Selinexor - A Small Molecule Drug Targeting XPO1
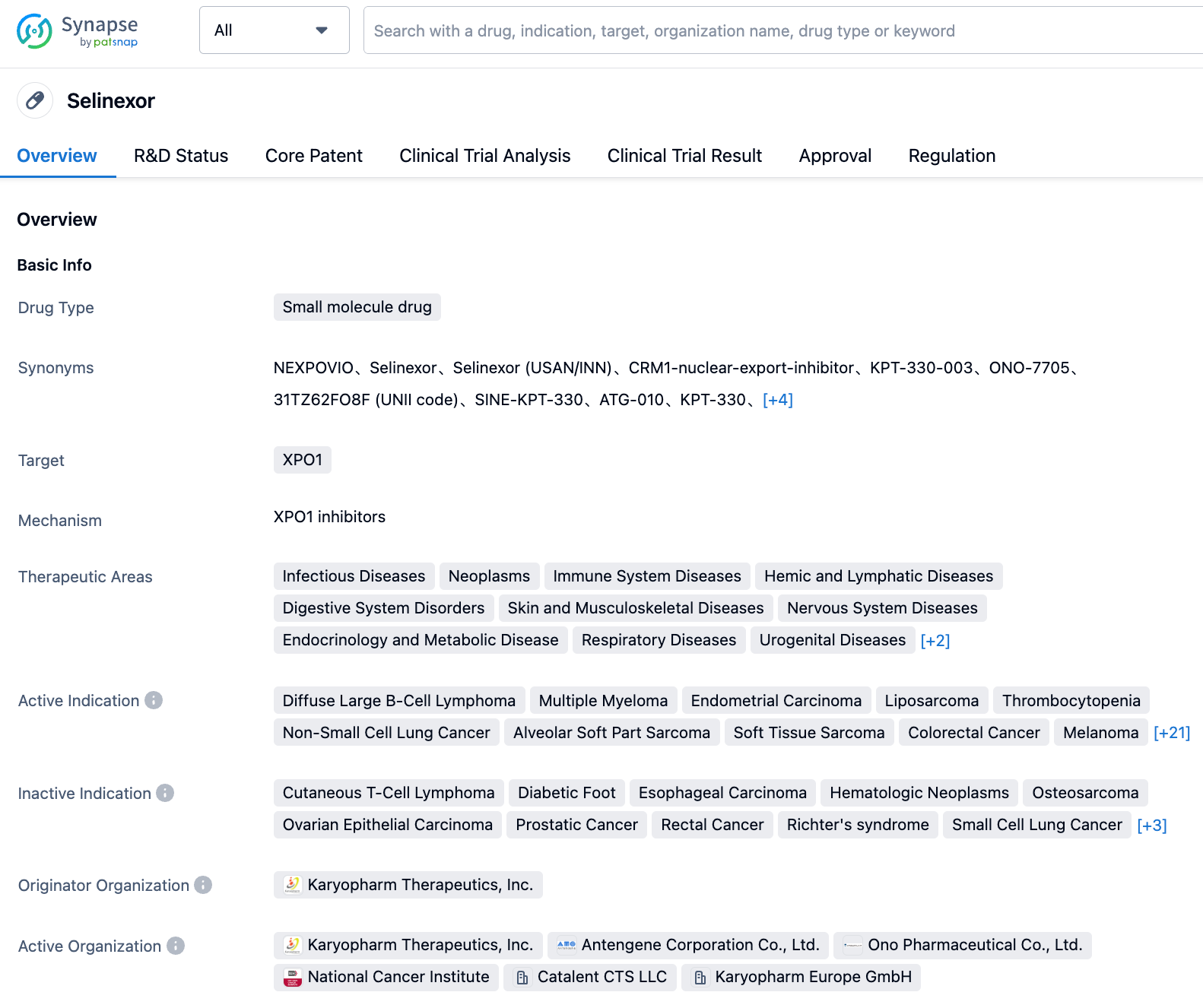
Selinexor, a small molecule drug targeting XPO1, is developed by Karyopharm Therapeutics, Inc. This drug was first approved in the United States on July 3, 2019, for the treatment of multiple myeloma. Subsequently, it has been approved in several countries/regions including Israel, the European Union, the United Kingdom, and South Korea.
