Deep Scientific Insights on Metolazone's R&D Progress, Mechanism of Action
Metolazone's R&D Progress
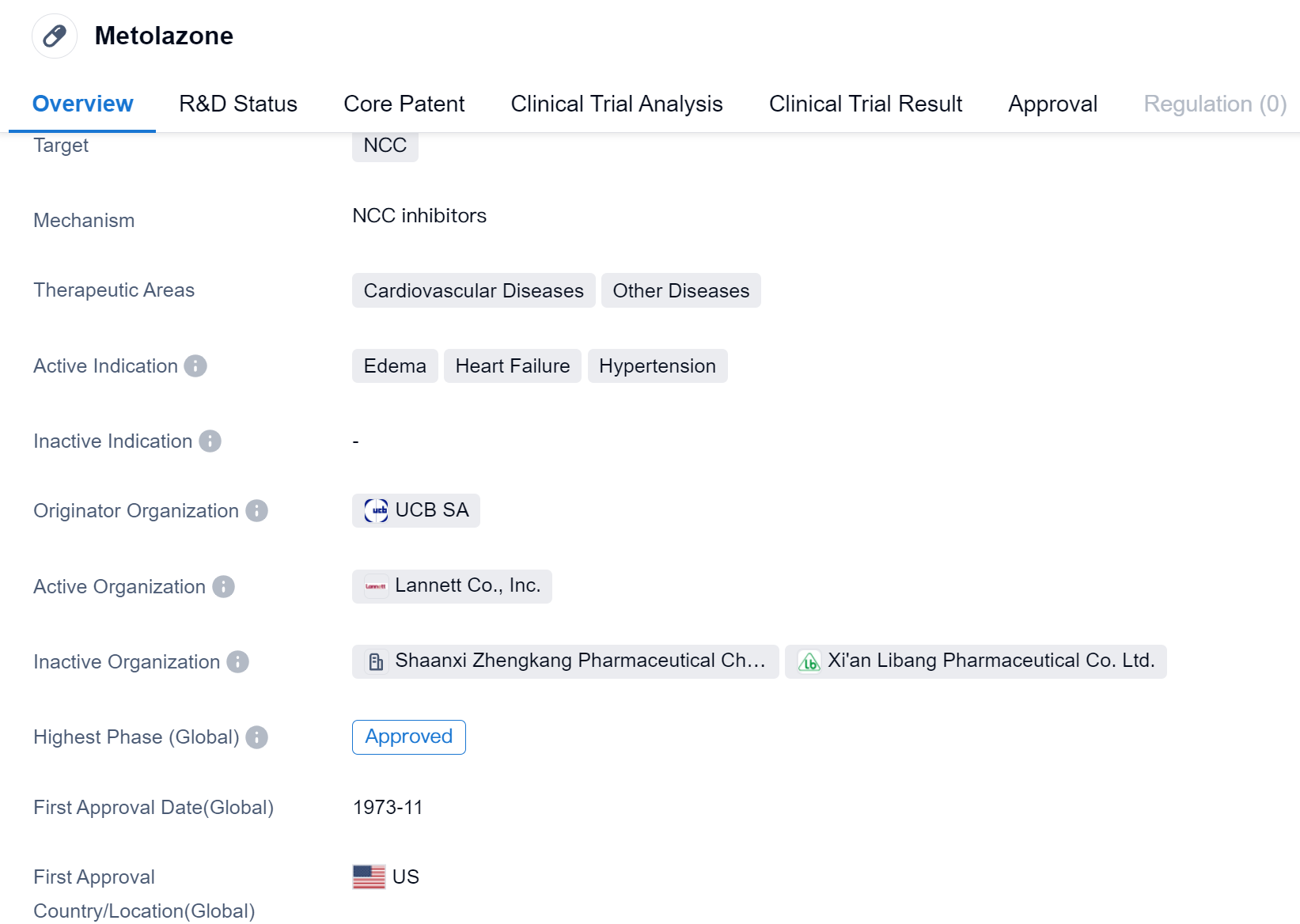
Metolazone is a small molecule drug that primarily targets the NCC (sodium-chloride cotransporter). It is used in the treatment of various cardiovascular diseases and other conditions. The drug is indicated for the management of edema, heart failure, and hypertension.
Metolazone was first approved for use in the United States in November 1973. It is classified as a small molecule drug, which means it consists of low molecular weight compounds that can easily penetrate cell membranes. This characteristic allows for efficient absorption and distribution within the body. The drug's primary therapeutic areas are cardiovascular diseases, including heart failure and hypertension.
Metolazone's originator organization is UCB SA, a multinational pharmaceutical company. The drug has reached the highest phase of development, which is approval, on a global scale. This indicates that it has successfully undergone clinical trials and met the necessary regulatory requirements for market authorization.
However, in China, Metolazone is still pending approval, suggesting that it has not yet received regulatory clearance for use in this country. The reasons for the delay in approval are not specified.
👇Please click on the image below to directly access the latest data (R&D Status | Core Patent | Clinical Trial | Approval status in Global countries) of this drug.
Mechanism of Action for Metolazone: NCC inhibitors
NCC inhibitors are a type of medication that target the sodium-chloride cotransporter (NCC) in the kidneys. The NCC is responsible for reabsorbing sodium and chloride ions from the urine back into the bloodstream. By inhibiting the activity of NCC, these inhibitors reduce the reabsorption of sodium and chloride, leading to increased excretion of these ions in the urine. This, in turn, promotes diuresis (increased urine production) and helps regulate blood pressure.
