Johnson & Johnson’s $14.6 Billion Acquisition of Intra-Cellular Therapies: Caplyta® as a Game-Changer in Mental Health Treatment
At the 43rd J.P. Morgan Healthcare Conference held from January 13 to 16, 2025, Johnson & Johnson announced its acquisition of Intra-Cellular Therapies, a biopharmaceutical company focused on the research, development, and commercialization of treatments for central nervous system (CNS) disorders, for $14.6 billion. This blockbuster deal not only became one of the highlights of this year's JPM Conference but also marked the largest merger and acquisition transaction in the biotechnology sector since 2023.
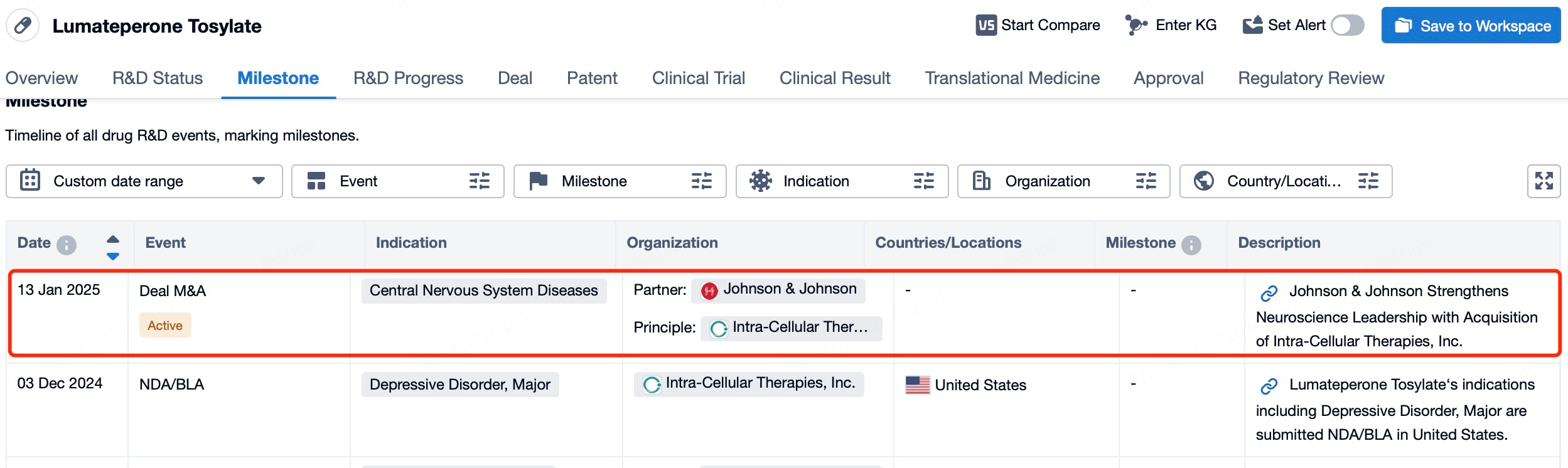
Johnson & Johnson's Major Acquisition: Caplyta® to Drive Innovation in Neuroscience
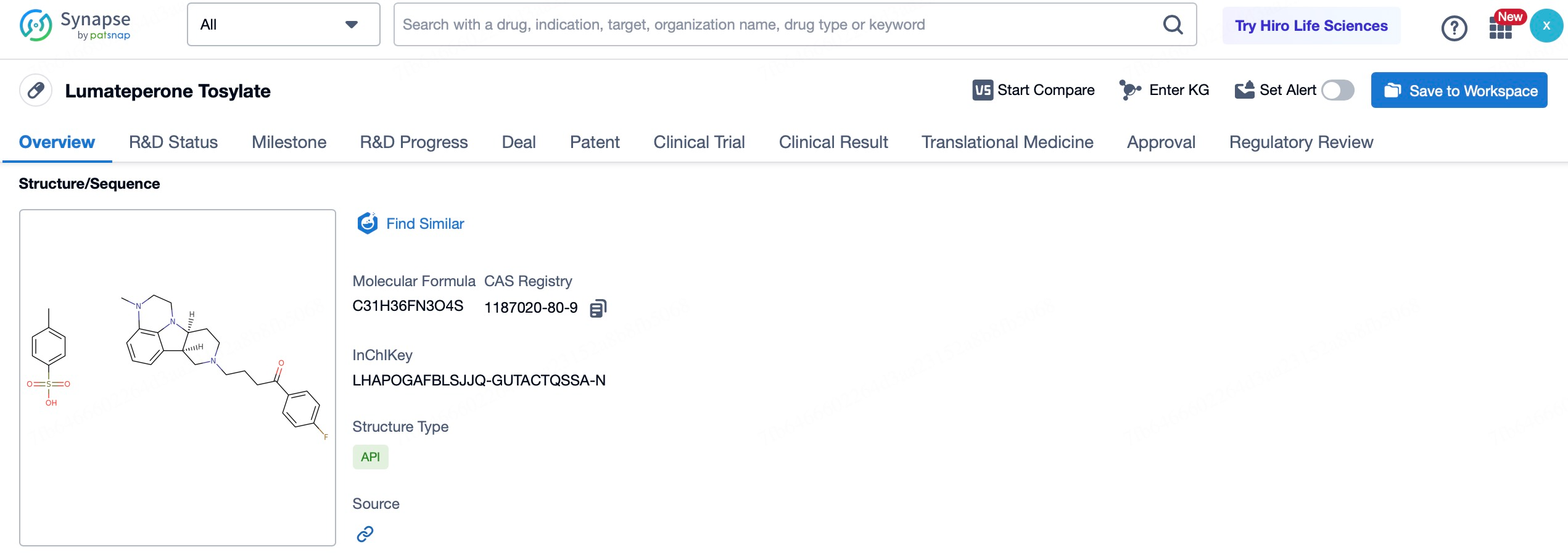
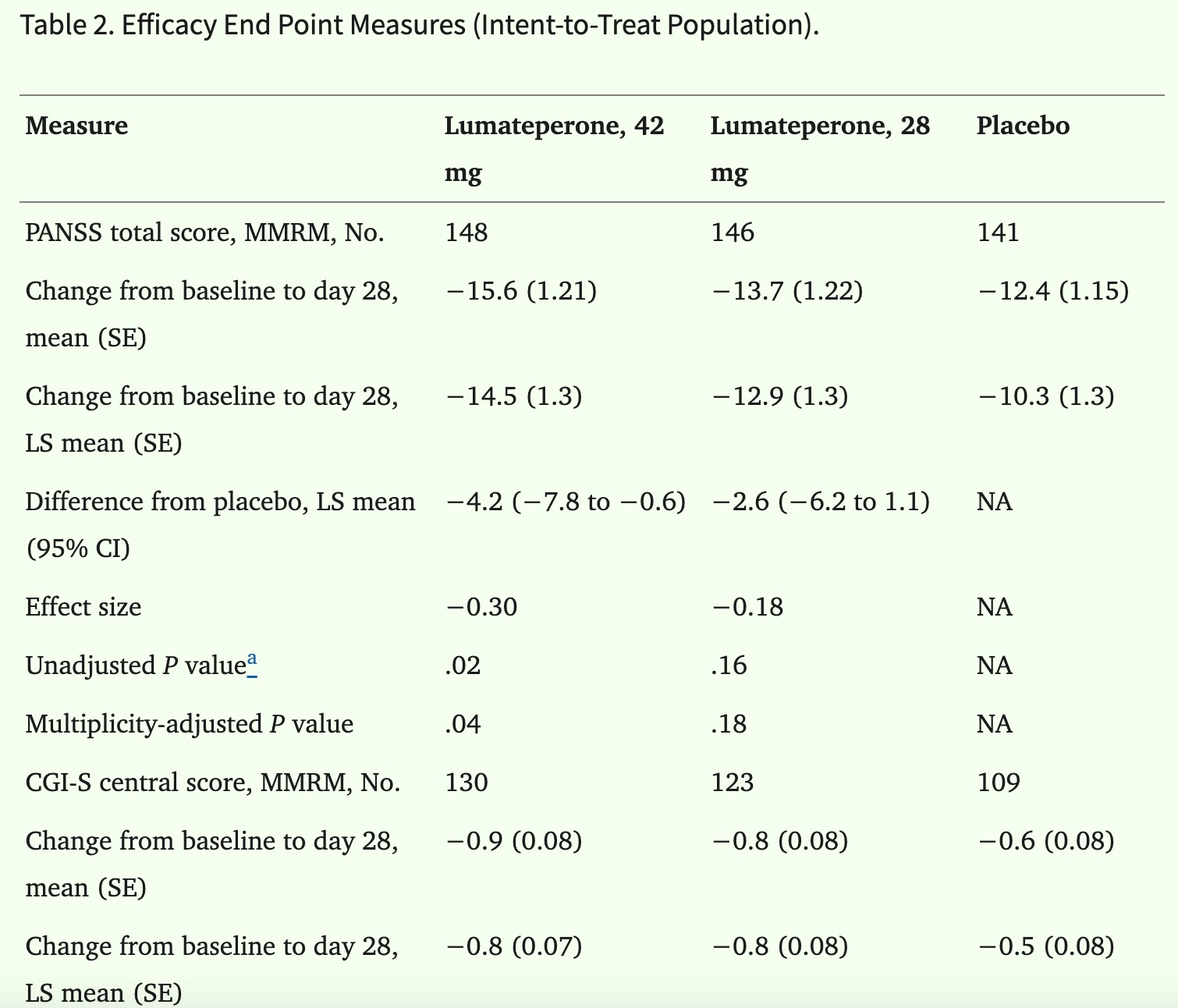
This acquisition underscores Johnson & Johnson's commitment to the field of neuroscience and its strategic intent to strengthen its leadership position in this area through this transaction. Intra-Cellular's flagship product, Caplyta® (lumateperone), is the first FDA-approved drug for both adjunctive and monotherapy treatment of bipolar I and II depression, as well as for the treatment of schizophrenia in adults.
