MAO Inhibitors -the Redemption of Depression
Monoamine Oxidase(MAO) is a naturally existing oxidase in the human body, located on the outer membrane of mitochondria. It can catalyze the oxidation of amine compounds (primary, secondary, and tertiary amines) to lose ammonia, and the oxidative reactions it catalyzes do not require the participation of cofactors. There are two subtypes of MAO, namely, MAO-A and MAO-B. Among them, MAO-A can metabolize biological amines neurotransmitters, such as dopamine and serotonin. Common substrates of MAO-B include beta-phenylethylamine, benzylamine, and selegiline.
Various free monoamines, such as dopamine and serotonin, exist in the human body. These substances are neurotransmitters at neuronal synapses and are usually stored in cells. During a nerve impulse, they are released into the synaptic cleft, bind to receptors, and facilitate impulse conduction. The monoamines in the synaptic cleft are oxidized and decomposed by MAO. MAO-A plays a role in regulating the concentration of monoamines within neurons and synaptic clefts in a healthy brain. In a depressed brain, the levels of MAO-A are high, leading to a decrease in the concentration of monoamines in the synapse. MAO inhibitors can inhibit MAO-A, reducing the degradation of synaptic monoamines and increasing their levels. Therefore, MAO inhibitors can play a role in treating depression.
In addition to treating depression, MAO inhibitors can also treat a variety of other diseases, such as hypertension, anxiety, nicotine dependence, mild cognitive impairment, Parkinson's disease, and so on.
MAO Competitive Landscape
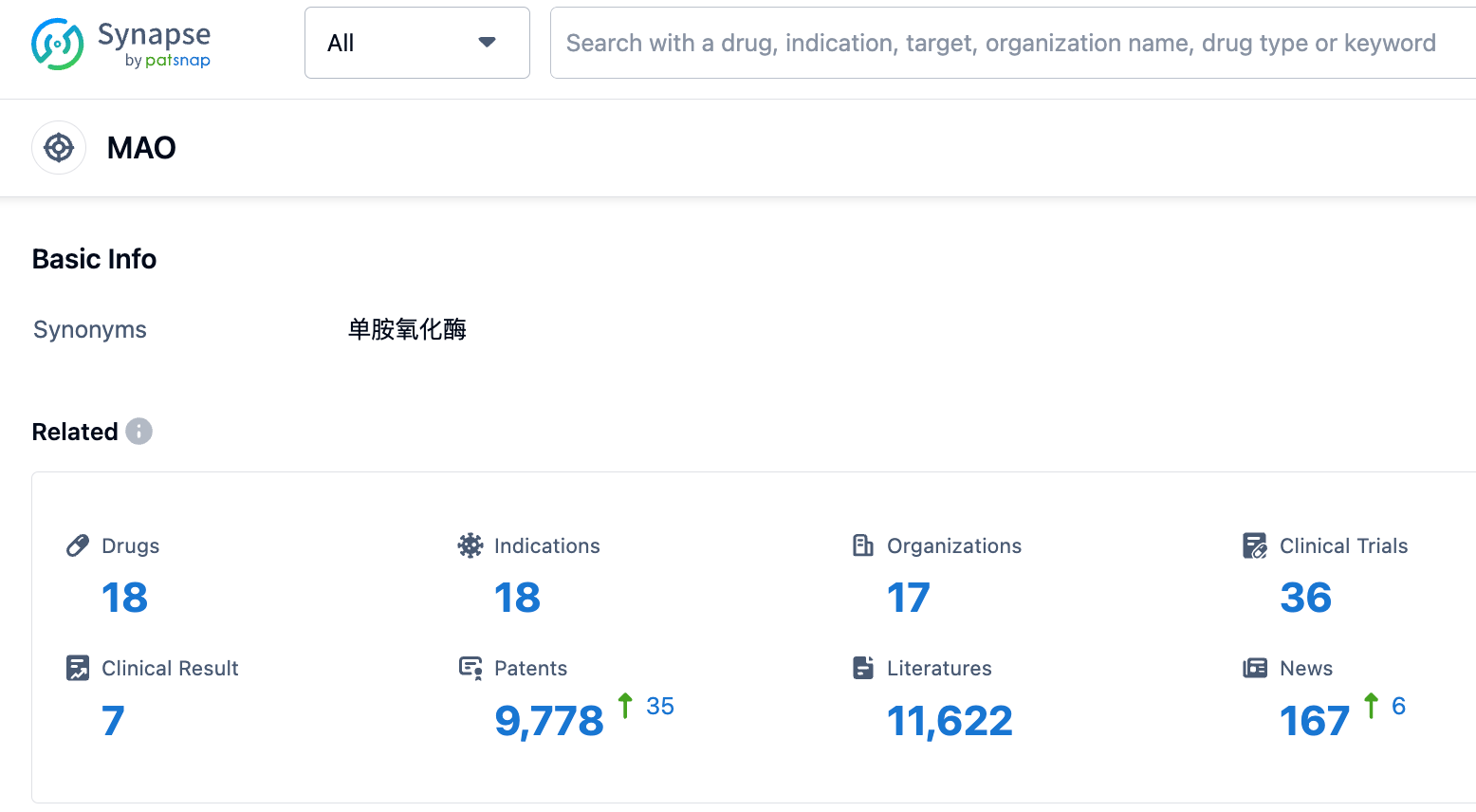
According to the data provided by Patsnap Synapse-Global Drug Intelligence Database: the following figure shows that as of 3 Sep 2023, there are a total of 18 MAO drugs worldwide, from 17 organizations, covering 18 indications, and conducting 36 clinical trials.
