Deep Scientific Insights on salmeterol xinafoate's R&D Progress
Salmeterol xinafoate's R&D Progress
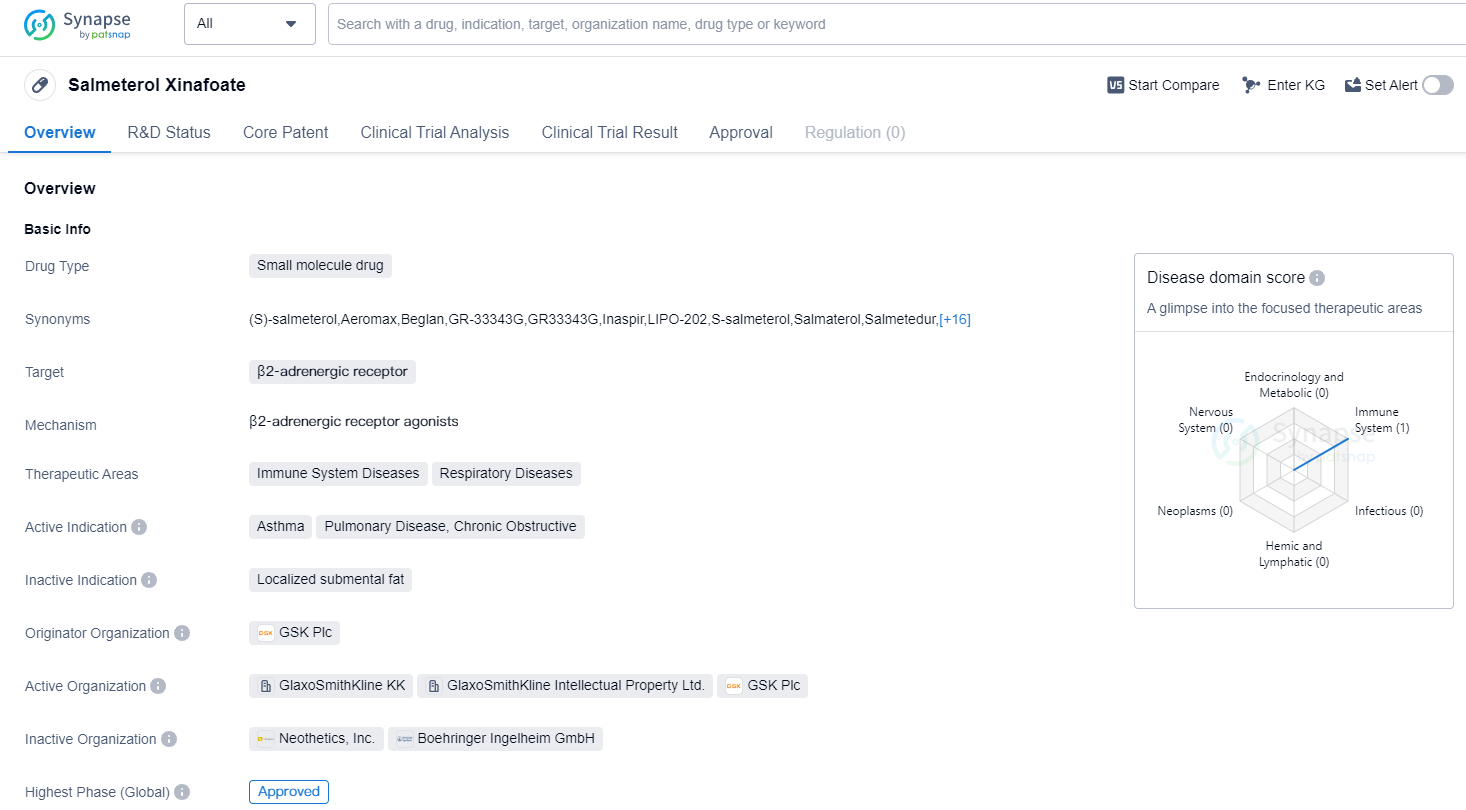
Salmeterol Xinafoate is a small molecule drug that targets the β2-adrenergic receptor. It is primarily used in the treatment of immune system diseases and respiratory diseases, specifically asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). The drug was first approved for use in the United States in February 1994.
Salmeterol Xinafoate is developed and marketed by GSK Plc, a pharmaceutical company known for its expertise in the field of biomedicine. The drug has reached the highest phase of development which is approved globally.
As a β2-adrenergic receptor agonist, Salmeterol Xinafoate works by relaxing the smooth muscles in the airways, thereby improving breathing and reducing symptoms such as wheezing, shortness of breath, and coughing. It is commonly prescribed as a long-acting bronchodilator, providing sustained relief for patients with asthma and COPD.
The approval of Salmeterol Xinafoate in 1994 marked a significant milestone in the treatment of respiratory diseases. Since then, it has become a widely used medication for managing asthma and COPD symptoms. The drug's effectiveness in improving lung function and reducing exacerbations has been well-documented in clinical trials and real-world studies.
👇Please click on the image below to directly access the latest data (R&D Status | Core Patent | Clinical Trial | Approval status in Global countries) of this drug.
Mechanism of Action for salmeterol xinafoate: B2-adrenergic receptor agonists
β2-adrenergic receptor agonists are a type of medication that activate the β2-adrenergic receptors in the body. These receptors are found primarily in the smooth muscle of the airways, such as in the lungs. When β2-adrenergic receptor agonists bind to these receptors, they cause relaxation and dilation of the airway smooth muscles, leading to bronchodilation.
