Exploring rituximab-pvvr's Revolutionary R&D Successes and its Mechanism of Action on Drug Target
Rituximab-pvvr's R&D Progress
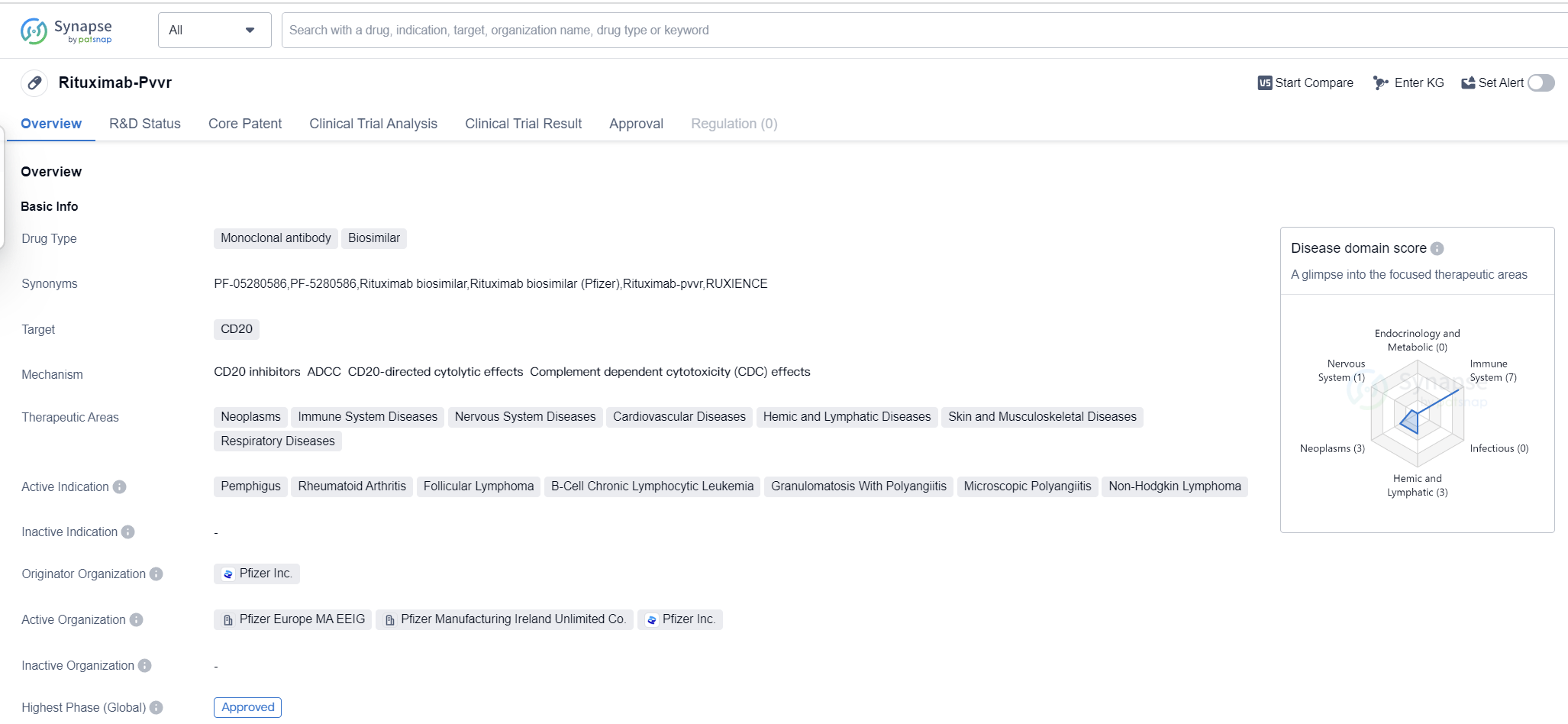
Rituximab-Pvvr is a monoclonal antibody biosimilar drug that targets CD20. It has been approved for use in various therapeutic areas including neoplasms, immune system diseases, nervous system diseases, cardiovascular diseases, hemic and lymphatic diseases, skin and musculoskeletal diseases, and respiratory diseases. The drug is indicated for the treatment of pemphigus, rheumatoid arthritis, follicular lymphoma, B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia, granulomatosis with polyangiitis, microscopic polyangiitis, and non-Hodgkin lymphoma.
The drug was developed by Pfizer Inc., a renowned pharmaceutical company. The highest R&D phase of this drug is approved. Rituximab-Pvvr received its first approval in the United States in July 2019.
As a monoclonal antibody biosimilar, Rituximab-Pvvr is designed to mimic the effects of the original drug, Rituximab, which is used to treat similar conditions. Biosimilars are highly similar to the reference product in terms of quality, safety, and efficacy. They offer a more affordable alternative to the original drug, providing patients with increased access to essential treatments.
The approval of Rituximab-Pvvr signifies its demonstrated effectiveness and safety profile in treating the indicated conditions. This approval allows healthcare professionals to prescribe the drug to patients in need, potentially improving their quality of life and overall health outcomes.
The first approval of Rituximab-Pvvr in the United States highlights the drug's significance in the American pharmaceutical market. It signifies the recognition of its clinical benefits and the regulatory authorities' confidence in its safety and efficacy.
👇Please click on the image below to directly access the latest data (R&D Status | Core Patent | Clinical Trial | Approval status in Global countries) of this drug.