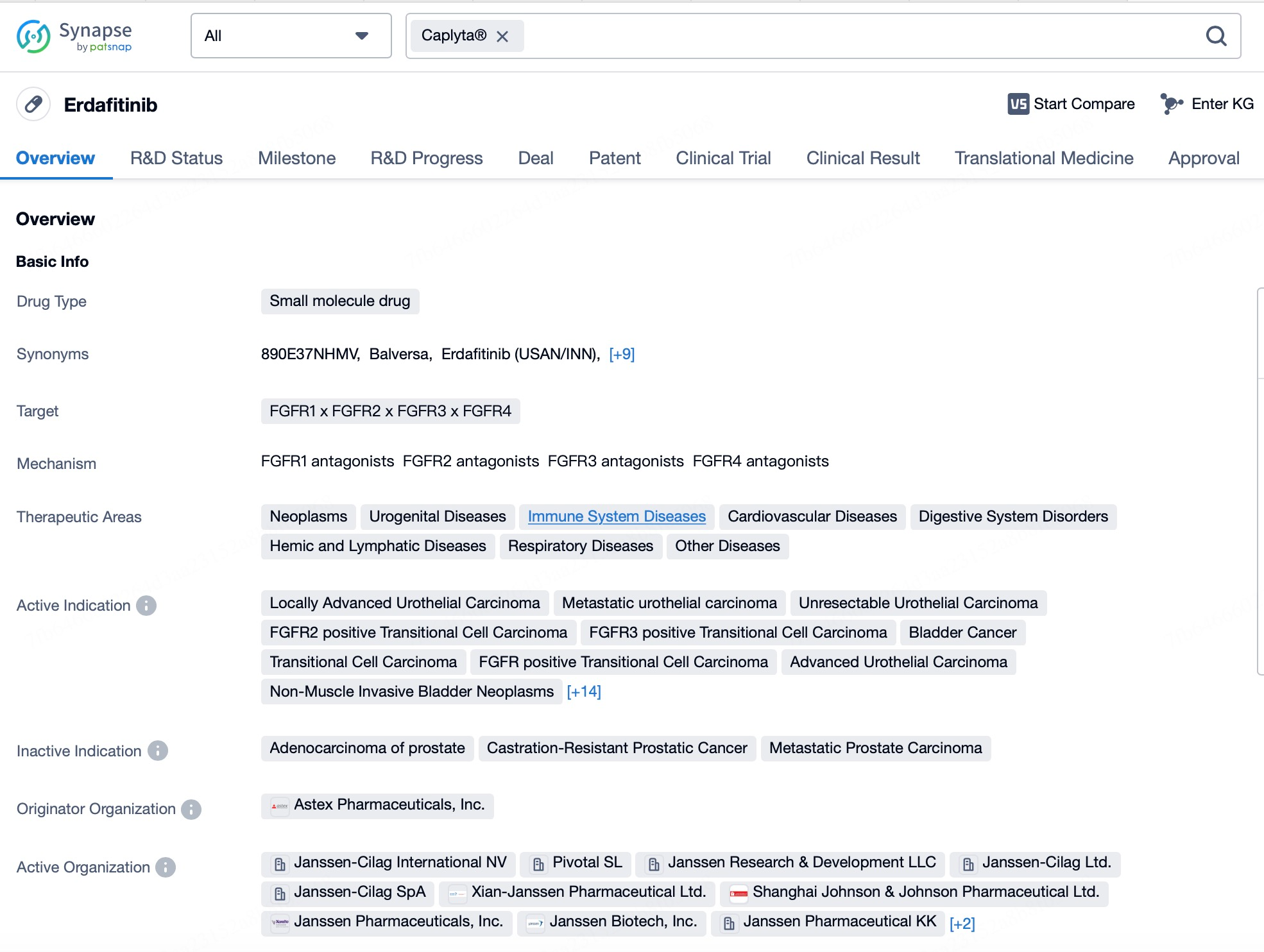
Since receiving FDA approval in 2019, Caplyta® has rapidly gained favor among physicians and patients, with sales experiencing robust growth. In the first three quarters of 2024, Caplyta® generated $482 million in sales revenue, representing a 39% year-over-year increase, demonstrating strong growth momentum. As more physicians recognize the efficacy of Caplyta® and prescribing habits solidify, its market share is expected to expand further in the coming years. Johnson & Johnson's strategic rationale for acquiring Intra-Cellular Therapies is to bolster its position in the neuroscience field, not only to expand market share but also to drive sustainable growth for the company.
