Griseofulvin: Detailed Review of its Transformative R&D Success
Griseofulvin's R&D Progress
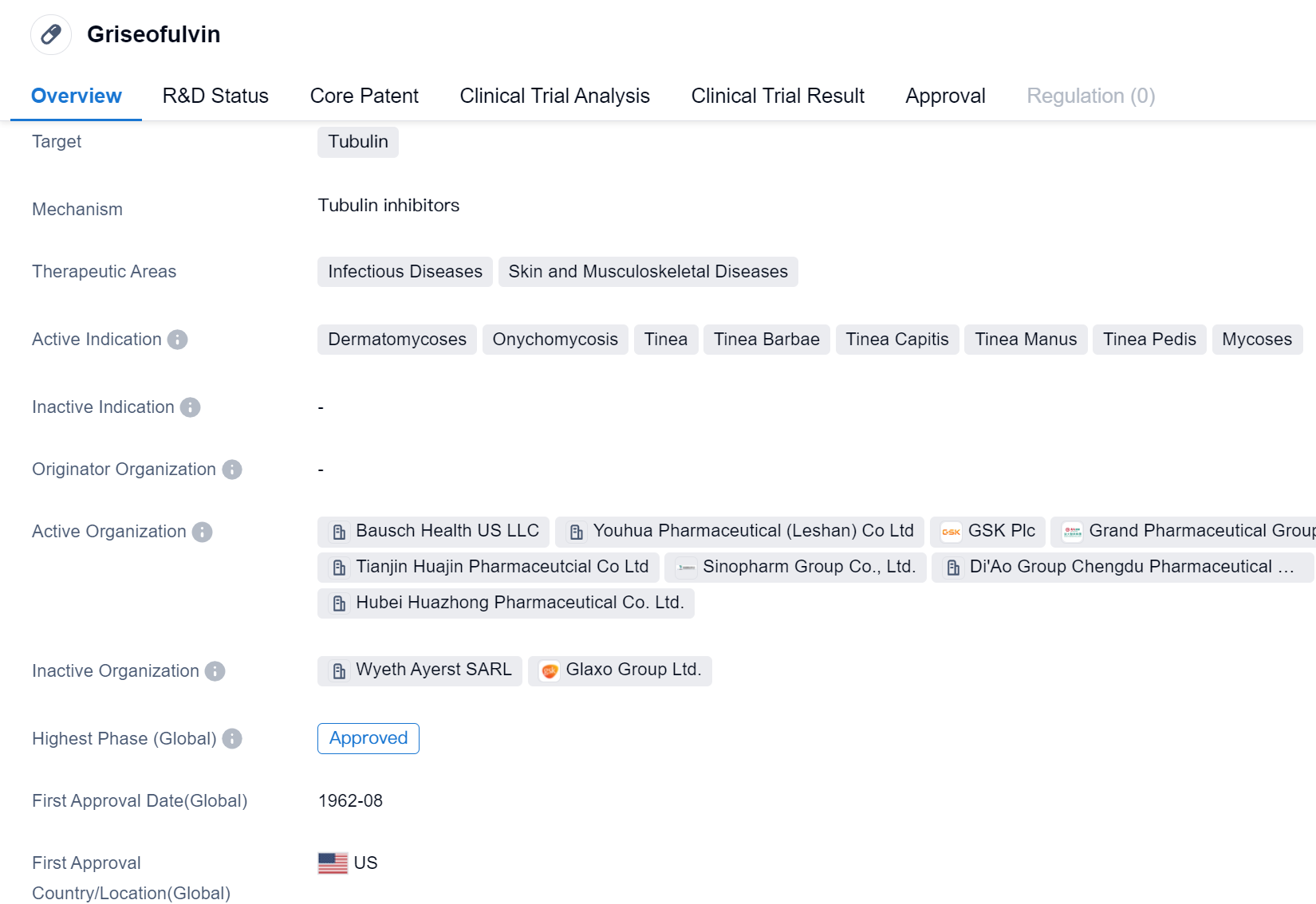
Griseofulvin is a small molecule drug that primarily targets tubulin, a protein involved in cell division. It is used in the treatment of various infectious diseases and skin and musculoskeletal diseases. The drug has been approved for use in multiple indications, including dermatomycoses, onychomycosis, tinea, tinea barbae, tinea capitis, tinea manus, tinea pedis, and mycoses.
Griseofulvin was first approved for use in the United States in August 1962, making it a well-established drug in the pharmaceutical market. It has also received approval in China, indicating its global recognition and acceptance. Being in the highest phase of approval in both countries further emphasizes its established status.
The drug's primary therapeutic areas are infectious diseases and skin and musculoskeletal diseases. Infectious diseases encompass a wide range of conditions caused by pathogens such as bacteria, viruses, fungi, and parasites. Skin and musculoskeletal diseases refer to disorders affecting the skin, muscles, bones, and joints. Griseofulvin's approval for these therapeutic areas suggests its efficacy in combating infections and treating various skin and musculoskeletal conditions.
