Exploring polatuzumab vedotin-piiq's Revolutionary R&D Successes and its Mechanism of Action on Drug Target
Polatuzumab vedotin-piiq's R&D Progress
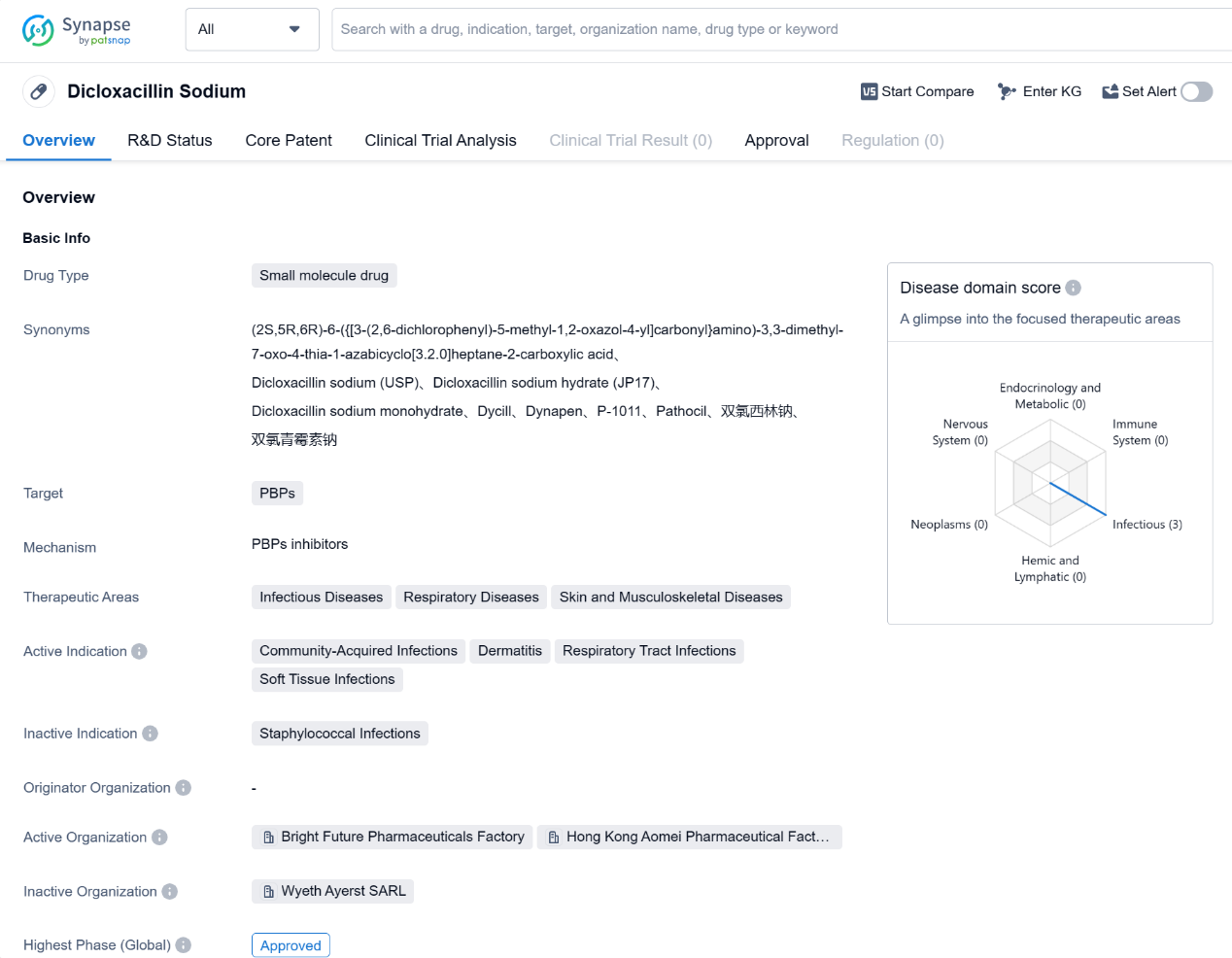
Polatuzumab Vedotin-Piiq is a drug classified as a monoclonal antibody and an antibody drug conjugate (ADC). It targets CD79B and Tubulin, making it suitable for the treatment of various neoplasms, immune system diseases, and hemic and lymphatic diseases. The drug has been specifically indicated for Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma, B-Cell Lymphoma, Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma, Follicular Lymphoma, and Marginal Zone B-Cell Lymphoma.
The originator organization of Polatuzumab Vedotin-Piiq is GeneTech, Inc. It has received approval for use in the United States, with its first approval date being in June 2019.
Polatuzumab Vedotin-Piiq has been granted several regulatory designations, including Accelerated Approval, PRIME (Priority Medicines), Orphan Drug, and Breakthrough Therapy. These designations highlight the drug's potential to address unmet medical needs and expedite its development and approval process.
As a monoclonal antibody and ADC, Polatuzumab Vedotin-Piiq represents an innovative approach in the field of biomedicine. Monoclonal antibodies are designed to target specific proteins or cells in the body, while ADCs combine the specificity of antibodies with the cytotoxic effects of chemotherapy drugs. By targeting CD79B and Tubulin, Polatuzumab Vedotin-Piiq aims to inhibit the growth and proliferation of cancer cells, particularly in lymphomas.
