2024 Global New Drug Approvals: A Comprehensive Review of Breakthrough Therapies and Innovations
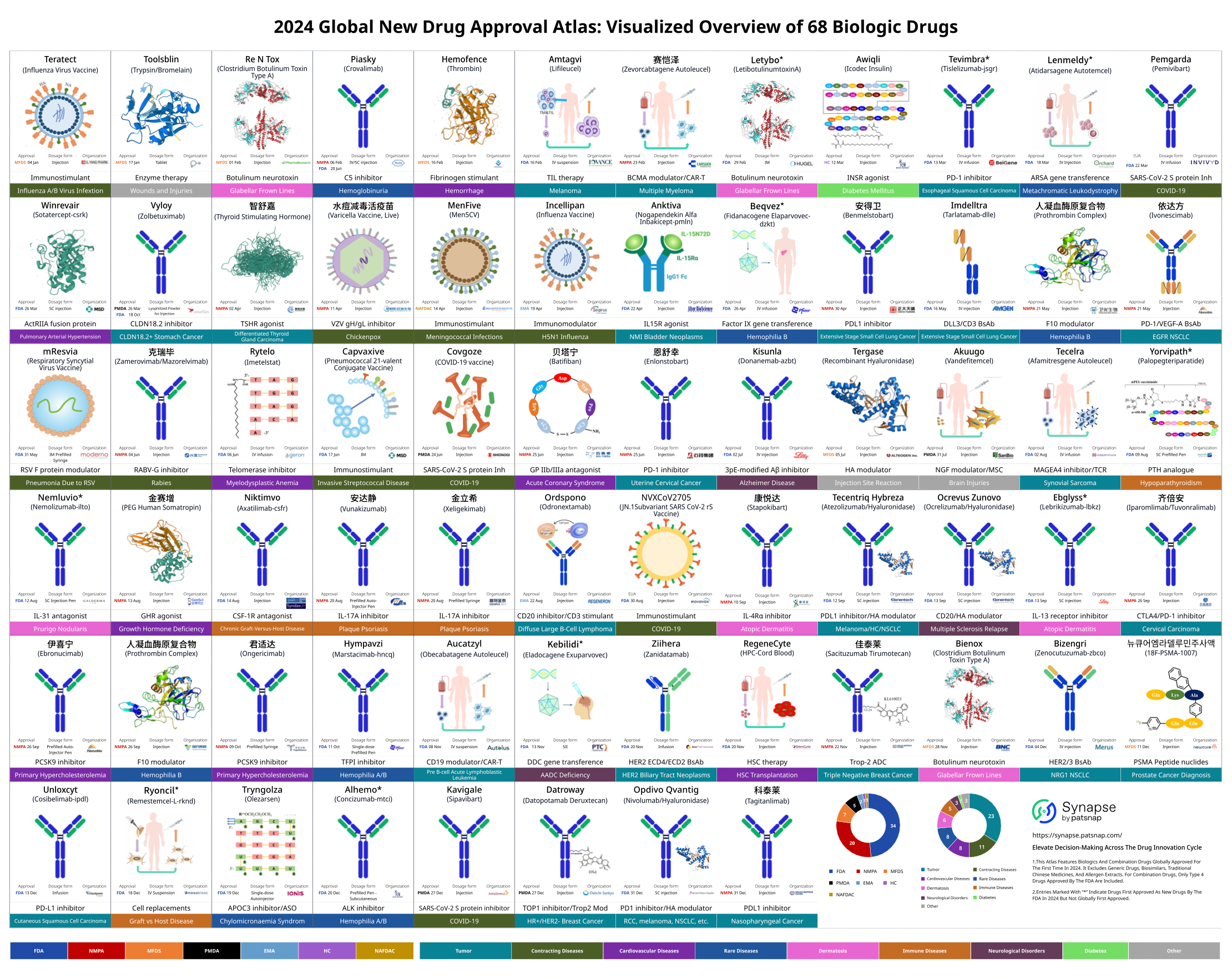
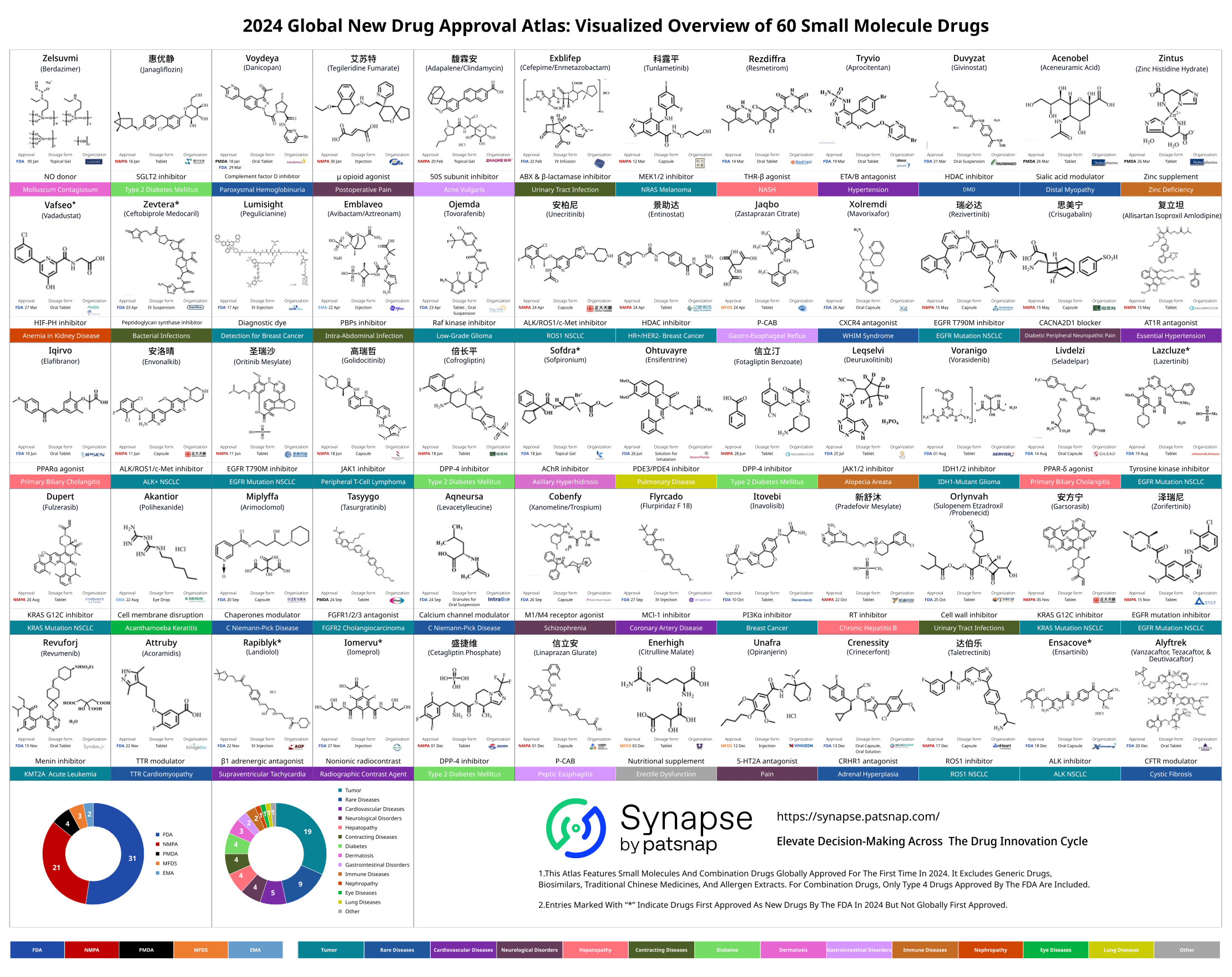
In 2024, the range of diseases treated by globally approved new drugs was diverse, with cancer and rare diseases leading in the total number of new drug approvals. Several new drugs were also approved in the fields of anti-infectives and cardiovascular diseases.
Among the approved small molecule drugs, 8 were designated as "first-in-class" therapies with breakthrough therapy status. These drugs not only possess unique mechanisms of action but also provide significant therapeutic improvements over previous treatments.