Griseofulvin's mechanism of action involves targeting tubulin, a protein essential for cell division. By interfering with tubulin function, the drug inhibits the growth and replication of microorganisms responsible for infectious diseases and helps alleviate symptoms associated with skin and musculoskeletal diseases.
With its long history of approval and widespread use, Griseofulvin has established itself as a reliable and effective treatment option. Its approval in both the United States and China indicates its global recognition and availability. The drug's broad range of indications further highlights its versatility in treating various infectious and dermatological conditions.
👇Please click on the image below to directly access the latest data (R&D Status | Core Patent | Clinical Trial | Approval status in Global countries) of this drug.
Mechanism of Action for Griseofulvin: Tubulin inhibitors
Tubulin inhibitors are a type of drug that target tubulin, a protein involved in cell division. Tubulin is a key component of the cytoskeleton, which provides structural support to cells and plays a crucial role in various cellular processes, including cell division.
From a biomedical perspective, tubulin inhibitors are used in cancer treatment as they disrupt the normal function of tubulin, preventing the formation of microtubules. Microtubules are essential for the assembly and maintenance of the mitotic spindle, which is necessary for proper chromosome segregation during cell division. By inhibiting tubulin, these drugs interfere with the cell division process, ultimately leading to cell death.
Tubulin inhibitors can be further classified into different subtypes based on their mechanism of action. For example, taxanes such as paclitaxel stabilize microtubules, preventing their disassembly and causing cell cycle arrest. Vinca alkaloids like vincristine, on the other hand, bind to tubulin and inhibit microtubule assembly, leading to mitotic arrest.
Overall, tubulin inhibitors are important therapeutic agents in cancer treatment, specifically targeting the abnormal cell division that occurs in cancer cells.
Drug Target R&D Trends for Griseofulvin
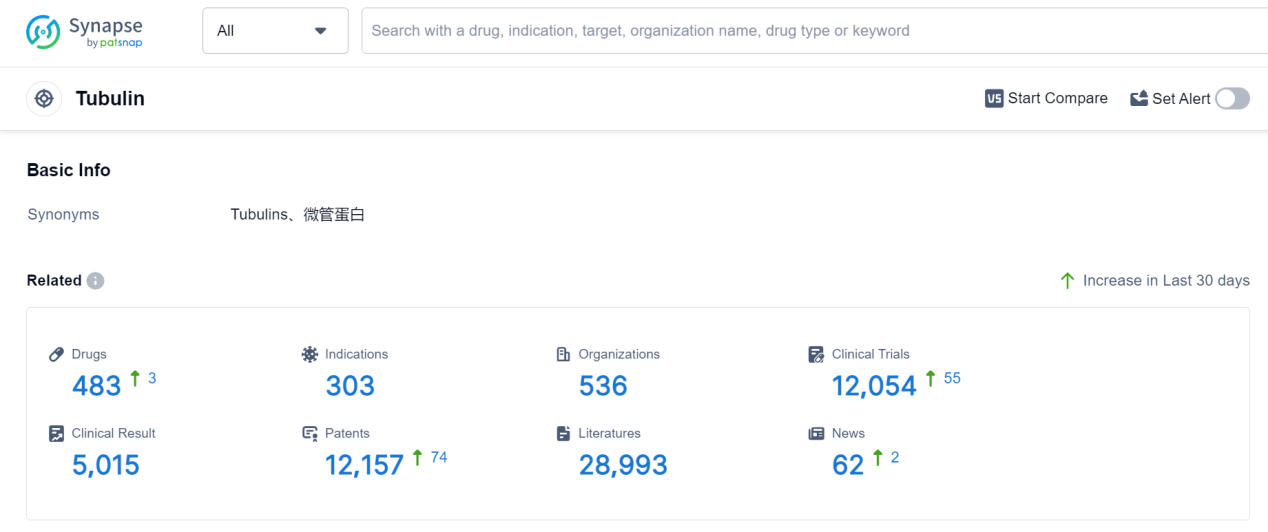
Tubulin is a vital protein found in the human body that plays a crucial role in various cellular processes. It forms the building blocks of microtubules, which are essential for cell division, intracellular transport, and maintaining cell shape. Tubulin also acts as a target for several anti-cancer drugs, as it is involved in the regulation of cell growth and proliferation. Additionally, tubulin is responsible for the movement of cilia and flagella, which are important for cell motility and sensory functions. Overall, tubulin's multifaceted functions make it a key player in maintaining cellular integrity and facilitating various physiological processes in the human body.
According to Patsnap Synapse, as of 7 Sep 2023, there are a total of 483 Tubulin drugs worldwide, from 536 organizations, covering 303 indications, and conducting 12054 clinical trials.
👇Please click on the picture link below for free registration or log in directly if you have a freemium account, you can browse the latest research progress on drugs, indications, organizations, clinical trials, clinical results, and drug patents related to this target
Conclusion
In conclusion, Griseofulvin is a small molecule drug that targets tubulin and is primarily used in the treatment of infectious diseases and skin and musculoskeletal diseases. Its approval in multiple countries, along with its long history of use, solidifies its position as a trusted and effective therapeutic option in the pharmaceutical industry.