Mechanism of Action of Caplyta®
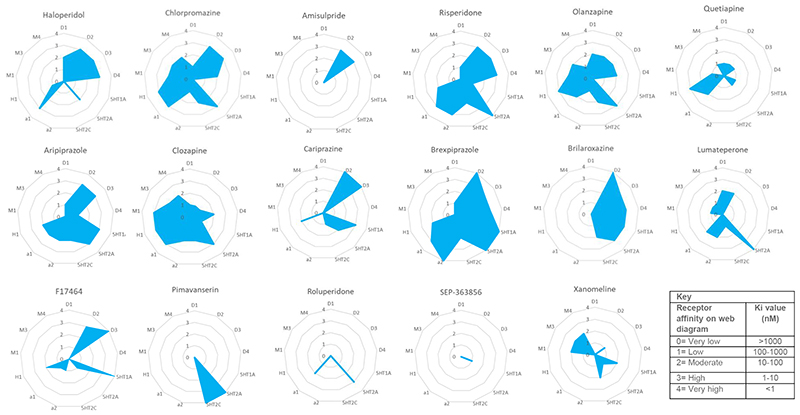
Caplyta®, as an innovative antipsychotic drug, distinguishes itself from traditional antipsychotics through its unique mechanism of action. It is a first-in-class small molecule drug capable of selectively and simultaneously modulating three neurotransmitter pathways—serotonin, dopamine, and glutamate—which are implicated in severe mental illnesses.
Caplyta®'s effect on the serotonin system is primarily manifested through its potent antagonism of the 5-HT2A receptor. This means it can block signal transmission at the 5-HT2A receptor, thereby reducing abnormal activity associated with this receptor. The 5-HT2A receptor is widely distributed in the brain and is involved in various physiological functions, such as mood regulation and cognitive processes. By blocking these receptors, Caplyta® can alleviate symptoms such as hallucinations and delusions.
In addition to its direct action on the 5-HT2A receptor, Caplyta® also indirectly modulates serotonin levels by inhibiting the serotonin transporter protein (SERT). SERT is responsible for reuptaking serotonin from the synaptic cleft back into neurons, terminating its signaling and preparing for the next release cycle. When SERT function is inhibited, more serotonin remains in the synaptic cleft, prolonging its action and increasing extracellular serotonin concentration. This mechanism enhances the efficacy of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) in combating depression and provides a new therapeutic approach for treatment-resistant depression.
Because Caplyta® possesses both of these properties—acting as a potent 5-HT2A receptor antagonist and a SERT inhibitor—it can improve psychiatric symptoms while potentially mitigating some of the common side effects associated with traditional antipsychotics, such as weight gain or metabolic disturbances. This is because traditional antipsychotics often exert strong effects on the dopamine D2 receptor, whereas Caplyta® tends to selectively target the 5-HT2A receptor, reducing interference with other neurotransmitter systems.
Role of Caplyta® in Dopamine System Modulation
In the modulation of the dopamine system, Caplyta® exhibits unique properties. The dopamine D2 receptor is a critical target in the treatment of schizophrenia, as it is involved in regulating the brain's reward pathways, motor control, and other behavioral responses. Traditional antipsychotic drugs typically alleviate symptoms such as hallucinations and delusions by blocking D2 receptors, but this can also lead to extrapyramidal symptoms (EPS), such as muscle rigidity and tremors. However, Caplyta® is capable of performing two distinct functions at the D2 receptor: as a presynaptic partial agonist, it moderately increases dopamine release, while as a postsynaptic antagonist, it inhibits excessive dopamine signaling. This design allows Caplyta® to effectively manage the core symptoms of schizophrenia while reducing the risk of movement disorders caused by excessive D2 receptor blockade.
