Phase 1 study outcomes of exidavnemab published in The Journal of Clinical Pharmacology
BioArctic AB (publ) (Nasdaq Stockholm: BIOA B) revealed the publication of the findings from two phase-1 trials involving exidavnemab(ABBV-0805) in The Journal of Clinical Pharmacology. Exidavnemab is a potential therapeutic agent being developed for conditions including Parkinson's disease. This monoclonal antibody specifically targets aggregated α-synuclein proteins, without affecting the normal form of the protein.
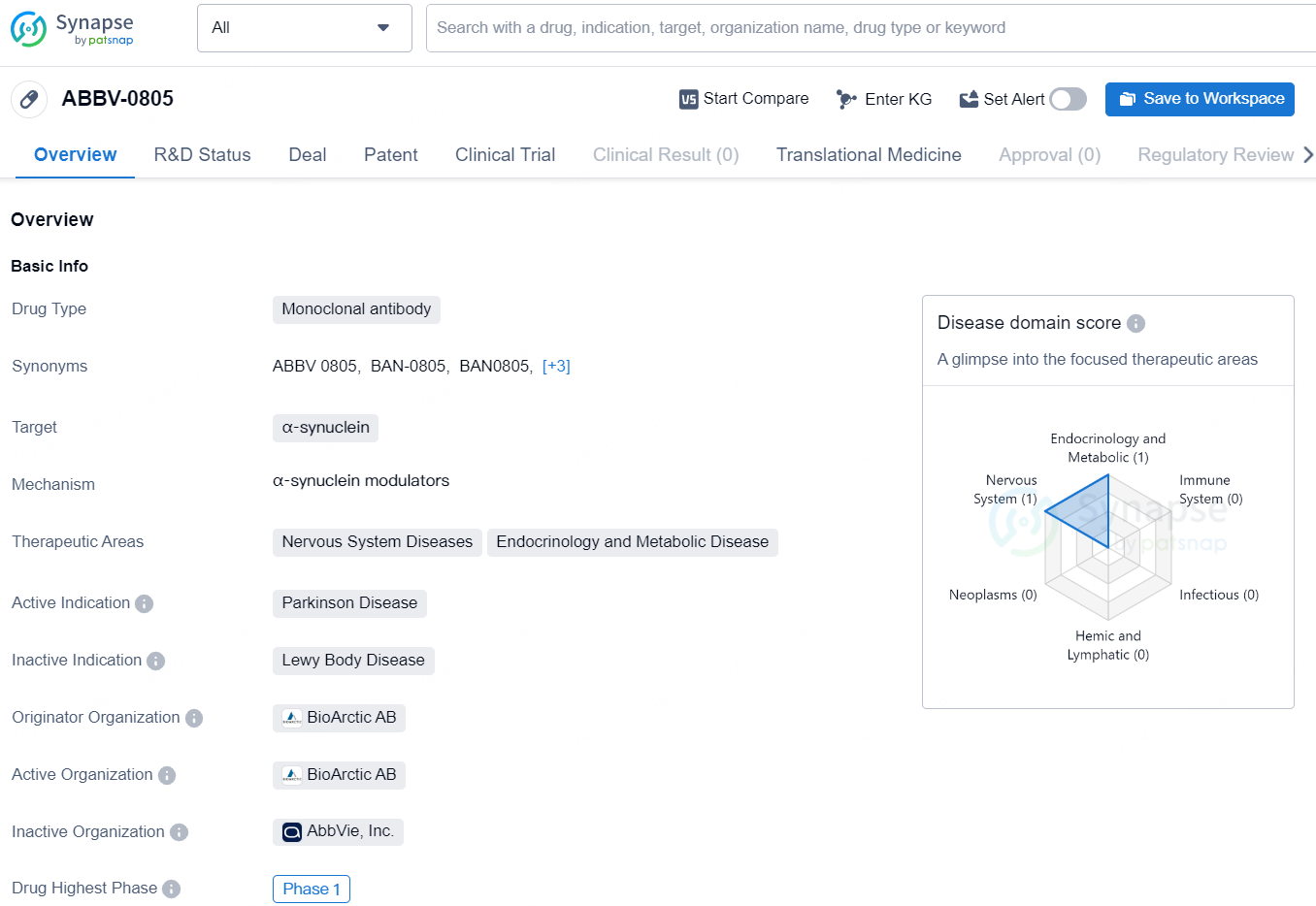
👇Unlock in-depth information about this drug - its R&D Status, Core Patent, Clinical Trials, and Global Approval Status. Click on the image below and explore the latest data immediately.
In two distinct phase 1 clinical trials conducted in collaboration with AbbVie, exidavnemab was administered to healthy subjects to evaluate its safety, tolerability, and pharmacokinetics. A total of 98 participants from various ethnic backgrounds took part in the studies, with 85 of them receiving exidavnemab. The dosage included intravenous injections ranging from 100 to 6000 mg, as well as a 300 mg subcutaneous injection.
