have side effects, and their use should be carefully monitored by healthcare professionals. Additionally, further research is needed to fully understand the potential benefits and limitations of ODC inhibitors in various disease contexts.
Drug Target R&D Trends for eflornithine hydrochloride
The ODC, or ornithine decarboxylase, is an enzyme that plays a crucial role in the human body. It is involved in the synthesis of polyamines, which are essential for cell growth, proliferation, and differentiation. Polyamines are involved in various physiological processes, including DNA replication, protein synthesis, and cell signaling. ODC regulates the production of polyamines by catalyzing the decarboxylation of ornithine, an amino acid, to form putrescine. Dysregulation of ODC activity has been linked to various diseases, including cancer, inflammation, and neurodegenerative disorders. Understanding the role of ODC is important for developing therapeutic strategies targeting polyamine metabolism in the pharmaceutical industry.
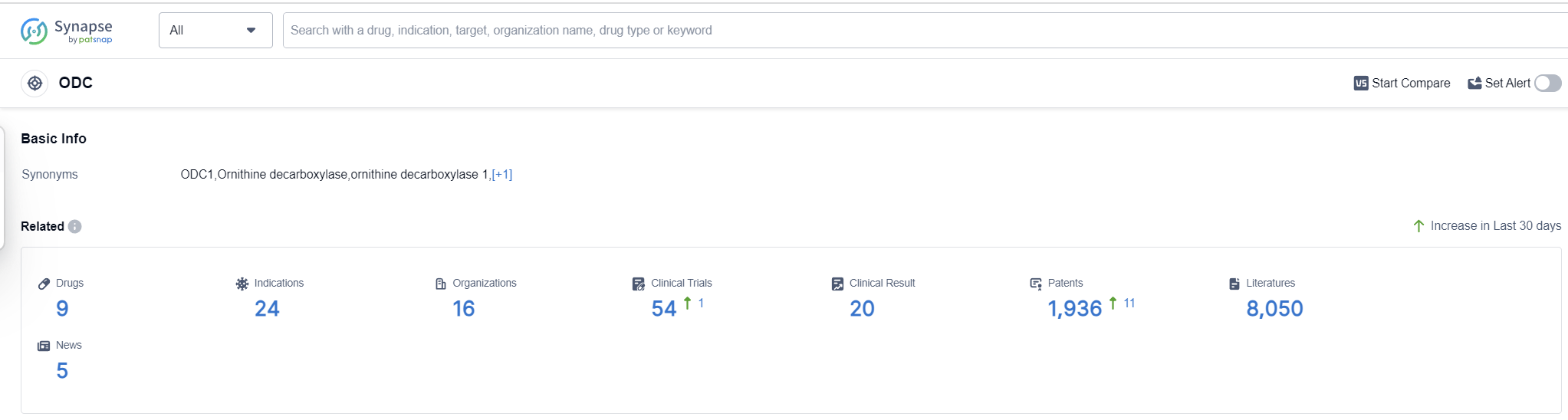
According to Patsnap Synapse, as of 13 Sep 2023, there are a total of 9 ODC drugs worldwide, from 16 organizations, covering 24 indications, and conducting 54 clinical trials.
Target ODC Analysis Report
The analysis of the target ODC reveals a competitive landscape with multiple companies actively developing drugs in various stages. Panbela Therapeutics, Inc. stands out with the highest stage of development, followed by Sanofi, GSK Plc, and Clinuvel Pharmaceuticals Ltd. The approved drugs under the target ODC cover a wide range of indications, indicating the potential to address diverse medical needs. Small molecule drugs are progressing rapidly, with a focus on innovation and potential competition from biosimilars. The development of drugs under the target ODC is spread across different countries/locations, with the United States, European Union, and Australia leading the way. However, the progress in China is not mentioned in the provided data, suggesting a need for further investigation. Overall, the target ODC shows promise for future development and addressing unmet medical needs.
👇Please click on the picture link below for free registration or log in directly if you have a freemium account, you can browse the latest research progress on drugs, indications, organizations, clinical trials, clinical results, and drug patents related to this target
Conclusion
In summary, Eflornithine Hydrochloride is a small molecule drug developed by Sanofi. It targets the enzyme ODC and has been approved for use in various therapeutic areas, including skin and musculoskeletal diseases, neoplasms, immune system diseases, digestive system disorders, endocrinology and metabolic disease, and nervous system diseases. The drug has shown efficacy in treating hirsutism, diabetes mellitus type 1, neuroblastoma, stomach cancer, glioblastoma multiforme, and glioblastoma with IDH-Wildtype. It received its first approval in the United States in November 1990 and has been designated as an orphan drug.