In addition to its effects on the D2 receptor, Caplyta® also interacts with the D1 receptor. The D1 receptor is primarily distributed in the basal ganglia and prefrontal cortex, regions crucial for cognitive functions. Research indicates that activation of the D1 receptor can enhance working memory, attention, and learning abilities. Therefore, Caplyta®'s action on the D1 receptor may promote cognitive improvement in patients, which is particularly important for enhancing the quality of life and social functioning of individuals with schizophrenia. By neither fully blocking nor simply stimulating the dopamine system, Caplyta® provides a more balanced approach to modulating dopamine levels in the brain. Furthermore, its lower D2 receptor occupancy translates to a reduced risk of inducing EPS, which is significant for improving long-term patient adherence and quality of life.
Role of Caplyta® in Glutamate System Modulation
In addition to its effects on the serotonin and dopamine systems, Caplyta® may also indirectly modulate the glutamate system by influencing NMDA and AMPA receptors, two types of glutamate receptors. Glutamate is one of the most abundant and widely distributed excitatory neurotransmitters in the brain, playing a critical role in learning, memory, and neuroplasticity. Dysregulation of the glutamate system has also been implicated in schizophrenia, particularly in the hippocampus and cortical regions. By modulating glutamate system activity, Caplyta® can help restore cognitive abilities and social functioning in patients, which is crucial for the long-term recovery of individuals with schizophrenia.
As the most abundant and widely distributed excitatory neurotransmitter in the central nervous system, glutamate participates in brain functions such as learning and memory by activating glutamate receptors on the postsynaptic membrane. In schizophrenia research, the glutamate hypothesis suggests that dysfunction in glutamatergic neurotransmission may be a fundamental component of the disease's pathophysiology. Specifically, impaired NMDA receptor function is thought to be closely associated with schizophrenia symptoms, as NMDA receptor antagonists can induce psychosis-like symptoms.