Primarily focused on the field of oncology, it involves dozens of subdivided tumor types, several of which have ceased development. On July 17, 2023, for the three indications of primary myelofibrosis, post-polycythemia vera myelofibrosis and post-primary thrombocythe-mia myelofibrosis, FDA granted Selinexor Fast Track designation.
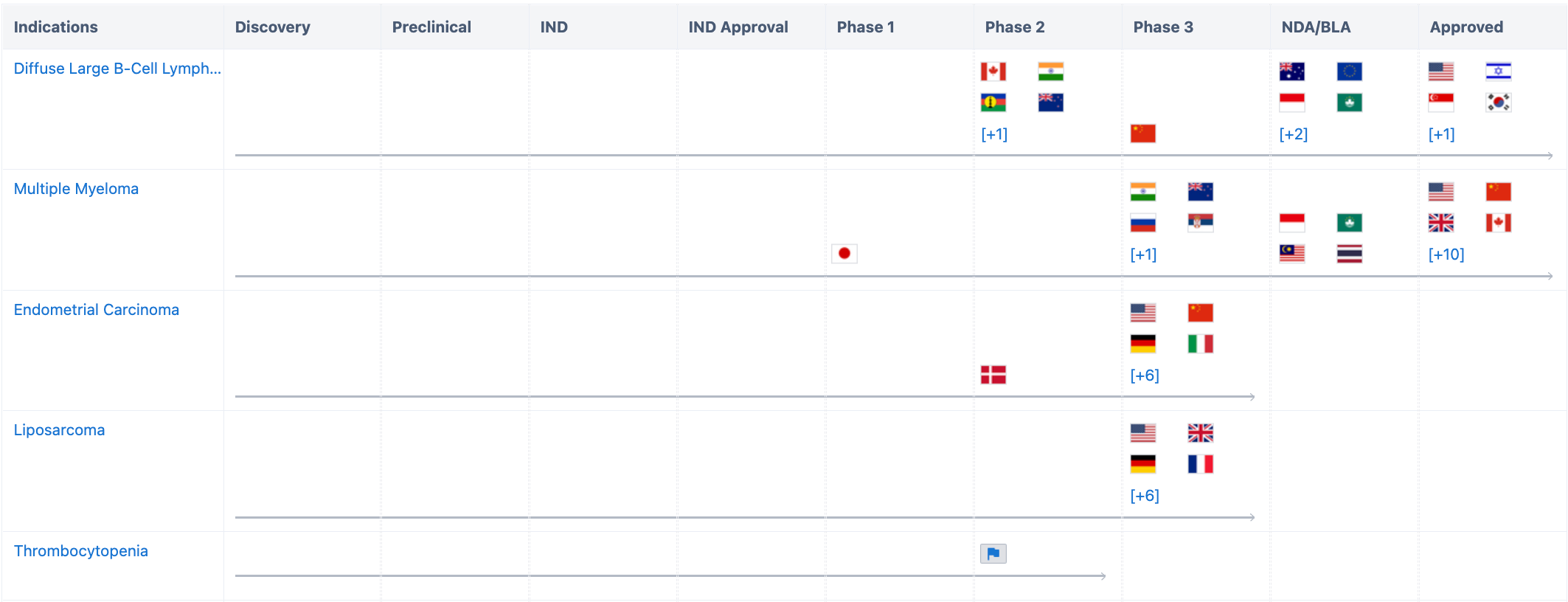
According to the "Synapse" database, diffuse large B-cell lymphoma has been approved in the US, Israel, Singapore, South Korea; multiple myeloma has been approved in more than ten countries including China and the United States; endometrial cancer has entered phase 3 in several countries. In addition, the indications developed include liposarcoma, non-small cell lung cancer, alveolar soft part sarcoma, soft tissue sarcoma, colorectal cancer, melanoma, myelofibrosis, and novel coronavirus infection, etc.
Selinexor has been granted seventeen regulatory designations, most of which are "orphan drug“ for different indications. Next is "fast track (US)". In addition to the three indications this time, it also includes multiple myeloma certified in 2019, and diffuse large B-cell lymphoma certified in 2020.
