Pharmaceutical Insights: osimertinib mesylate's R&D Progress and its Mechanism of Action on Drug Target
Osimertinib mesylate's R&D Progress
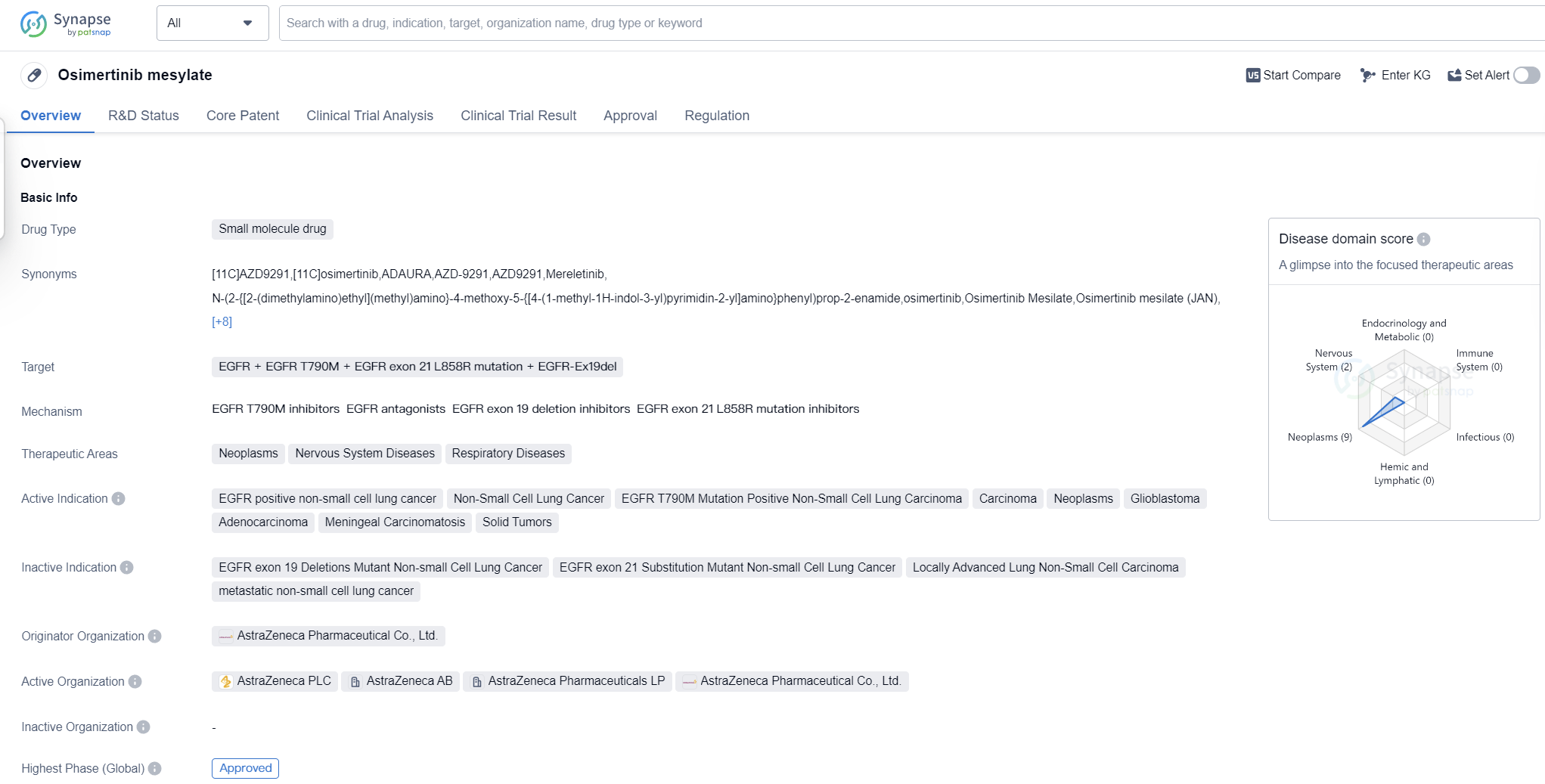
Osimertinib mesylate is a small molecule drug that is primarily used to target various mutations of the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) in the treatment of certain types of cancer. It is indicated for the treatment of EGFR positive non-small cell lung cancer, non-small cell lung cancer, EGFR T790M mutation positive non-small cell lung carcinoma, carcinoma, neoplasms, glioblastoma, adenocarcinoma, meningeal carcinomatosis, and solid tumors.
The drug was first approved in the United States in November 2015 and is currently approved in multiple countries globally. It is developed by AstraZeneca Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., a well-known pharmaceutical company in the industry.
Osimertinib mesylate has undergone various regulatory processes and has received several designations to expedite its development and approval. These include priority review, accelerated approval, fast track, accelerated assessment, breakthrough therapy, orphan drug, and special review project. These designations highlight the potential significance and urgency of the drug in addressing unmet medical needs.
The drug's therapeutic areas include neoplasms, nervous system diseases, and respiratory diseases. This suggests that it has the potential to be used in the treatment of various types of cancers, as well as diseases related to the nervous and respiratory systems.
👇Please click on the image below to directly access the latest data (R&D Status | Core Patent | Clinical Trial | Approval status in Global countries) of this drug.