Pharmacodynamic studies indicate that Caplyta®, as a potent antagonist, exhibits high binding affinity for the 5-HT2A receptor. Additionally, it acts as a postsynaptic D2 receptor antagonist, a presynaptic partial agonist, and a serotonin transporter (SERT) reuptake inhibitor. These properties enable Caplyta® to influence glutamate signaling at multiple levels. For example, by blocking the 5-HT2A receptor, it can indirectly enhance the activity of AMPA and NMDA receptors, thereby strengthening glutamate-mediated excitatory synaptic transmission.
Other Potential Indications for Caplyta®
In addition to its approved indications, Caplyta® is being explored for a broader range of potential applications, including major depressive disorder (MDD), bipolar I disorder with manic or mixed episodes (bipolar mania), generalized anxiety disorder (GAD), as well as Alzheimer’s disease-related psychosis and agitation.
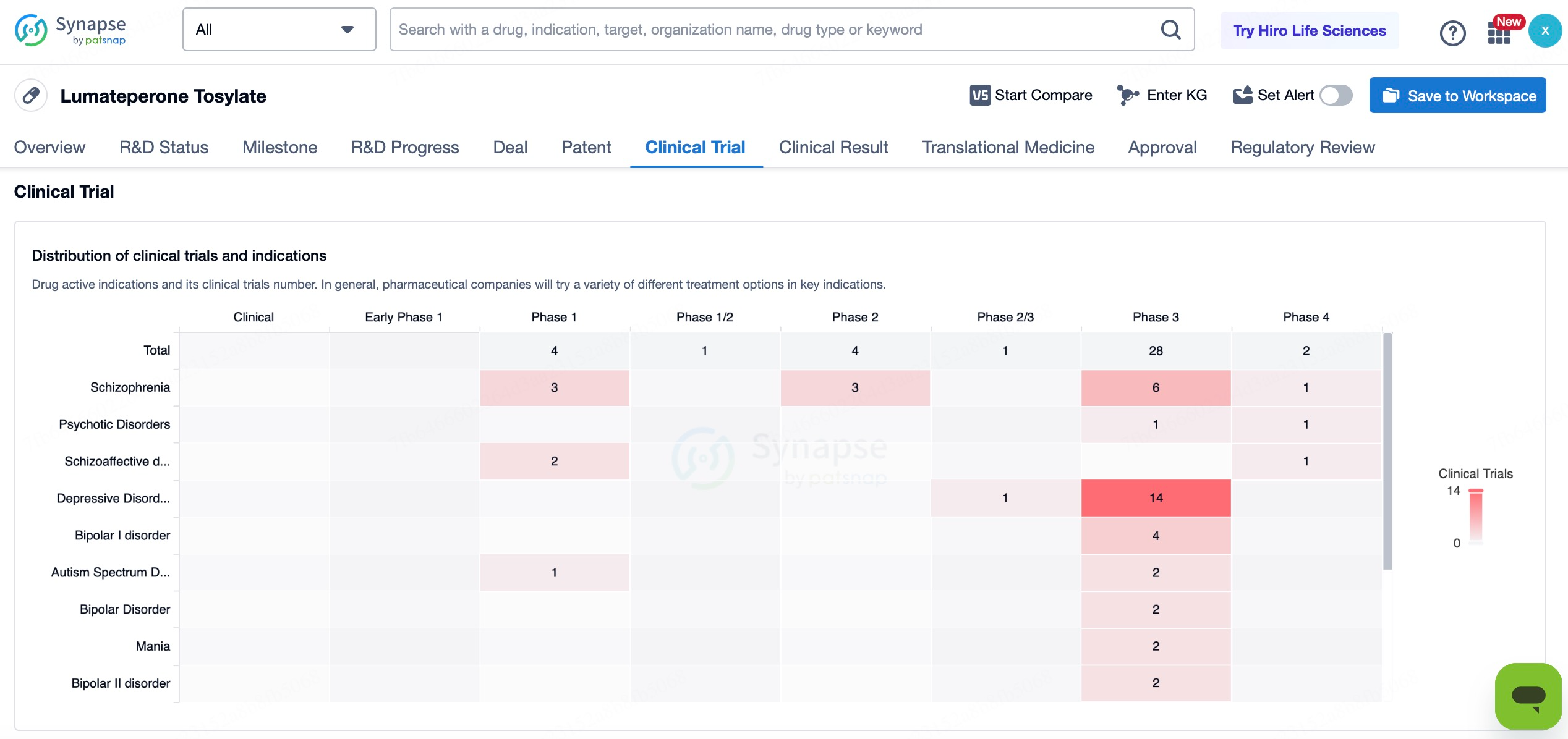
1.Major Depressive Disorder (MDD)
Intra-Cellular Therapies has submitted a supplemental New Drug Application (sNDA) to the U.S. FDA for Caplyta® as an adjunctive treatment for major depressive disorder (MDD). If approved, this would mark the first new drug for this indication in 15 years. Given the large population affected by major depressive disorder globally—approximately 21 million adults in the United States alone—this new indication would significantly expand Caplyta®'s application scope and substantially enhance its commercial value. Furthermore, for patients who respond inadequately to traditional antidepressants or cannot tolerate their side effects, Caplyta® may offer a novel treatment option.
2.Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD)
Additionally, Caplyta® is undergoing a pivotal Phase III clinical trial to evaluate its efficacy in treating generalized anxiety disorder (GAD). GAD is a common anxiety disorder characterized by persistent worry and tension, even in the absence of obvious triggers. The increasing prevalence of anxiety symptoms in modern society has led to a growing demand for treatments targeting such conditions.