The findings indicated that exidavnemab was generally well tolerated and exhibited an impressive half-life of about 30 days. This, alongside its high affinity and selectivity for pathological aggregated forms of α-synuclein, is crucial for maintaining a strong target binding within the brain.
"These data from the two studies support the ongoing clinical development of exidavnemab, and we are excited to initiate the phase 2a study later this year," commented Gunilla Osswald, CEO of BioArctic.
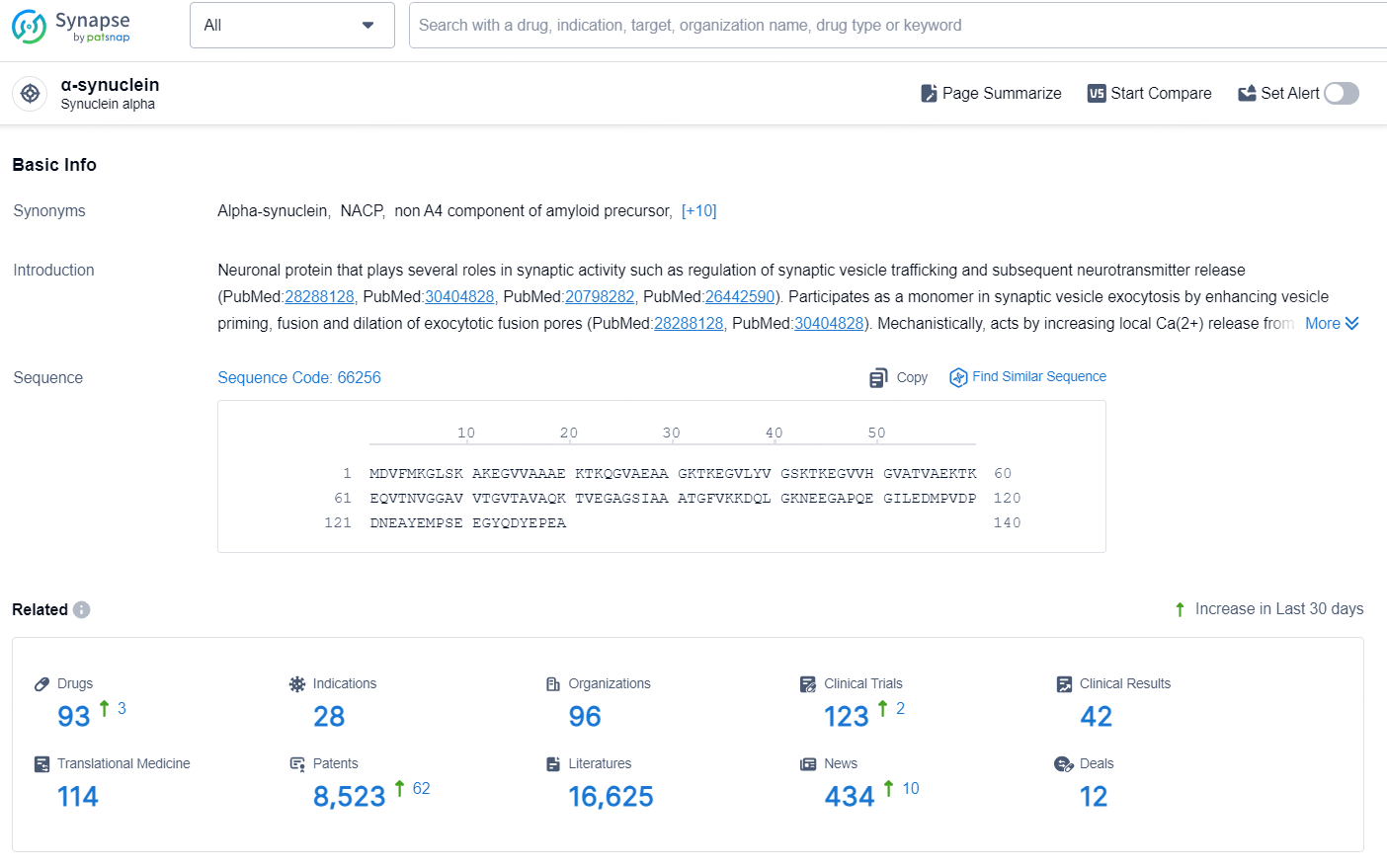
👇Explore the latest research progress on drug-related developments, indications, therapeutic organizations, clinical trials, results, and patents by clicking on the targeted picture link below. Unfold a world of comprehensive information on this target in just a click!
According to the data provided by the Synapse Database, As of August 29, 2024, there are 93 investigational drugs for the α-synuclein target, including 28 indications, 96 R&D institutions involved, with related clinical trials reaching 123, and as many as 8523 patents.
Exidavnemab is a monoclonal antibody drug candidate that is designed to selectively bind and eliminate aggregated forms of alpha-synuclein such as oligomers and protofibrils and fibrillar forms, which participates in neurodegenerative disorders including Parkinson’s disease. The goal is to develop a disease modifying treatment that stops or slow down the progression of Parkinson’s disease.