Progress in the Research of COX-1 Inhibitors
Cyclooxygenase, also known as Prostaglandin-endoperoxide Synthase, is a bifunctional enzyme with both cyclooxygenase and peroxidase activity. It is the key enzyme that catalyzes the conversion of arachidonic acid into prostaglandins. Two types of cyclooxygenase have been discovered so far, namely COX-1 and COX-2 isoenzymes.
COX-1 is constitutive, mainly located in blood vessels, stomach, kidneys, and other tissues. It is involved in the regulation of blood vessel dilation and contraction, platelet aggregation, gastric mucosal blood flow, stomach mucus secretion, and renal function. Its functions are related to the protection of the gastrointestinal mucosa, the regulation of platelet aggregation, the regulation of the resistance of peripheral blood vessels, and the regulation of the distribution of kidney blood flow.
COX-2 is inducible. Inflammation and injury mainly stimulate monocytes, macrophages, fibroblasts, vascular smooth muscle cells or endothelial cells, inducing the production of COX-2. COX-2 is a key link in triggering subsequent inflammatory responses. Currently, it is believed that COX-1 and COX-2 have overlapping and complementary functions and jointly contribute to the protective effects on the body.
COX-1 Competitive Landscape
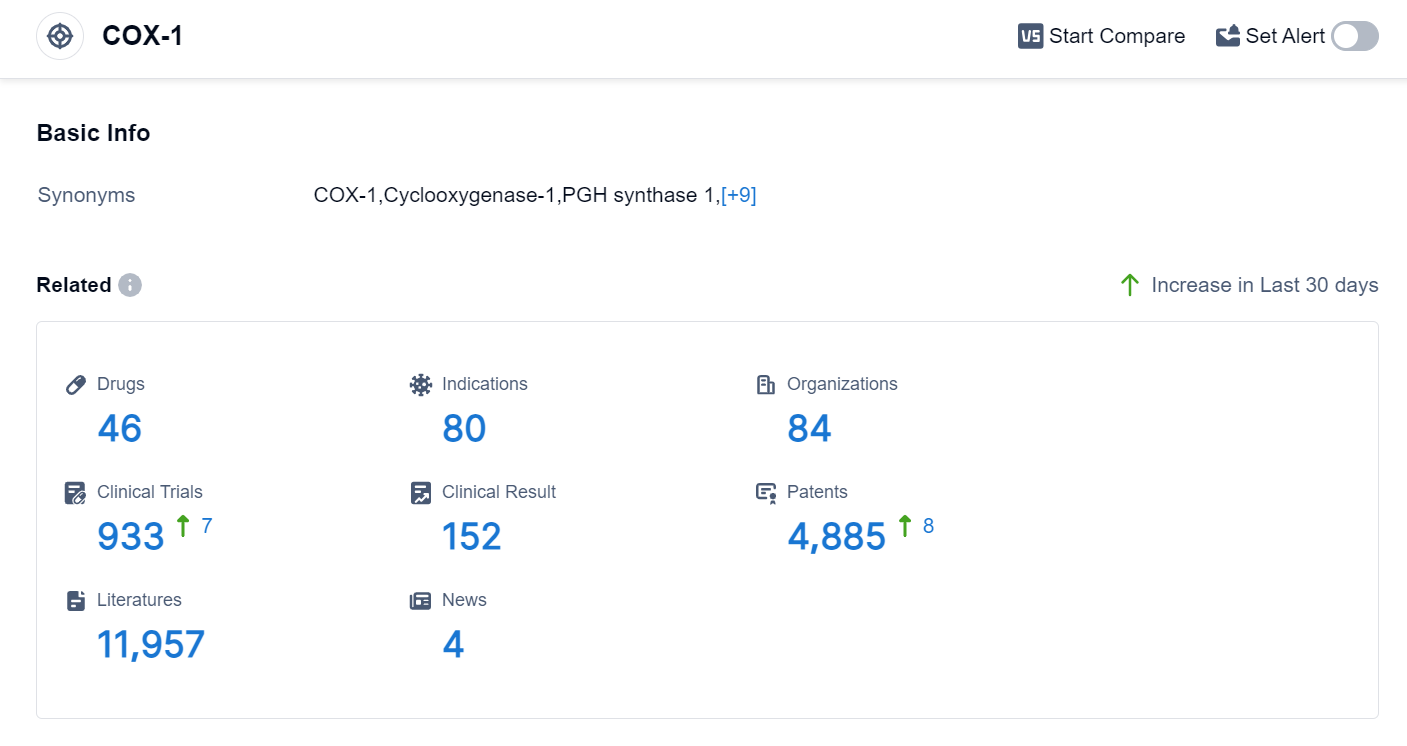
According to the data provided by Patsnap Synapse-Global Drug Intelligence Database: the following figure shows that as of 18 Sep 2023, there are a total of 46 COX-1 drugs worldwide, from 84 organizations, covering 80 indications, and conducting 933 clinical trials..
👇Please click on the picture link below for free registration or login directly if you have freemium accounts, you can browse the latest research progress on drugs , indications, organizations, clinical trials, clinical results, and drug patents related to this target.
The analysis of target COX-1 reveals a competitive landscape with multiple companies actively involved in research and development. Mitsubishi Chemical Group Corp., AbbVie, Inc., Viatris Inc., A. Menarini Industrie Farmaceutiche Riunite SRL, and Assertio Holdings, Inc. are the companies growing fastest under this target. Pain is the most common indication for drugs targeting COX-1, followed by various inflammatory conditions and other pain-related indications. Small molecule drugs are the primary focus of research and development for COX-1 inhibitors. Japan, the United States, and the European Union are leading in terms of drug development, with China also showing progress. The future development of target COX-1 is expected to continue with a focus on pain management and inflammatory conditions, driven by the advancements in small molecule drug research and development.