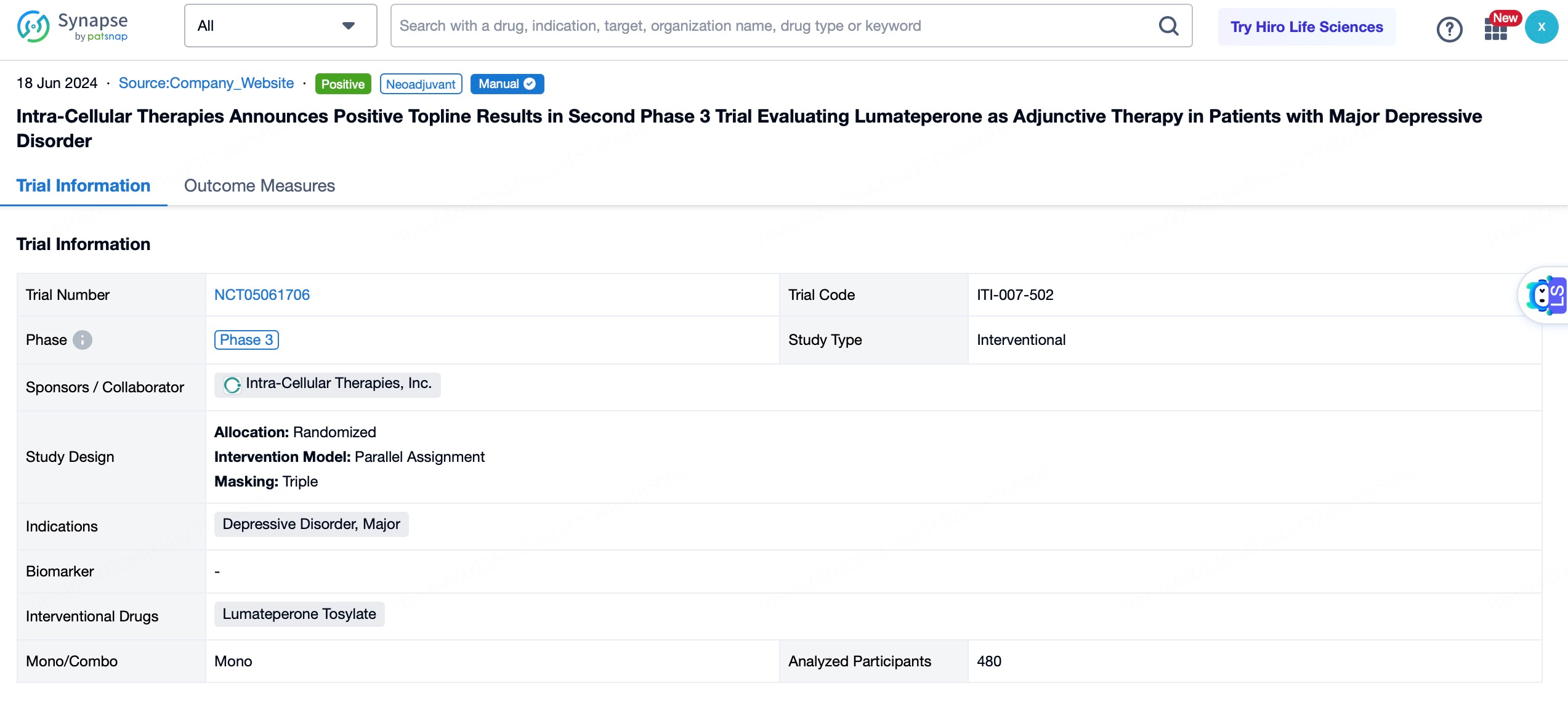
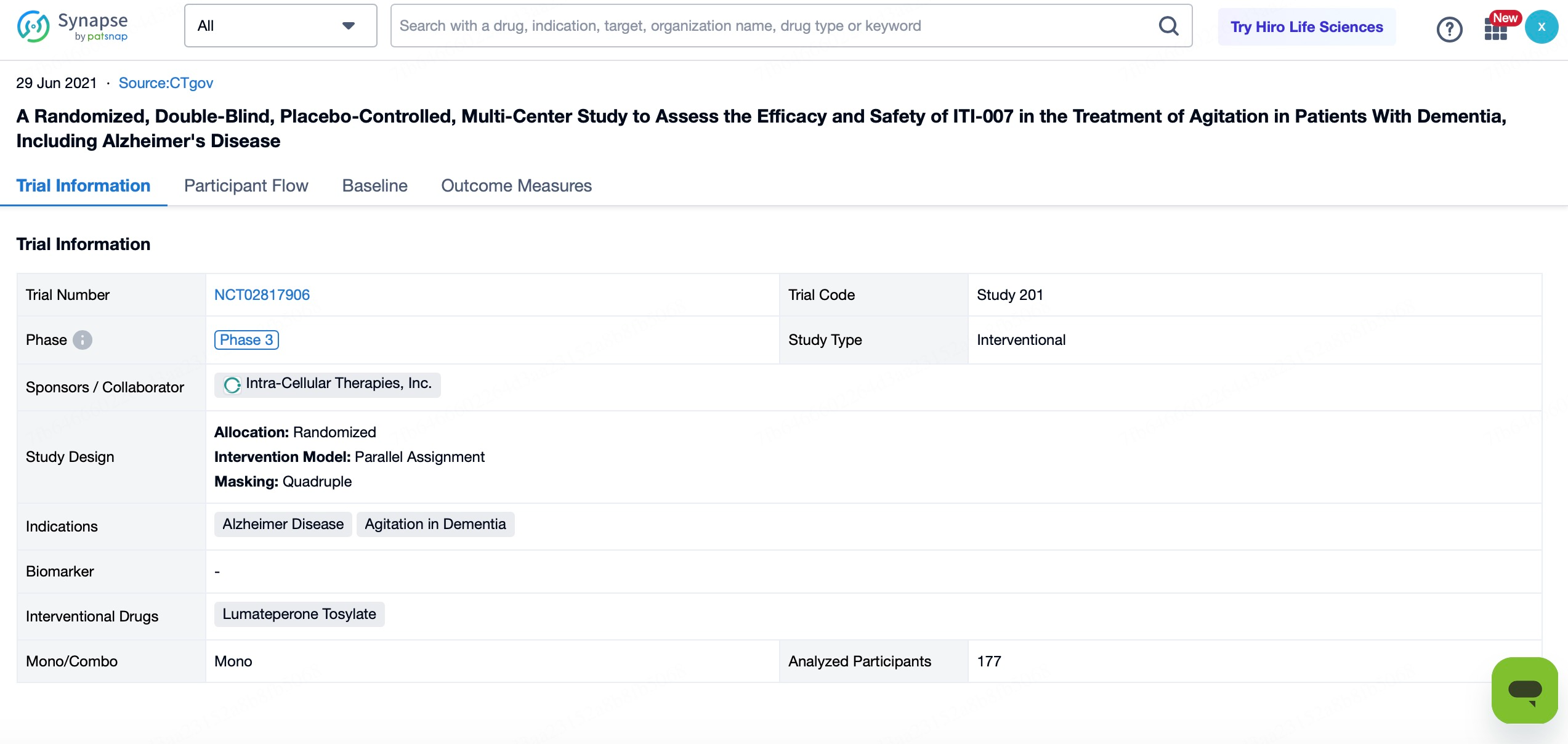
3.Alzheimer’s Disease-Related Psychosis and Agitation
Another ongoing pivotal Phase III clinical trial is testing Caplyta® for its effects on psychotic symptoms (such as hallucinations and delusions) and agitation in patients with Alzheimer’s disease. As the global population ages, it is projected that over 150 million people worldwide will suffer from dementia by 2050, with Alzheimer’s disease accounting for the majority of cases. Alzheimer’s disease-related psychosis and agitation are common complications during the progression of the disease, significantly impacting the quality of life for both patients and their caregivers. Given Caplyta®'s strong safety and tolerability profile, as well as its performance in treating other psychiatric disorders, it holds promise as a better treatment option for this specific population.
Conclusion
By integrating Intra-Cellular’s research team and technology platform, Johnson & Johnson will enhance its internal innovation capabilities, fostering the development of novel treatments for mental health and neurological disorders. With the escalating mental health crisis and global aging population, over 1 billion people worldwide—1 in 8 individuals—are affected by neuropsychiatric or neurodegenerative diseases. As such, Caplyta® not only has the potential to become a new standard of care for some of the most prevalent and debilitating mental health disorders today but also heralds significant transformation and growth opportunities in the future of mental health treatment.
How to obtain the latest research advancements in the field of biopharmaceuticals?