As the development technologies for peptide and nucleic acid-based drugs have matured, their proportion among FDA-approved new drugs has stabilized. In 2024, the approved nucleic acid-based drugs included the first telomerase inhibitor, Rytelo (imetelstat). This drug targets and binds to the RNA template of telomerase, inhibiting its activity. It received FDA approval in June 2024 for the treatment of adult patients with myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS).
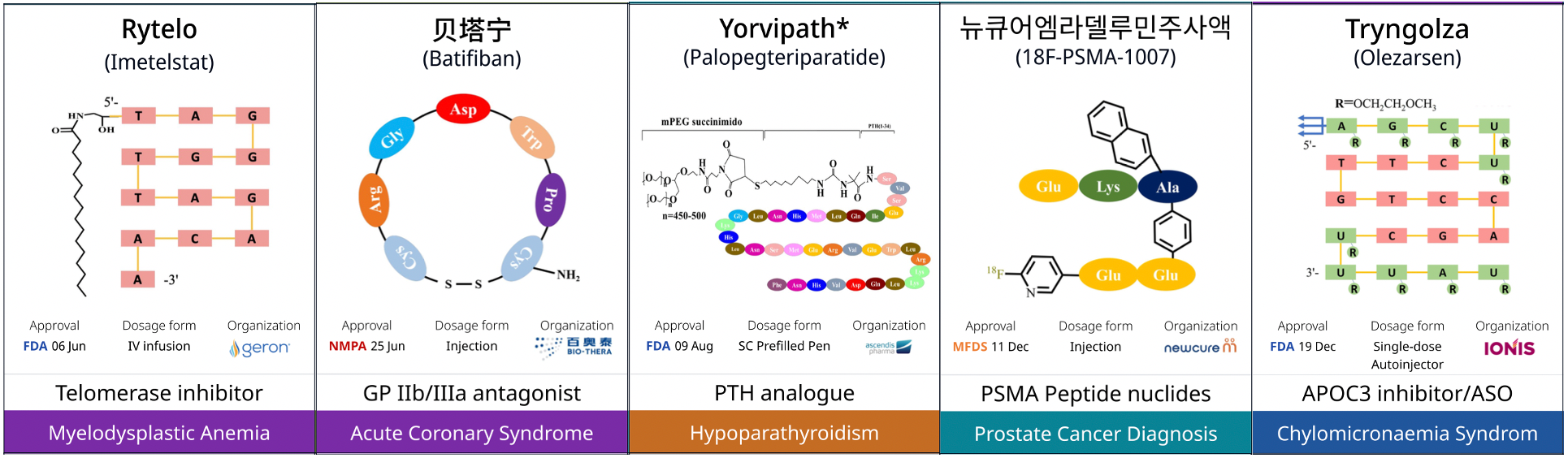
A major challenge for peptide-based drugs is their susceptibility to degradation in the human body, making it difficult to maintain their efficacy. However, advancements in peptide modification technologies have led to longer half-lives for these drugs, offering patients long-acting therapies with reduced treatment burdens. Yorvipath, a long-acting parathyroid hormone prodrug approved in 2024, links the parathyroid hormone prodrug to a polyethylene glycol carrier to control the hormone's release in the body. It received FDA approval in August 2024 as the first treatment for adult hypoparathyroidism.
In 2024, CBER approved 8 cell and gene therapies. These therapies not only represent technological innovations but also provide the first approved treatments for patients with various types of diseases.
