Deep Scientific Insights on Levomepromazine's R&D Progress, Mechanism of Action, and Drug Target
Levomepromazine's R&D Progress
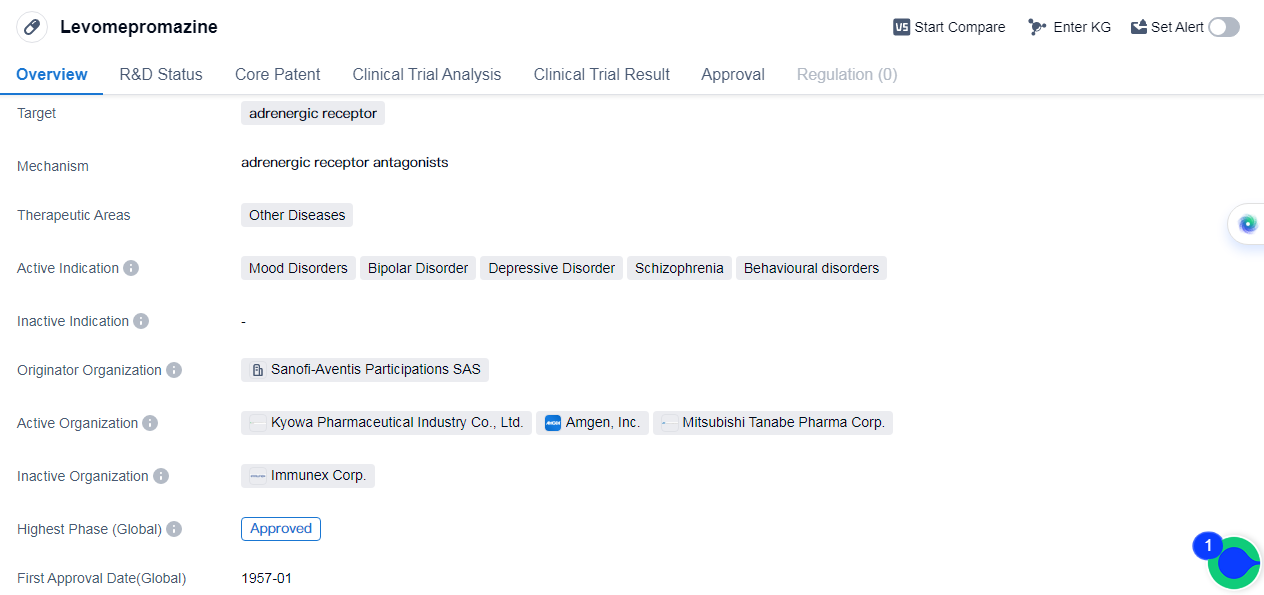
Levomepromazine is a small molecule drug that targets the adrenergic receptor. The drug was first approved globally in January 1957. Levomepromazine is primarily used in the treatment of psychiatric disorders such as mood disorders, bipolar disorder, depressive disorder, schizophrenia, and behavioral disorders. It acts by targeting the adrenergic receptor, which plays a crucial role in regulating the body's response to stress and anxiety. By modulating the activity of this receptor, Levomepromazine helps to alleviate the symptoms associated with these disorders.
The drug is classified as a small molecule, indicating that it consists of relatively low molecular weight and can easily penetrate cell membranes. This property allows Levomepromazine to efficiently interact with its target receptor and exert its therapeutic effects.
The originator organization of Levomepromazine is Sanofi-Aventis Participations SAS, a renowned pharmaceutical company with a strong presence in the industry. As the highest phase of development for this drug is approved, it suggests that Levomepromazine has successfully undergone rigorous clinical trials and demonstrated its safety and efficacy in treating the indicated conditions.
Levomepromazine's first approval date globally can be date to January 1957, indicating that it has been used for several decades. This long history of approval suggests that the drug has stood the test of time and has been widely accepted as an effective treatment option for the specified psychiatric disorders.
👇Please click on the image below to directly access the latest data (R&D Status | Core Patent | Clinical Trial | Approval status in Global countries) of this drug.