In the Synapse database, you can keep abreast of the latest research and development advances in drugs, targets, indications, organizations, etc., anywhere and anytime, on a daily or weekly basis. Click on the image below to embark on a brand new journey of drug discovery!
Reference
- 1.Correll CU, Davis RE, Weingart M, Saillard J, O'Gorman C, Kane JM, Lieberman JA, Tamminga CA, Mates S, Vanover KE. Efficacy and Safety of Lumateperone for Treatment of Schizophrenia: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Psychiatry. 2020 Apr 1;77(4):349-358. doi: 10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2019.4379. Erratum in: JAMA Psychiatry. 2020 Apr 1;77(4):438. doi: 10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2020.0055. PMID: 31913424; PMCID: PMC6990963.
- 2.Okaty BW, Commons KG, Dymecki SM. Embracing diversity in the 5-HT neuronal system. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2019 Jul;20(7):397-424. doi: 10.1038/s41583-019-0151-3. PMID: 30948838.
- 3.Lobo MC, Whitehurst TS, Kaar SJ, Howes OD. New and emerging treatments for schizophrenia: a narrative review of their pharmacology, efficacy and side effect profile relative to established antipsychotics. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2022 Jan;132:324-361. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2021.11.032. Epub 2021 Nov 24. PMID: 34838528; PMCID: PMC7616977.
- 4.Lee HG, Wheeler MA, Quintana FJ. Function and therapeutic value of astrocytes in neurological diseases. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2022 May;21(5):339-358. doi: 10.1038/s41573-022-00390-x. Epub 2022 Feb 16. PMID: 35173313; PMCID: PMC9081171.