👇Please click on the picture link below for free registration or login directly if you have freemium accounts, you can browse the latest research progress on drugs , indications, organizations, clinical trials, clinical results, and drug patents related to this target.
Several drugs under the current target MAO have been approved for relevant indications. The approved indications include Depressive Disorder, Depressive Disorder Major, Pulmonary Tuberculosis, and Consciousness Disorders.
Based on the analysis of the data, the current competitive landscape for the target MAO indicates that several companies have successfully developed drugs and received approval for various indications. The majority of drugs are small molecule drugs, suggesting intense competition in this area. The United States, Japan, and China are leading in terms of drug development for the target MAO.
In the future, it is expected that more companies will enter the market and develop drugs targeting MAO. The competition is likely to intensify, especially in the small molecule drug category. Further research and development efforts are needed to explore additional indications and improve treatment options for patients.
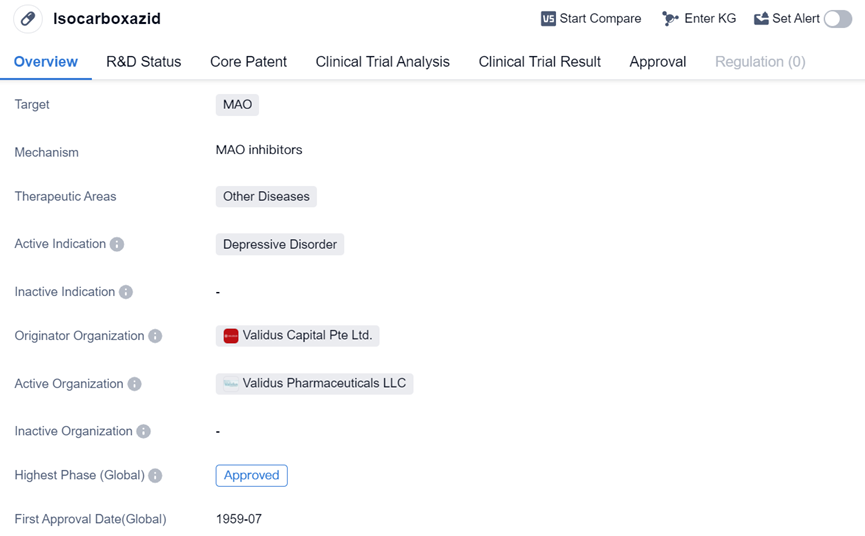
Irreversible MAO Inhibitor:Isocarboxazid
Isocarboxazid's approval in 1959 highlights its long-standing presence in the pharmaceutical market. It has been used for several decades to address Depressive Disorder. The drug's mechanism of action involves inhibiting the activity of MAO, an enzyme responsible for breaking down neurotransmitters such as serotonin, norepinephrine, and dopamine. By inhibiting MAO, Isocarboxazid helps to increase the levels of these neurotransmitters in the brain, which can alleviate symptoms of depression.