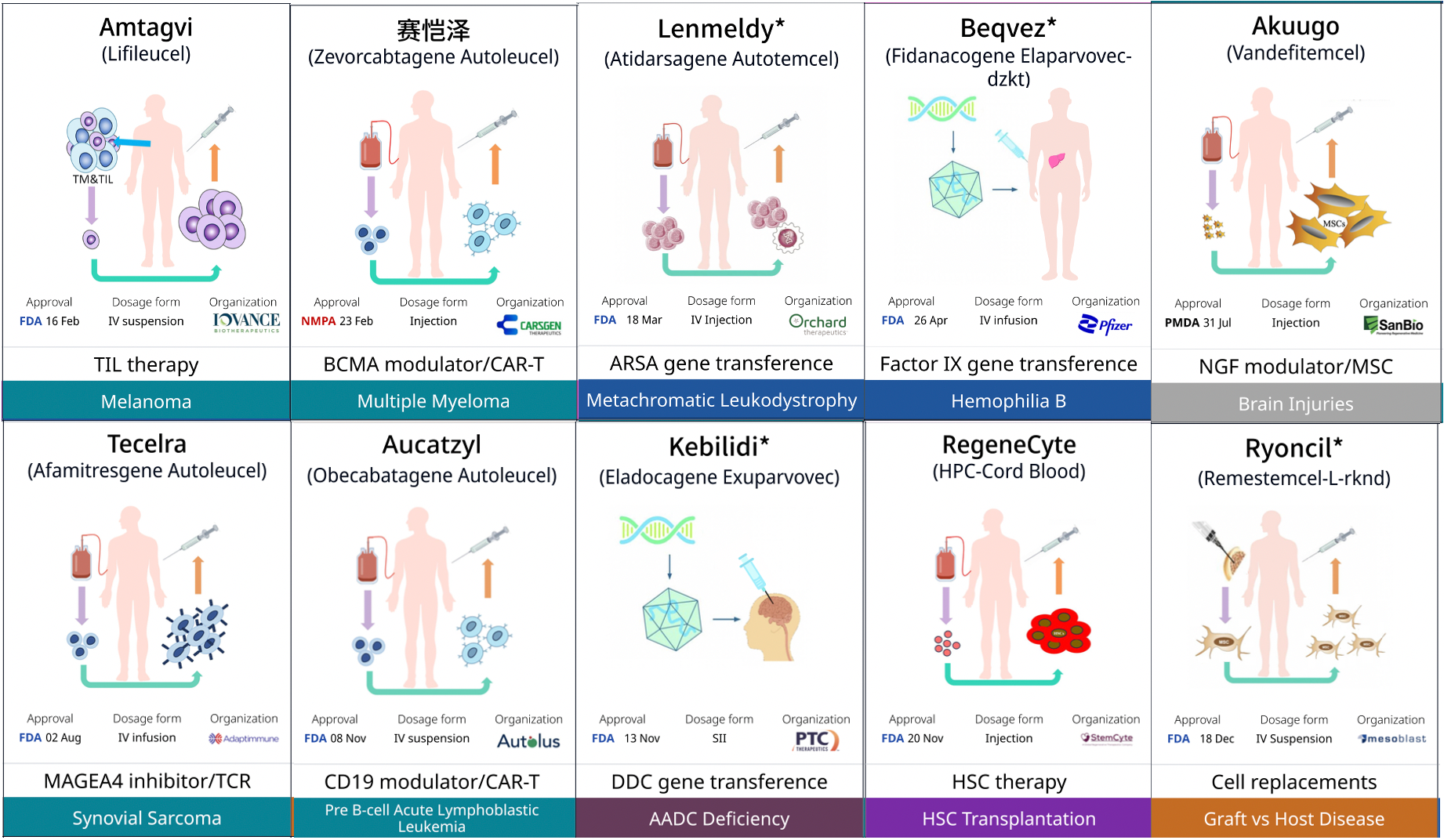
On February 16, 2024, the U.S. FDA granted accelerated approval to Iovance Biotherapeutics' tumor-infiltrating lymphocyte (TIL) therapy, Amtagvi (lifileucel), for the treatment of advanced melanoma. Amtagvi is the first approved TIL therapy and the first T-cell therapy approved for solid tumors, marking another milestone in cell therapy.
Lenmeldy (atidarsagene autotemcel):
On March 18, 2024, the FDA approved Lenmeldy (atidarsagene autotemcel, arsa-cel), a gene therapy developed by Orchard Therapeutics, for the treatment of pediatric patients with metachromatic leukodystrophy (MLD) who meet specific criteria. This is the first FDA-approved gene therapy for this rare genetic disorder.
Tecelra (afamitresgene autoleucel):
On August 1, 2024, the FDA approved Adaptimmune Therapeutics' engineered T-cell therapy, Tecelra (afami-cel), for the treatment of adult patients with advanced MAGE-A4+ synovial sarcoma of certain HLA types who have previously received chemotherapy. Tecelra is the first engineered T-cell therapy approved for solid tumors and the first effective treatment for synovial sarcoma in over a decade.