Mechanism of Action for Levomepromazine: Adrenergic Receptor Antagonists
Adrenergic receptor antagonists, also known as adrenergic blockers or adrenergic antagonists, are a class of drugs that block the effects of adrenergic receptors. Adrenergic receptors are specific receptors located on the surface of cells that bind to and are activated by neurotransmitters called catecholamines, such as adrenaline and noradrenaline.
These receptors are part of the sympathetic nervous system, which is responsible for the "fight or flight" response. By blocking the adrenergic receptors, adrenergic receptor antagonists inhibit the actions of catecholamines, leading to various physiological effects.
In a biomedical perspective, adrenergic receptor antagonists are commonly used in the treatment of conditions such as hypertension, angina, arrhythmias, heart failure, and certain types of glaucoma. By blocking the effects of catecholamines on the heart and blood vessels, these drugs can help lower blood pressure, reduce heart rate, and improve blood flow.
Adrenergic receptor antagonists can also be used to manage symptoms of conditions like anxiety disorders, migraines, and hyperthyroidism. Additionally, they may be employed during surgical procedures to prevent certain physiological responses, such as elevated blood pressure and heart rate.
It's important to note that there are different subtypes of adrenergic receptors, such as alpha and beta receptors, and adrenergic receptor antagonists can selectively target these subtypes. This selectivity allows for more specific therapeutic effects and can minimize unwanted side effects.
Overall, adrenergic receptor antagonists play a crucial role in regulating the sympathetic nervous system and are valuable therapeutic agents in the management of various medical conditions.
Drug Target R&D Trends for Levomepromazine
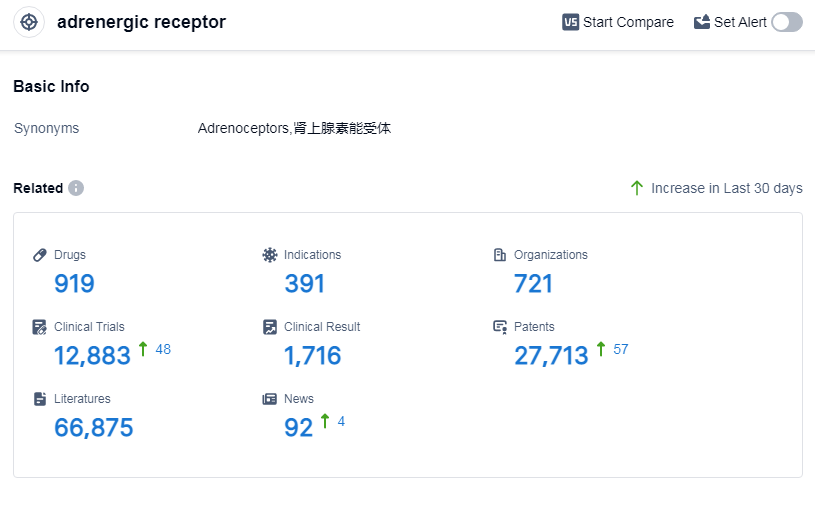
According to Patsnap Synapse, as of 7 Sep 2023, there are a total of 919 adrenergic receptor drugs worldwide, from 721 organizations, covering 391 indications, and conducting 12883 clinical trials.
The target adrenergic receptor is a highly competitive area in the pharmaceutical industry, with companies like Novartis AG, GSK Plc, and AstraZeneca PLC leading the way in R&D progress. The most common indications for drugs targeting this receptor include hypertension, asthma, and common cold. Small molecule drugs are the most rapidly progressing drug type, indicating intense competition in this area. China, the United States, and Japan are the fastest-developing countriesorlocations for drugs targeting the adrenergic receptor. Overall, the future development of the target adrenergic receptor looks promising, with ongoing research and development efforts focused on addressing various indications and improving patient outcomes.
👇Please click on the picture link below for free registration or log in directly if you have a freemium account, you can browse the latest research progress on drugs, indications, organizations, clinical trials, clinical results, and drug patents related to this target
Conclusion
In summary, Levomepromazine is a small molecule drug that targets the adrenergic receptor and is approved for the treatment of various psychiatric disorders. It was first approved globally in 1957 and is developed by Sanofi-Aventis Participations SAS. With its long history of use and established therapeutic indications, Levomepromazine continues to play a significant role in the field of biomedicine.