The approval of Polatuzumab Vedotin-Piiq in the United States and China signifies its efficacy and safety profile in treating the indicated lymphomas. The drug's regulatory designations further emphasize its potential as a breakthrough therapy and its ability to address unmet medical needs.
👇Please click on the image below to directly access the latest data (R&D Status | Core Patent | Clinical Trial | Approval status in Global countries) of this drug.
Mechanism of Action for polatuzumab vedotin-piiq: CD79B inhibitors Tubulin inhibitors Tubulin polymerisation inhibitors
CD79B inhibitors are a type of drugs that specifically target and inhibit the activity of CD79B protein. CD79B is a component of the B-cell receptor (BCR) complex, which plays a crucial role in the activation and survival of B-cells, a type of white blood cell involved in the immune response. By inhibiting CD79B, these drugs can disrupt the signaling pathways involved in B-cell activation, proliferation, and survival, thereby potentially suppressing the growth of certain B-cell malignancies, such as B-cell lymphomas and leukemias.
Tubulin inhibitors, on the other hand, are a class of drugs that interfere with the function of tubulin, a protein involved in the formation of microtubules. Microtubules are essential structures for various cellular processes, including cell division, intracellular transport, and maintenance of cell shape. By targeting tubulin, these inhibitors disrupt the dynamic assembly and disassembly of microtubules, leading to cell cycle arrest and inhibition of cell proliferation. Tubulin inhibitors are commonly used in cancer chemotherapy, as they can selectively target rapidly dividing cancer cells.
Tubulin polymerization inhibitors specifically target the polymerization process of tubulin, preventing the formation of microtubules. This disruption of microtubule formation can interfere with cell division and other cellular functions that rely on microtubules. These inhibitors have been extensively studied and utilized in cancer treatment, as they can selectively target and kill rapidly dividing cancer cells.
In summary, CD79B inhibitors target a specific protein involved in B-cell signaling, while tubulin inhibitors and tubulin polymerization inhibitors interfere with the function and assembly of tubulin, respectively. These drugs have important therapeutic implications in the treatment of various diseases, particularly in the field of oncology.
Drug Target R&D Trends for polatuzumab vedotin-piiq
CD79B is a protein that plays a crucial role in the functioning of B cells, a type of white blood cell involved in the immune response. It forms a complex with another protein called Tubulin, which is responsible for maintaining the structural integrity of cells and facilitating intracellular transport. This CD79B + Tubulin complex is essential for the proper development and activation of B cells, enabling them to recognize and respond to foreign substances, such as pathogens. Understanding the role of CD79B + Tubulin in the human body is important for developing targeted therapies and treatments for diseases involving B cell dysfunction, such as certain types of cancer and autoimmune disorders.
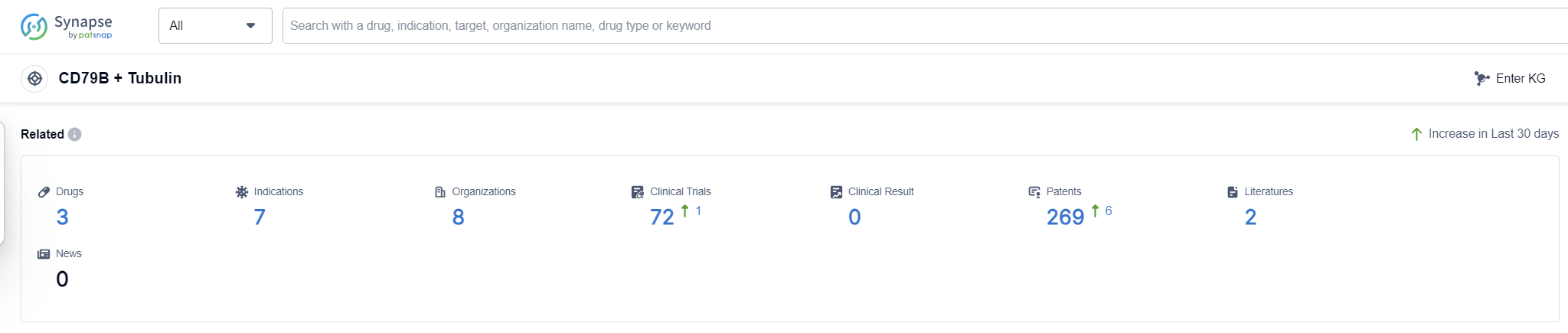
According to Patsnap Synapse, as of 13 Sep 2023, there are a total of 3 CD79B + Tubulin drugs worldwide, from 8 organizations, covering 7 indications, and conducting 72 clinical trials.
Overall, the analysis suggests a promising future for the development of drugs targeting CD79B + Tubulin, with a competitive landscape and a focus on innovative therapies. Continued research and development efforts in this area have the potential to address unmet medical needs and improve patient outcomes.
👇Please click on the picture link below for free registration or log in directly if you have a freemium account, you can browse the latest research progress on drugs, indications, organizations, clinical trials, clinical results, and drug patents related to this target
Conclusion
In summary, Polatuzumab Vedotin-Piiq is a monoclonal antibody and ADC that targets CD79B and Tubulin. It has been approved for the treatment of various lymphomas, including Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma and Follicular Lymphoma. Developed by GeneTech, Inc., the drug has received regulatory designations and has been approved in both the United States and China. Its approval and designations highlight its potential as an innovative and effective treatment option for patients with lymphomas.