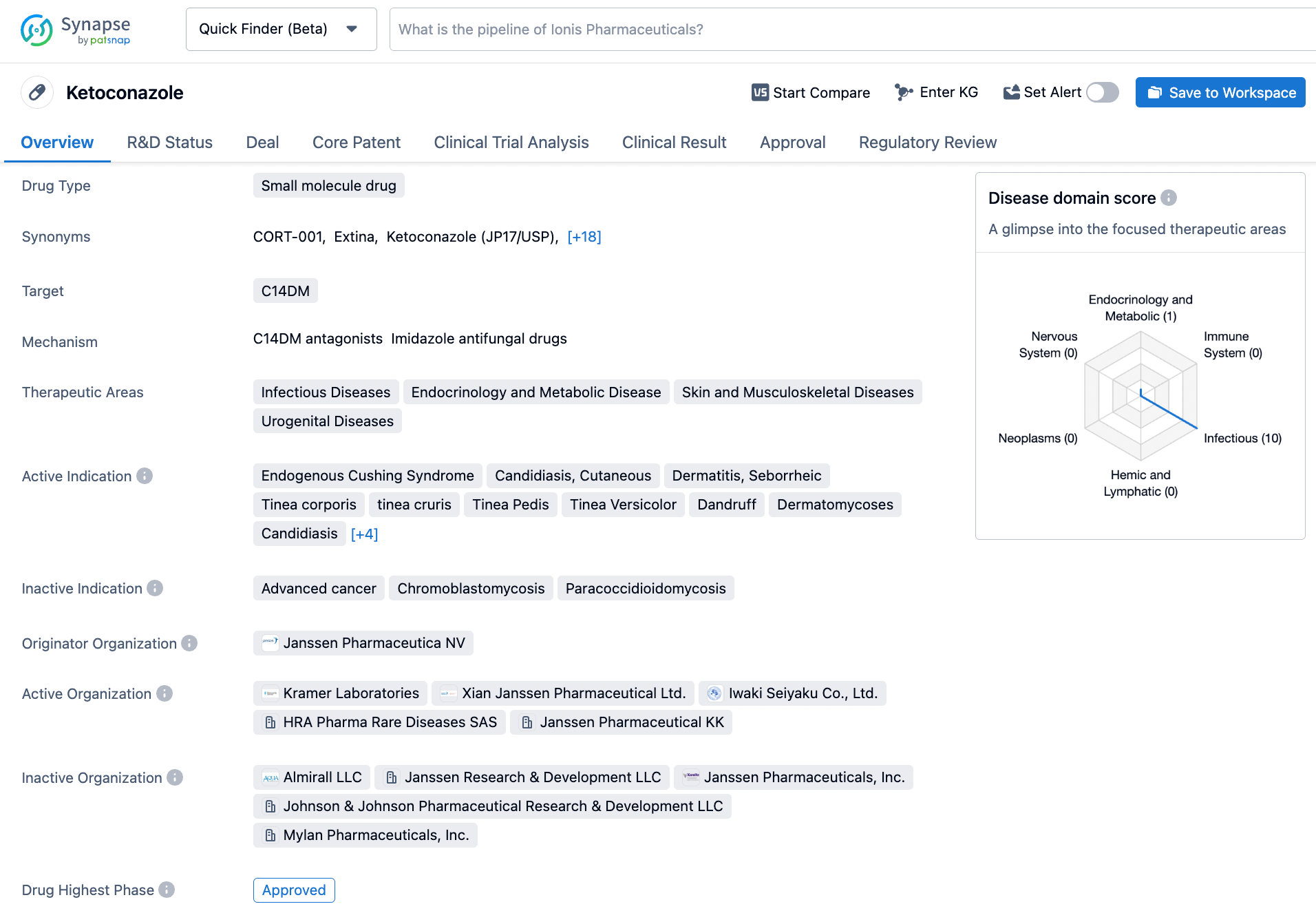
Synapse Simplified: How to Find Ketoconazole Information
Ketoconazole, a diminutive molecular compound, functions as an inhibitor of CYP51A1. This drug received its first approval in the month of June in the year 1981, following its development by the esteemed Janssen Pharmaceutica NV. As an inhibitor of CYP51A1, its mechanism of action hinges on the impediment of the fungal enzyme lanosterol 14α-demethylase. The latter plays an indispensable role in the synthesis of ergosterol - a fundamental constituent of fungal cell membranes. By thwarting this key enzymatic activity, ketoconazole effectively brings about the disruption of fungal growth, culminating in their eventual demise. Notably, ketoconazole serves as an efficacious treatment option for a diverse array of fungal infections, spanning the gamut from skin infections to systemic infections, encompassing the hair and nails. Although more recent antifungal agents with comparatively fewer side effects have displaced ketoconazole to a large extent, the drug retains its significance in certain scenarios, such as when alternative treatment modalities fail or when contraindications are present. Ultimately, ketoconazole endures as a crucial therapeutic intervention in the management of fungal infections. Click on the image below to begin the exploration journey of Ketoconazole through the Synapse database!
You can search for the latest pharmaceutical information such as drugs, targets, patents, transactions, clinical results, etc. through the Synapse database. Come and experience it!