Kebilidi (eladocagene exuparvovec):
On November 13, 2024, the FDA granted accelerated approval to Kebilidi (eladocagene exuparvovec), a gene therapy developed by PTC Therapeutics, for the treatment of pediatric and adult patients with aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase deficiency (AADCD), regardless of disease severity. This is the first FDA-approved gene therapy administered via direct injection into the brain.
On December 18, 2024, the FDA approved Ryoncil (remestemcel), developed by Mesoblast, for the treatment of steroid-refractory acute graft-versus-host disease (SR-aGVHD) in pediatric patients aged 2 months and older. The FDA's press release highlighted that this is the first FDA-approved mesenchymal stromal cell (MSC) therapy.
In addition, the FDA approved Moderna's respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) vaccine, Mresvia, marking the first approval of an mRNA vaccine for a disease other than COVID-19, demonstrating the potential of mRNA technology.
Top 10 Potential Blockbuster Therapies of 2024
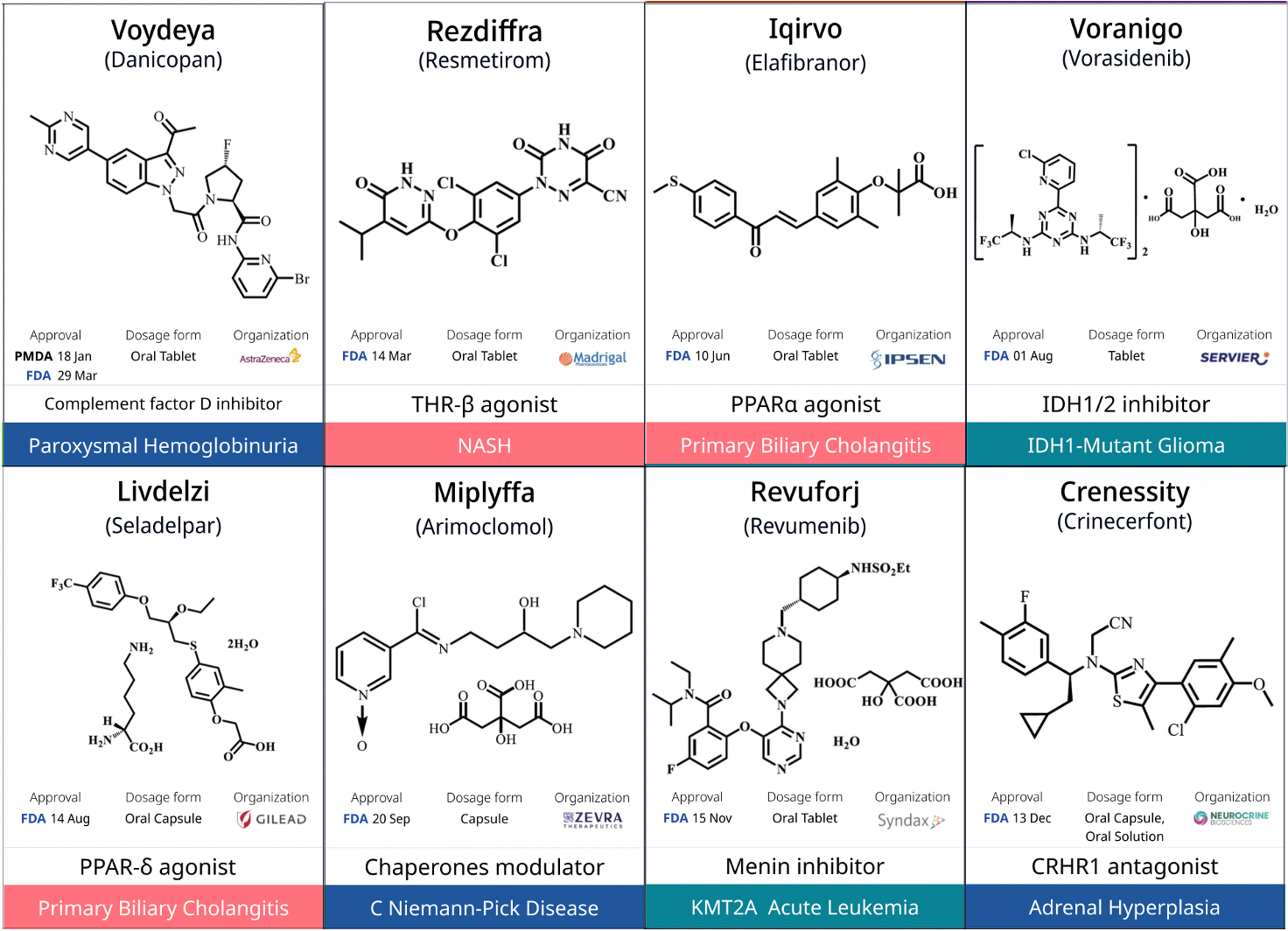
1. Rezdiffra (resmetirom): The First FDA-Approved Therapy for Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatohepatitis (MASH)
Rezdiffra (resmetirom), developed by Madrigal Pharmaceuticals, is a "first-in-class," once-daily, oral thyroid hormone receptor (THR)-β selective agonist designed to target the underlying causes of MASH. Thyroid hormone plays a central role in liver function by activating β receptors in hepatocytes, influencing a range of health parameters, from serum cholesterol and triglyceride levels to the pathological accumulation of fat in the liver.