Mechanism of Action
XPO1 is a nuclear export protein in the nucleus, which is involved in the process of transporting a large number of proteins from the nucleus to the cytoplasm. Overexpression or mutation of XPO1 enhances export ability and affects cell proliferation. Selinexor inhibits the nuclear export protein XPO1, promoting intranuclear storage and activation of tumor suppressor proteins and other growth regulating proteins, and downregulating several oncogenic protein levels in the cytoplasm, which induces tumor cell apoptosis and activates the glucocorticoid receptor (GR) pathway.
Core Clinical Trials
Refractory plasmacytoma: In NCT03589222 (phase 2), the ORR of the Selinexor-DVd group was 50.0%. In NCT0311-0562(phase 3), the ORR was 67.9% treated with Selinexor + Bortezomib + Dexamethasone, compared with 47.2% for those treated with Bortezomib and Dexamethasone.
Refractory B-cell lymphoma: In the phase 2 clinical trial (NCT05322330), the ORR of the Selinexor group was 66.7%.
Glioblastoma Multiforme: In phase 2 NCT04421378, the tumor growth inhibition (TGI) rate of the Selinexor group was 64.5%, and the TGI of the Temozolomide group was 67.2%.
Multiple myeloma: In phase 3 NCT03110562, the mPFS of the Bortezomib+ Dexamethasone + Selinexor group was 16.6 months, compared with 9.2 months for the Bortezomib + Dexamethasone group.
Competitive Landscape
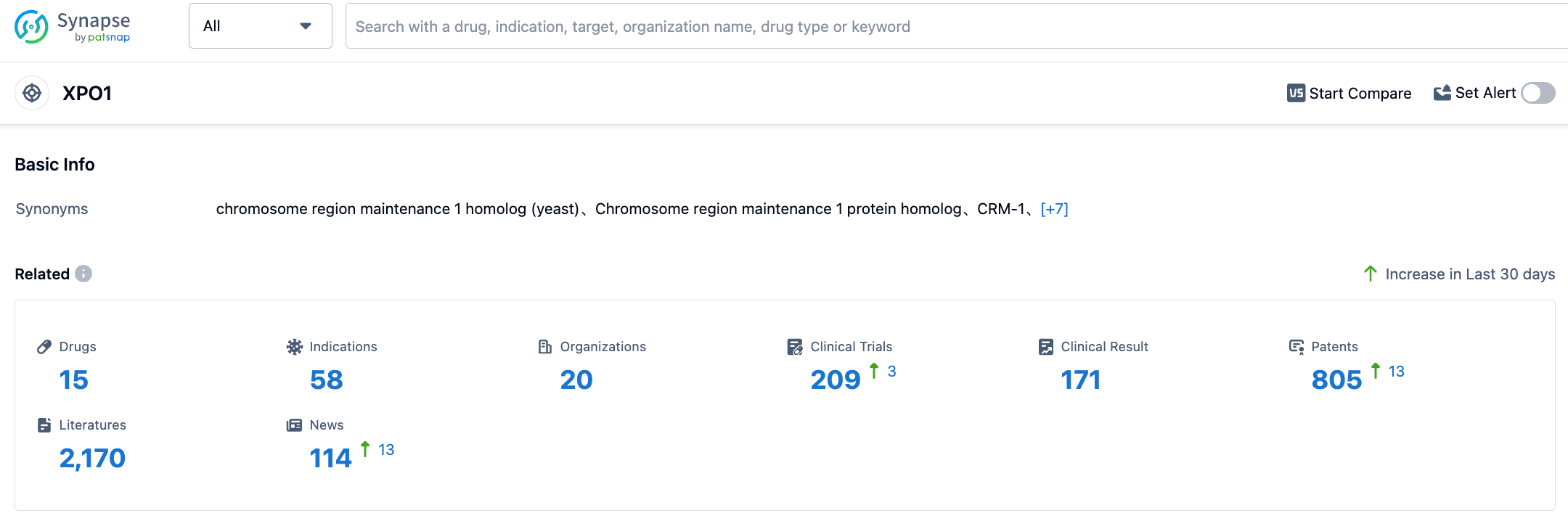
As of August 5, 2023, there are only 15 XPO1 drugs worldwide, and Selinexor is the only approved XPO1 targeted drug. Another drug, Eltanexor by the same company, is in phase 2, 6 are in phase 1, 5 are in pre-clinical, and 2 have ceased development, so Selinexor faces relatively little competition.