Mechanism of Action for osimertinib mesylate: EGFR T790M inhibitors EGFR antagonists EGFR exon 19 deletion inhibitors EGFR exon 21 L858R mutation inhibitors
EGFR T790M inhibitors are a type of drugs that specifically target and inhibit the activity of the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) with the T790M mutation. This mutation is commonly found in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients who have developed resistance to other EGFR inhibitors. By blocking the activity of EGFR with the T790M mutation, these inhibitors can help to overcome resistance and potentially slow down the progression of NSCLC.
EGFR antagonists are drugs that inhibit the activity of the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), a protein involved in cell growth and division. By blocking the EGFR, these antagonists can interfere with the signaling pathways that promote cancer cell growth, potentially inhibiting tumor growth and progression. They are used in the treatment of various types of cancer, including lung, colorectal, and head and neck cancers.
EGFR exon 19 deletion inhibitors are a specific type of EGFR inhibitors that target and inhibit the activity of EGFR with exon 19 deletion mutation. Exon 19 deletion is a common mutation in NSCLC patients, and drugs targeting this mutation can help to block the abnormal signaling pathways mediated by EGFR, thereby inhibiting cancer cell growth and proliferation.
EGFR exon 21 L858R mutation inhibitors are drugs that specifically target and inhibit the activity of EGFR with the L858R mutation in exon 21. This mutation is also commonly found in NSCLC patients and is associated with increased EGFR activity and cancer cell growth. By inhibiting the activity of EGFR with the L858R mutation, these inhibitors can help to slow down tumor growth and improve patient outcomes.
In summary, the text refers to different types of drugs that target specific mutations in the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) to inhibit its activity. These drugs are used in the treatment of various cancers, particularly non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), to interfere with abnormal signaling pathways and inhibit cancer cell growth.
Drug Target R&D Trends for osimertinib mesylate
EGFR (Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor) is a protein found on the surface of cells that plays a crucial role in cell growth and division. Mutations in EGFR can lead to abnormal cell signaling, resulting in uncontrolled cell growth and the development of cancer. The EGFR T790M mutation, EGFR exon 21 L858R mutation, and EGFR-Ex19del mutation are specific genetic alterations commonly found in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients. These mutations can affect the response to targeted therapies, such as EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs), which are designed to inhibit the abnormal activity of EGFR and slow down cancer progression. Understanding these mutations is essential for developing effective treatments and improving patient outcomes.
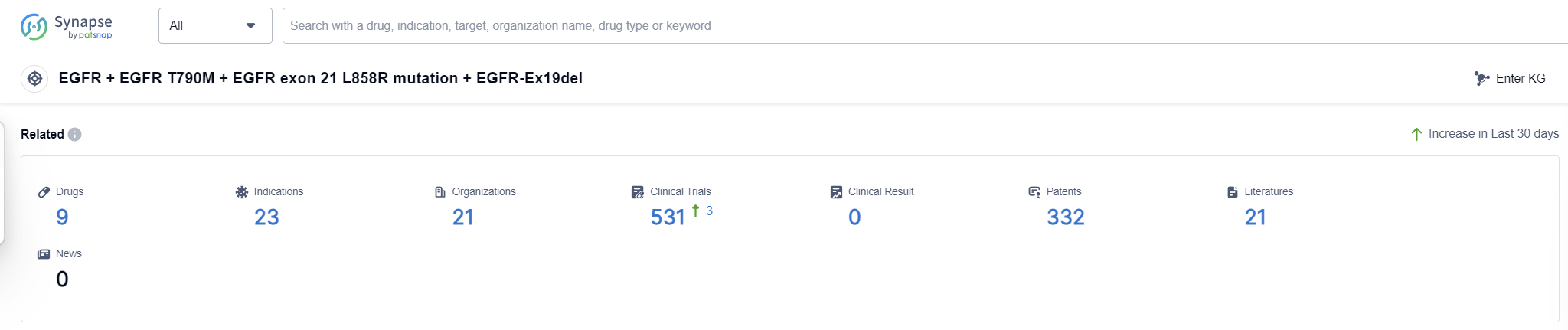
According to Patsnap Synapse, as of 16 Sep 2023, there are a total of 9 EGFR + EGFR T790M + EGFR exon 21 L858R mutation + EGFR-Ex19del drugs worldwide, from 21 organizations, covering 23 indications, and conducting 531 clinical trials.
The analysis of the target EGFR + EGFR T790M + EGFR exon 21 L858R mutation + EGFR-Ex19del reveals a competitive landscape with multiple companies actively involved in R&D. AstraZeneca PLC, Hansoh Pharma International Limited, and Shanghai Allist Pharmaceuticals Co., Ltd. are leading in terms of development stages. The approved drugs under this target primarily focus on treating lung cancer and related indications. Small molecule drugs are the most common drug type, with a presence of PROTACs in the discovery stage. China and South Korea are the countries showing significant progress, but other countries also contribute to the development of drugs targeting this mutation. Overall, the target EGFR + EGFR T790M + EGFR exon 21 L858R mutation + EGFR-Ex19del has a promising future in the pharmaceutical industry, with ongoing research and development efforts to address the unmet medical needs in lung cancer treatment.
👇Please click on the picture link below for free registration or log in directly if you have a freemium account, you can browse the latest research progress on drugs, indications, organizations, clinical trials, clinical results, and drug patents related to this target
Conclusion
Overall, osimertinib mesylate is a small molecule drug developed by AstraZeneca Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. It is primarily used to target specific mutations of the EGFR in the treatment of various types of cancer. The drug has received multiple regulatory designations and is approved in several countries globally. Its therapeutic areas include neoplasms, nervous system diseases, and respiratory diseases.