From a biomedical perspective, NCC inhibitors are used in the treatment of hypertension (high blood pressure) and certain kidney disorders. By blocking the reabsorption of sodium and chloride, these inhibitors help lower blood pressure by reducing the volume of fluid in the bloodstream. They can be prescribed as standalone medications or in combination with other antihypertensive drugs to achieve optimal blood pressure control.
Examples of NCC inhibitors include thiazide diuretics such as hydrochlorothiazide and chlorthalidone. These medications are commonly used in clinical practice and have proven to be effective in managing hypertension. It's important to note that NCC inhibitors should be used under the guidance of a healthcare professional, as they may have potential side effects and interactions with other medications.
Drug Target R&D Trends for Metolazone
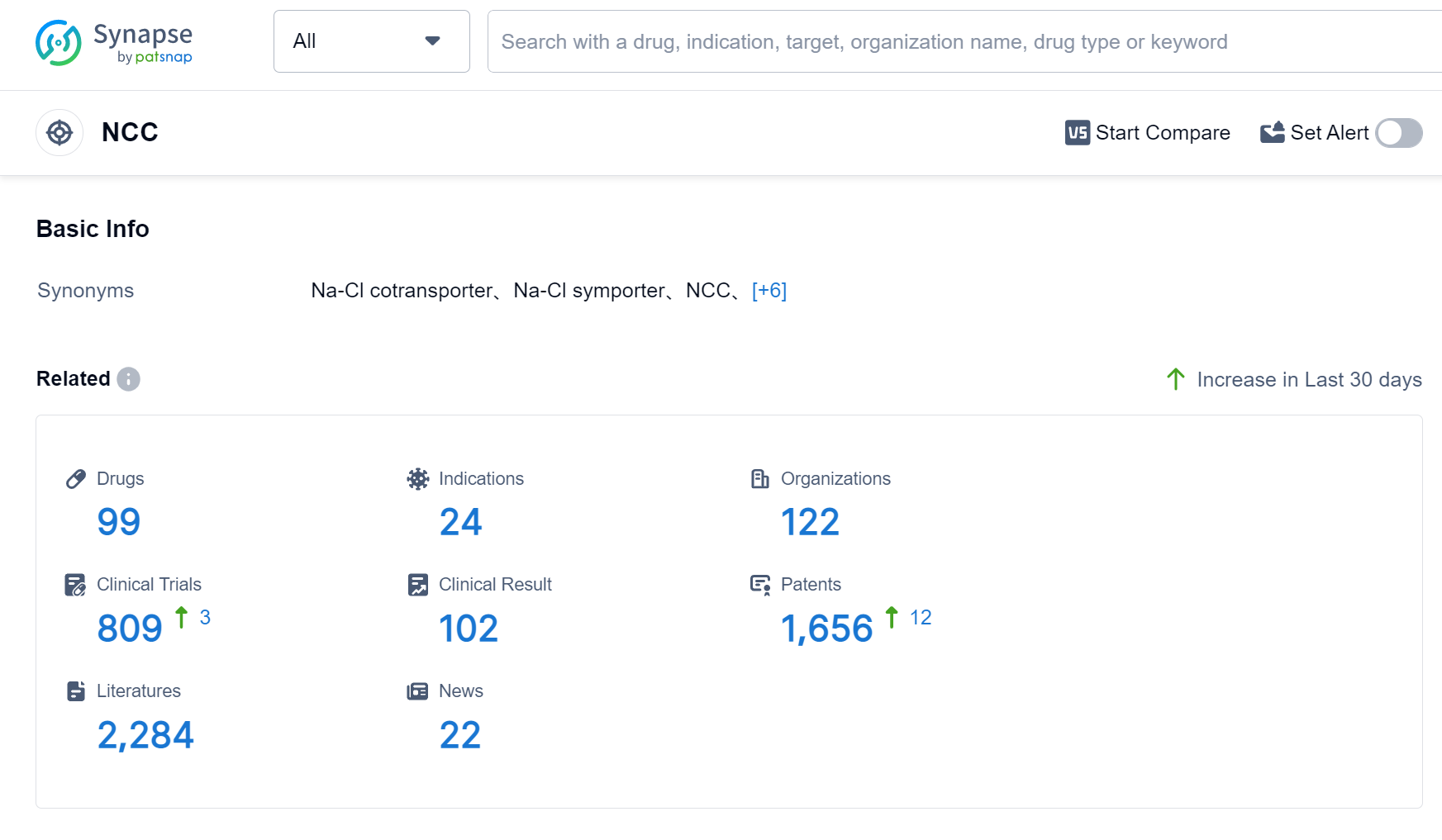
The NCC, or the Sodium-Chloride Cotransporter, plays a crucial role in the human body by facilitating the transport of sodium and chloride ions across cell membranes. This cotransporter is primarily found in the kidneys, where it helps regulate the reabsorption of sodium and chloride from the urine back into the bloodstream. By controlling the balance of these ions, the NCC contributes to the regulation of blood pressure and fluid balance in the body. Dysfunction of the NCC can lead to various health conditions, such as hypertension and electrolyte imbalances, highlighting its significance in maintaining overall physiological homeostasis.
According to Patsnap Synapse, as of 6 Sep 2023, there are a total of 99 NCC drugs worldwide, from 122 organizations, covering 24 indications, and conducting 809 clinical trials.
👇Please click on the picture link below for free registration or log in directly if you have a freemium account, you can browse the latest research progress on drugs, indications, organizations, clinical trials, clinical results, and drug patents related to this target
Conclusion
In summary, Metolazone is a small molecule drug developed by UCB SA. It primarily targets the NCC and is used in the treatment of cardiovascular diseases, including heart failure and hypertension. It was first approved in the United States in 1973 and has reached the highest phase of development globally. However, its approval in China is still pending.