👇Please click on the image below to directly access the latest data (R&D Status | Core Patent | Clinical Trial | Approval status in Global countries) of this drug.
As a small molecule drug, Isocarboxazid is likely administered orally in the form of tablets or capsules. The drug's approval in the United States suggests that it has undergone rigorous testing to ensure its safety and efficacy. It is important to note that Isocarboxazid's therapeutic area is classified as Other Diseases, indicating that it may have additional uses beyond Depressive Disorder. However, the provided information does not specify these other indications.
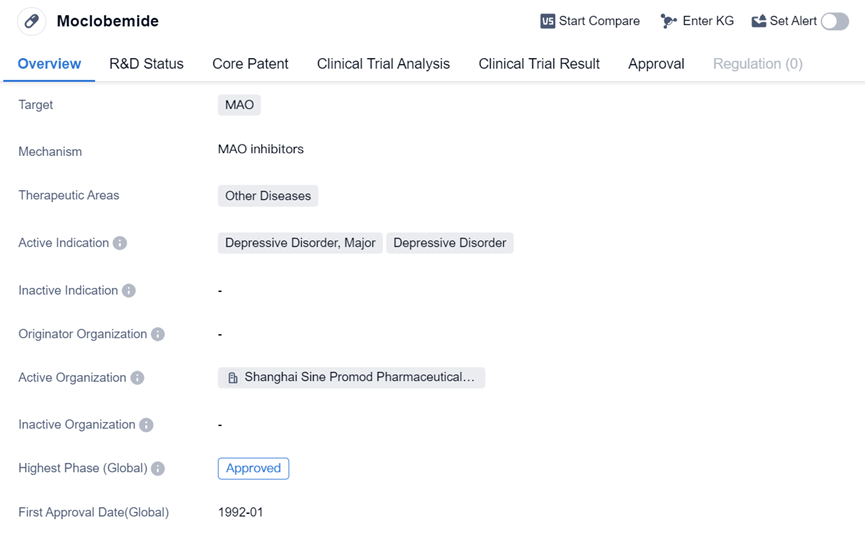
Reversible Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitor:Moclobemide
Moclobemide is a small molecule drug that targets the MAO enzyme and is approved for the treatment of Depressive Disorder, Major, and Depressive Disorder. It has received approvals in multiple regions, including Canada, and has been available since 1992. The drug aims to regulate neurotransmitter levels to alleviate symptoms associated with the indicated conditions.
👇Please click on the image below to directly access the latest data (R&D Status | Core Patent | Clinical Trial | Approval status in Global countries) of this drug.
The approval of Moclobemide in multiple regions suggests that it has undergone rigorous testing and evaluation to demonstrate its safety and efficacy. The drug has successfully completed the highest phase of clinical trials, indicating that it has met the necessary requirements to be considered a viable treatment option for the indicated conditions.
Given the information provided, it can be inferred that Moclobemide has been in use for several years, as it received its first approval in 1992. This suggests that it has a well-established track record and may have been widely prescribed to patients suffering from Depressive Disorder, Major, and Depressive Disorder.