Rezdiffra received FDA approval in March 2024, becoming the first approved therapy for MASH and marking a significant milestone in this field.
2. Winrevair (sotatercept): A "First-in-Class" Therapy for Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension
Winrevair is a "first-in-class" activin receptor type IIA (ActRIIA) fusion protein. It combines a modified extracellular domain of ActRIIA with the Fc region of an antibody. This therapy blocks the binding of activin to its cell membrane receptors, thereby reducing activin-mediated signaling.
Merck acquired this innovative therapy through its approximately $11.5 billion acquisition of Acceleron Pharma in 2021. Winrevair received FDA approval in March 2024 for the treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension. Merck believes it has the potential to become a cornerstone therapy for this condition.
3. Anktiva: A "First-in-Class" IL-15 Receptor Agonist for Non-Muscle Invasive Bladder Cancer (NMIBC)
Anktiva, developed by ImmunityBio's Altor BioScience, consists of an IL-15 mutant (IL-15N72D) bound to an IL-15 receptor α/IgG1 Fc fusion protein. Compared to natural IL-15, Anktiva exhibits superior pharmacokinetic properties in patients, persists longer in lymphoid tissues, and demonstrates enhanced anti-tumor activity.
In April 2024, Anktiva received FDA approval for use in combination with Bacillus Calmette-Guérin (BCG) to treat adult patients with BCG-unresponsive NMIBC accompanied by carcinoma in situ (CIS). In clinical trials, patients treated with Anktiva achieved a complete response rate of 62%.
4. mResvia: The First mRNA Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) Vaccine
Moderna's mRNA-based RSV vaccine, mResvia (mRNA-1345), received FDA approval in May 2024 for protecting adults aged 60 and older from lower respiratory tract disease (RSV-LRTD) caused by RSV infection. This is Moderna's second FDA-approved mRNA vaccine. It consists of an mRNA sequence encoding a stabilized prefusion F glycoprotein, delivered using the same lipid nanoparticle (LNP) technology as Moderna's COVID-19 vaccine.
5. Rytelo (imetelstat): The First Telomerase Inhibitor
In June 2024, the U.S. FDA approved Geron's "first-in-class" telomerase inhibitor, Rytelo (imetelstat), for the treatment of adult patients with low- to intermediate-1-risk myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS). This approval marked the arrival of the first telomerase-targeted therapy, nearly 40 years after the discovery of telomerase in 1984.
Telomeres are protective caps at the ends of chromosomes that naturally shorten with each cell division. In MDS, abnormal bone marrow cells often express telomerase, which rebuilds telomeres, leading to uncontrolled cell division. Preclinical and clinical data show that Rytelo inhibits telomerase activity, curbing the uncontrolled proliferation of cancerous stem and progenitor cells and inducing apoptosis in malignant cells, demonstrating disease-modifying activity.