From a biomedical perspective, β2-adrenergic receptor agonists are commonly used in the treatment of respiratory conditions such as asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). By activating the β2-adrenergic receptors, these medications help to relieve bronchospasm and improve airflow to the lungs, making it easier to breathe.
There are different types of β2-adrenergic receptor agonists, including short-acting and long-acting forms. Short-acting β2-adrenergic agonists provide quick relief of symptoms and are often used as rescue medications during acute asthma attacks. On the other hand, long-acting β2-adrenergic agonists are used for maintenance therapy to provide sustained bronchodilation and prevent symptoms.
It is important to note that while β2-adrenergic receptor agonists can be highly effective in managing respiratory conditions, they may also have potential side effects. These can include increased heart rate, tremors, and in rare cases, paradoxical bronchospasm. Therefore, it is crucial to use these medications under the guidance of a healthcare professional and follow the prescribed dosage.
Drug Target R&D Trends for salmeterol xinafoate
The β2-adrenergic receptor is a protein found on the surface of certain cells in the human body, particularly in the lungs and smooth muscles. It plays a crucial role in regulating various physiological processes. When activated by specific molecules called agonists, such as adrenaline or certain medications, the β2-adrenergic receptor triggers a cascade of intracellular events that result in relaxation of smooth muscles, particularly in the airways. This relaxation leads to bronchodilation, making it easier for individuals to breathe. Consequently, drugs targeting the β2-adrenergic receptor, known as β2-agonists, are commonly used in the treatment of respiratory conditions like asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
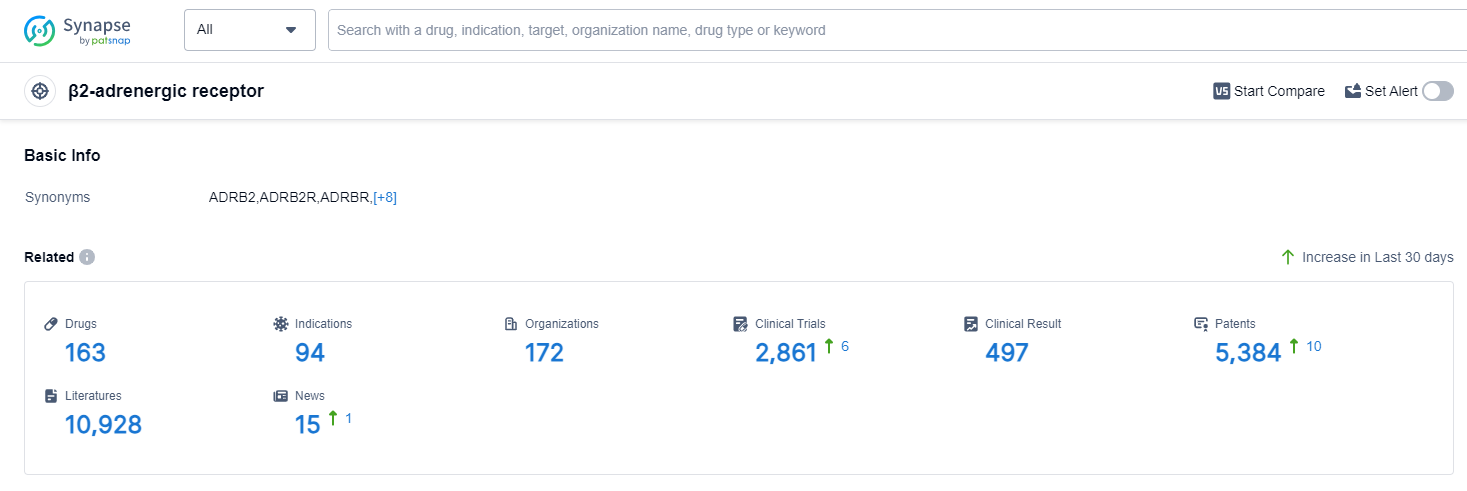
According to Patsnap Synapse, as of 12 Sep 2023, there are a total of 163 β2-adrenergic receptor drugs worldwide, from 172 organizations, covering 94 indications, and conducting 2861 clinical trials.
The analysis of the target β2-adrenergic receptor reveals a competitive landscape with several companies actively developing drugs for various indications. GSK Plc, AstraZeneca PLC, Novartis AG, and C.H. Boehringer Sohn AG & Co. KG are among the companies with the highest number of drugs in different development phases. Asthma and pulmonary disease (COPD) are the most common indications for approved drugs targeting the β2-adrenergic receptor. Small molecule drugs dominate the drug types, indicating intense competition and potential biosimilar development. China, Japan, the United States, and the European Union are the leading countries/locations in terms of drug development for the target β2-adrenergic receptor. Overall, the target β2-adrenergic receptor presents a promising area for pharmaceutical companies, with ongoing research and development efforts focused on addressing respiratory conditions and related indications.
👇Please click on the picture link below for free registration or log in directly if you have a freemium account, you can browse the latest research progress on drugs, indications, organizations, clinical trials, clinical results, and drug patents related to this target
Conclusion
In conclusion, Salmeterol Xinafoate is a small molecule drug that targets the β2-adrenergic receptor and is primarily used in the treatment of immune system diseases and respiratory diseases such as asthma and COPD. Developed by GSK Plc, the drug has reached the highest phase of development which is approved globally. Its approval in 1994 marked a significant advancement in the management of respiratory diseases, providing patients with a long-acting bronchodilator for sustained relief.