Mechanism of Action for rituximab-pvvr: CD20 inhibitors
CD20 inhibitors are a type of medication that target and inhibit the CD20 protein. CD20 is a protein found on the surface of B cells, which are a type of white blood cell involved in the immune response. By inhibiting CD20, these medications can affect the function and survival of B cells.
ADCC stands for Antibody-Dependent Cell-Mediated Cytotoxicity. It is an immune response mechanism in which certain cells of the immune system, such as natural killer cells, recognize and destroy target cells that are coated with antibodies. In the context of CD20 inhibitors, ADCC refers to the cytolytic effects (cell-killing effects) mediated by immune cells, such as natural killer cells, that are activated by the presence of the CD20-targeting antibodies.
CD20-directed cytolytic effects specifically refer to the cytotoxic effects induced by CD20-targeting antibodies. These antibodies bind to the CD20 protein on the surface of B cells, leading to their destruction. This can be achieved through various mechanisms, including ADCC.
Complement-dependent cytotoxicity (CDC) effects are another type of cell-killing effects mediated by the complement system, which is a part of the immune system. The complement system consists of a group of proteins that can be activated by antibodies bound to target cells. In the context of CD20 inhibitors, CDC refers to the cytotoxic effects induced by the activation of the complement system through the binding of CD20-targeting antibodies to B cells.
In summary, CD20 inhibitors are medications that target the CD20 protein on B cells. They can induce cytolytic effects through mechanisms such as ADCC and CDC, where immune cells or the complement system are activated to destroy CD20-expressing B cells.
Drug Target R&D Trends for rituximab-pvvr
CD20 is a transmembrane protein found on the surface of B cells, a type of white blood cell involved in the immune response. It plays a crucial role in the regulation of B cell activation, differentiation, and survival. CD20 acts as a target for therapeutic antibodies used in the treatment of various diseases, particularly B cell malignancies like non-Hodgkin's lymphoma and chronic lymphocytic leukemia. By binding to CD20, these antibodies can selectively destroy B cells, thereby suppressing the immune response and inhibiting the growth of cancer cells. The understanding of CD20's function has paved the way for the development of targeted therapies in the pharmaceutical industry.
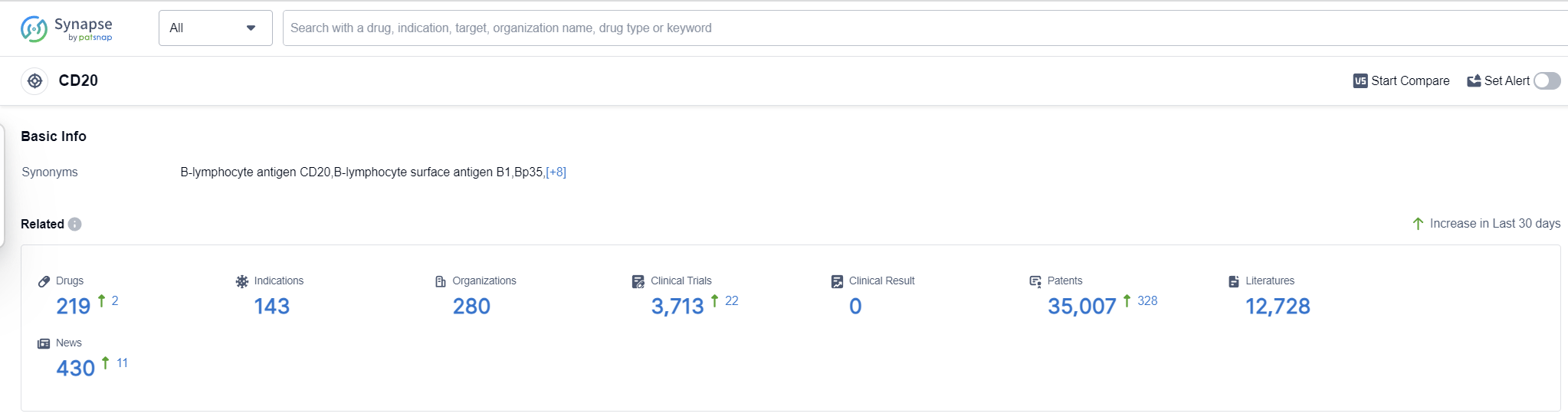
According to Patsnap Synapse, as of 13 Sep 2023, there are a total of 219 CD20 drugs worldwide, from 280 organizations, covering 143 indications, and conducting 3713 clinical trials.
The analysis of target CD20 reveals that Roche Holding AG is the leading company in terms of R&D progress, with drugs in various stages of development. The approved indications for drugs targeting CD20 include Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma, B-Cell Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia, Rheumatoid Arthritis, and others. Monoclonal antibodies and biosimilars are the most rapidly progressing drug types, indicating intense competition. China is making progress in the development of drugs targeting CD20. Overall, the competitive landscape for target CD20 is dynamic, with multiple companies and countries actively involved in research and development. The future development of target CD20 is expected to bring more innovative drugs and increased competition in the pharmaceutical industry.
👇Please click on the picture link below for free registration or log in directly if you have a freemium account, you can browse the latest research progress on drugs, indications, organizations, clinical trials, clinical results, and drug patents related to this target
Conclusion
Overall, Rituximab-Pvvr is a monoclonal antibody biosimilar drug that has been approved for the treatment of various diseases. Its approval in the United States marks an important milestone in the pharmaceutical industry, offering patients a more accessible treatment option for their medical conditions.