Loracarbef: Detailed Review of its Transformative R&D Success
Loracarbef's R&D Progress
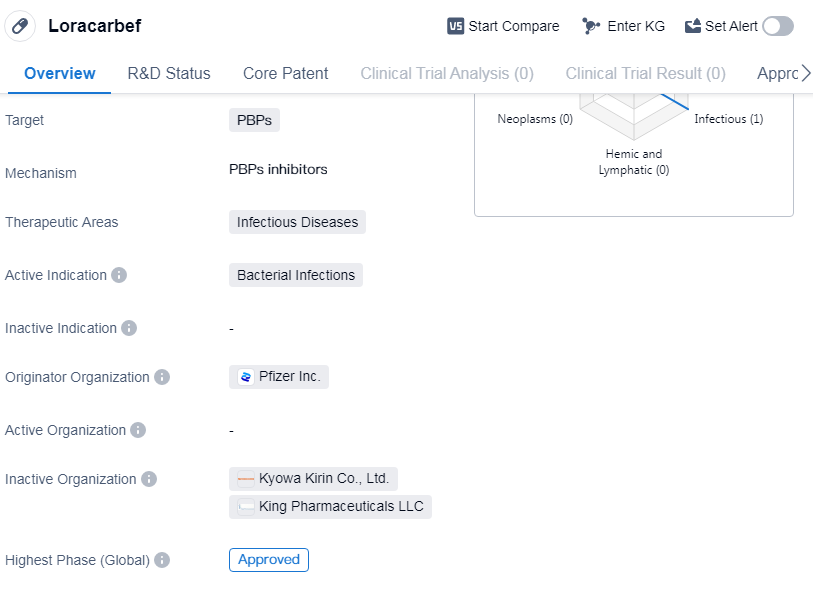
Loracarbef is a small molecule drug that falls under the therapeutic area of infectious diseases. It is primarily used for the treatment of bacterial infections. The drug targets penicillin-binding proteins (PBPs) to exert its therapeutic effects. Loracarbef was first approved by the United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in December 1991, making it available for use in the United States.
The originator organization of Loracarbef is Pfizer Inc., a renowned pharmaceutical company. Pfizer Inc. played a crucial role in the development and commercialization of this drug. Loracarbef has successfully completed all the necessary clinical trials and has reached the highest phase of development, which is the approved stage. This indicates that the drug has met the required safety and efficacy standards set by regulatory authorities.
The approval of Loracarbef in 1991 marked an important milestone in the field of biomedicine. It provided healthcare professionals with a new treatment option for bacterial infections, expanding the range of available therapeutic choices. The drug's mechanism of action, targeting PBPs, allows it to effectively combat bacterial infections by inhibiting cell wall synthesis.
Since its approval, Loracarbef has been widely used in the United States and potentially in other countries as well. Its efficacy and safety profile have been established through rigorous clinical trials and post-marketing surveillance. The drug has demonstrated its ability to effectively treat various types of bacterial infections, contributing to improved patient outcomes.
👇Please click on the image below to directly access the latest data (R&D Status | Core Patent | Clinical Trial | Approval status in Global countries) of this drug.
Mechanism of Action for Loracarbef: PBPs inhibitors
PBPs inhibitors are a type of drugs that target and inhibit the activity of PBPs. PBPs are enzymes found in the cell wall of bacteria and are involved in the synthesis of peptidoglycan, a crucial component of the bacterial cell wall. By inhibiting PBPs, these drugs disrupt the formation of the bacterial cell wall, leading to cell lysis and ultimately bacterial death.
From a biomedical perspective, PBPs inhibitors are important in the field of antimicrobial therapy. They are commonly used to treat bacterial infections caused by susceptible organisms. By specifically targeting PBPs, these inhibitors selectively affect bacteria while sparing human cells, as human cells do not have peptidoglycan in their cell walls. This specificity makes PBPs inhibitors effective antibiotics with a relatively low risk of toxicity to the host.
It's worth noting that different classes of PBPs inhibitors exist, such as beta-lactam antibiotics (e.g., penicillins, cephalosporins) and glycopeptides (e.g., vancomycin). Each class has its own mechanism of action and spectrum of activity against different types of bacteria. The choice of PBPs inhibitor depends on the specific bacterial infection being treated and its susceptibility profile.
Drug Target R&D Trends for Loracarbef
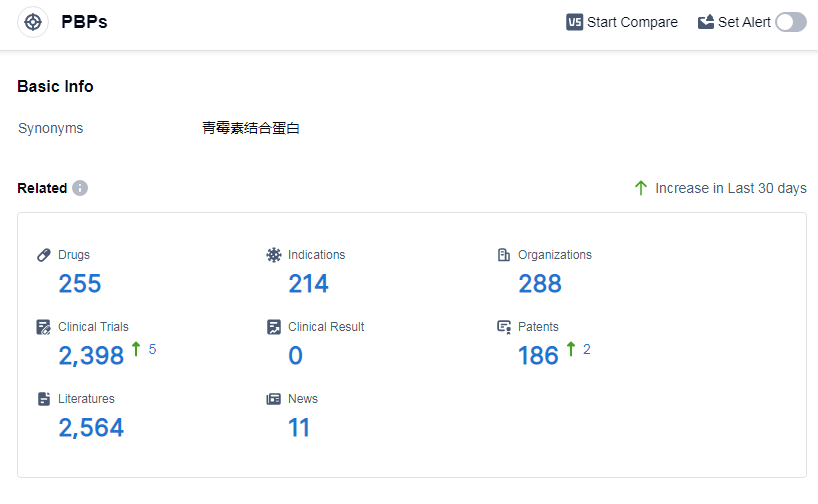
According to Patsnap Synapse, as of 11 Sep 2023, there are a total of 255 PBPs drugs worldwide, from 288 organizations, covering 214 indications, and conducting 2398 clinical trials.
The analysis of the target PBPs in the pharmaceutical industry reveals a competitive landscape with several companies actively developing drugs. Pfizer Inc., Meiji Holdings Co., Ltd., Takeda Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Shionogi & Co., Ltd., and Merck & Co., Inc. are the companies growing fastest under the current target. The indications for the approved drugs under the target PBPs primarily focus on bacterial infections and related diseases. Small molecule drugs and synthetic peptides are the drug types progressing most rapidly, indicating the potential for innovative treatments. China, Japan, the United States, and the European Union are the countries/locations developing fastest, with China showing significant progress in drug development. Overall, the target PBPs present opportunities for growth and innovation in the pharmaceutical industry.
👇Please click on the picture link below for free registration or log in directly if you have a freemium account, you can browse the latest research progress on drugs, indications, organizations, clinical trials, clinical results, and drug patents related to this target
Conclusion
In conclusion, Loracarbef is a small molecule drug developed by Pfizer Inc. for the treatment of bacterial infections. It targets PBPs and has been approved for use in the United States since December 1991. The drug's approval has provided healthcare professionals with an additional therapeutic option to combat infectious diseases.