The globally approved COX-1 inhibitor on the market: Mofezolac
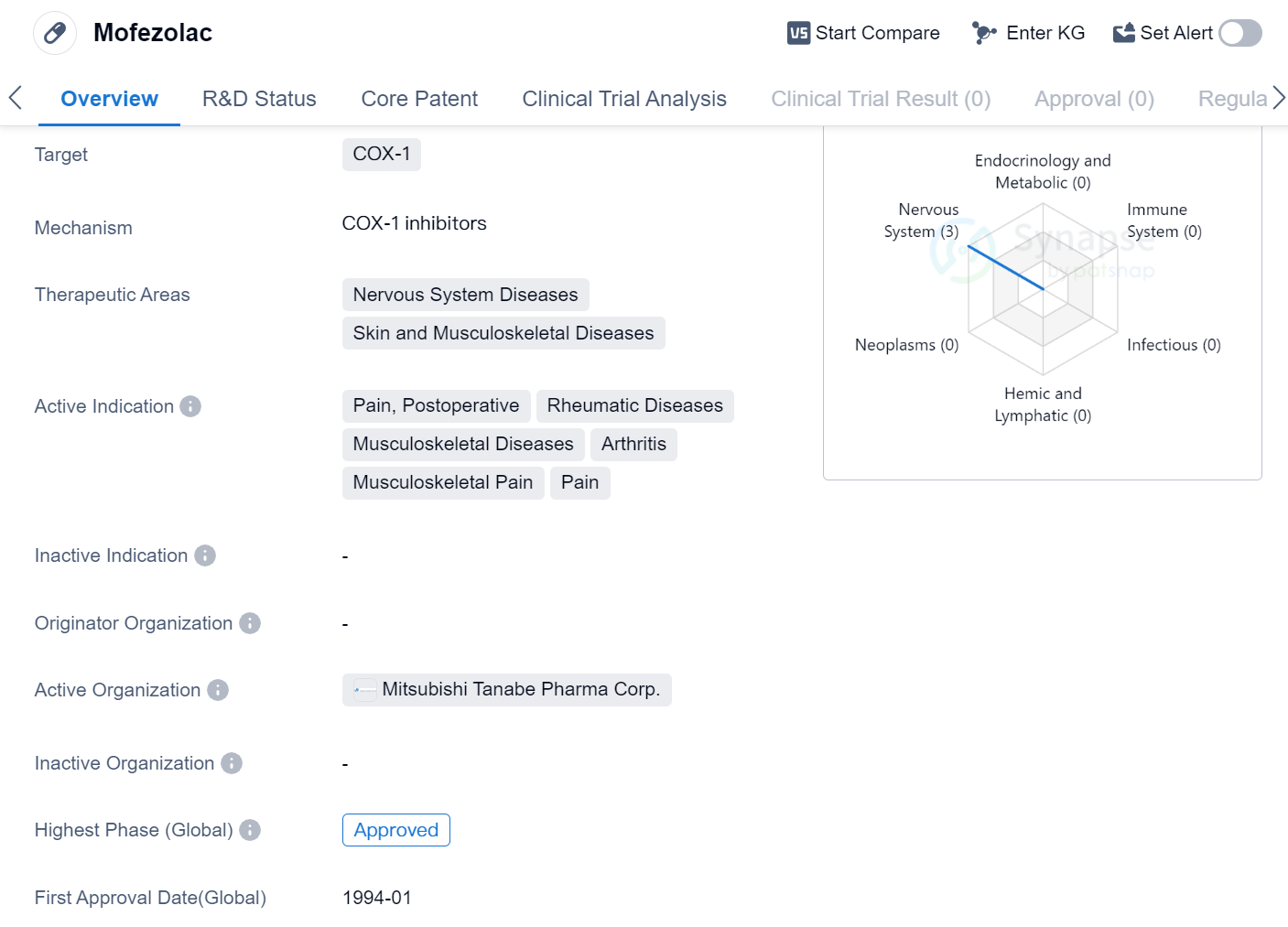
Mofezolac is a small molecule drug that primarily targets COX-1, an enzyme involved in the production of prostaglandins, which are responsible for inflammation and pain. This drug is primarily used in the treatment of various nervous system diseases, skin diseases, and musculoskeletal diseases.
👇Please click on the image below to directly access the latest data (R&D Status | Core Patent | Clinical Trial | Approval status in Global countries) of this drug.
The active indications for Mofezolac include pain management, particularly in postoperative cases, as well as the treatment of rheumatic diseases, musculoskeletal diseases, arthritis, musculoskeletal pain, and general pain. These indications suggest that Mofezolac is effective in alleviating pain associated with various conditions, making it a versatile drug in the field of biomedicine.
Mofezolac has successfully completed all phases of clinical trials and has received global approval. The drug was first approved in January 1994, indicating that it has been in use for several decades.
The therapeutic areas targeted by Mofezolac, including nervous system diseases, skin diseases, and musculoskeletal diseases, are broad and encompass a wide range of conditions. This indicates that Mofezolac has the potential to address multiple medical needs and provide relief to patients suffering from various ailments.
As a small molecule drug, Mofezolac is likely to have a well-defined chemical structure, which allows for easier synthesis and production. This characteristic may contribute to its widespread availability and accessibility in the pharmaceutical market.
In summary, Mofezolac is a small molecule drug that targets COX-1 and is primarily used in the treatment of nervous system diseases, skin diseases, and musculoskeletal diseases. It has been approved globally since 1994 and is indicated for pain management in various conditions.