6. Ohtuvayre (ensifentrine): The First Inhaled Therapy with a Novel Mechanism of Action for COPD Maintenance Treatment in Over 20 Years
Ohtuvayre, developed by Verona Pharma, is a "first-in-class" dual phosphodiesterase 3/4 (PDE3/4) inhibitor. It received FDA approval in June 2024 as a maintenance treatment for adult patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Ohtuvayre is the first inhaled COPD therapy to combine bronchodilator and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory effects. Additionally, it represents the first inhaled therapy with a novel mechanism of action for COPD maintenance treatment in over two decades.
Ohtuvayre works by inhibiting PDE3, leading to relaxation of airway smooth muscles and bronchodilation, while its inhibition of PDE4 reduces inflammation by decreasing the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines.
7. Kisunla (donanemab): The First Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) Therapy Allowing Treatment Discontinuation Upon Meeting Criteria
Kisunla, developed by Eli Lilly, is an anti-amyloid monoclonal antibody that specifically binds to the N3pG subtype of amyloid. By targeting this subtype, Kisunla selectively binds to amyloid plaques in the brain, facilitating their clearance.
In July 2024, it received FDA approval for the treatment of adult patients with early symptomatic AD, including those with mild cognitive impairment (MCI) or mild dementia stage AD, confirmed by the presence of amyloid pathology. According to the press release, Kisunla, administered monthly, is the first amyloid plaque-targeting therapy with evidence supporting treatment discontinuation after amyloid plaque clearance, potentially reducing treatment costs and the frequency of infusions.
8. Ebglyss (lebrikizumab): A New First-Line Biologic Therapy for Atopic Dermatitis
Ebglyss, co-developed by Almirall and Eli Lilly, is an anti-IL-13 antibody. It received FDA approval in September 2024 for the treatment of moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis (AD) in adults and adolescents (aged 12 years and older, weighing at least 40 kg) whose disease remains uncontrolled despite topical treatments.
IL-13 is a key cytokine in AD, driving type 2 inflammation in the skin, which leads to impaired skin barrier function, itching, skin thickening, and infections. Ebglyss's targeted mechanism of action, along with its demonstrated efficacy and safety in both short- and long-term use, makes it a compelling option for patients with moderate-to-severe AD inadequately controlled by topical therapies. Its once-monthly maintenance dosing offers convenience for patients.
9. Cobenfy (xanomeline, trospium chloride): The First Novel Mechanism Drug for Schizophrenia in Decades
Cobenfy received FDA approval in September 2024 for the treatment of adult patients with schizophrenia. The FDA press release highlighted that Cobenfy is the first antipsychotic drug targeting cholinergic receptors, diverging from the long-standing standard therapies that target dopamine receptors. This approval marks the first novel mechanism drug for schizophrenia in decades.
Cobenfy combines two active ingredients, xanomeline and trospium chloride, designed to activate muscarinic acetylcholine receptors in the brain while minimizing peripheral effects. By stimulating M1 and M4 muscarinic receptors, xanomeline alleviates negative symptoms such as apathy and reduced social drive, improves cognitive function, and helps manage other psychiatric symptoms like hallucinations and delusions. Originally developed by Karuna Therapeutics, Cobenfy was acquired by Bristol Myers Squibb in December 2023 through a merger agreement.
10. Attruby (acoramidis): The First Approved Product with Labeling Indicating Near-Complete Stabilization of Transthyretin (TTR)
In November 2024, the FDA approved Attruby (acoramidis), developed by BridgeBio Pharma, for the treatment of adults with transthyretin-mediated amyloidosis with cardiomyopathy (ATTR-CM) to reduce cardiovascular mortality and cardiovascular-related hospitalizations. The press release noted that Attruby is the first approved product with labeling indicating near-complete stabilization of TTR. The drug is designed to mimic the protective function of the TTR T119M mutation, maintaining the normal tetrameric conformation of TTR and preventing the formation of toxic amyloid deposits. In a Phase 3 clinical trial, Attruby reduced all-cause mortality and recurrent cardiovascular-related hospitalizations by 42% compared to placebo at 30 months of treatment.
How to obtain the latest research advancements in the field of biopharmaceuticals?
In the Synapse database, you can keep abreast of the latest research and development advances in drugs, targets, indications, organizations, etc., anywhere and anytime, on a daily or weekly basis. Click on the image below to embark on a brand new journey of drug discovery!