The Body's Inflammatory Messengers: COX-2 Inhibitors
Cyclooxygenase, also known as Prostaglandin-endoperoxide Synthase, is a bifunctional enzyme with both cyclooxygenase and peroxidase activity. It is a key enzyme in the transformation of arachidonic acid into prostaglandins. There are two discovered isozymes of cyclooxygenase, COX-1 and COX-2.
COX-1 is a structural type, mainly found in blood vessels, stomach, kidneys, and other tissues, involved in regulating the vascular contraction, platelet aggregation, gastric mucosal blood flow, gastric mucus secretion, and kidney function. Its function is related to the protection of gastric mucosa, regulation of platelet aggregation, adjustment of peripheral vascular resistance, and regulation of renal blood flow distribution.
COX-2 is the induced type. Inflammatory injuries mainly stimulate monocytes, macrophages, fibroblasts, vascular smooth muscle or endothelial cells, etc., to induce the generation of COX-2, which is a key link in triggering subsequent inflammation. Currently, it is believed that COX-1 and COX-2 have overlapping and complementary functions, cooperatively exerting protective effects on the body.
COX-2 is an enzyme used by the body to produce a family of inflammatory messengers called prostaglandins. Blocking or inhibiting COX-2 can reduce prostaglandins thereby reducing inflammation. Scientists have found that COX-2 is part of the inflammatory response produced by the body. But like many other molecules that function in inflammation and normal states, COX-2 is thought to protect the brain and support cognition. COX-1 is a similar enzyme that can also produce inflammatory prostaglandins, but it also protects the stomach wall.
COX-2 is associated with many inflammatory diseases, including rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis. Because COX-2 is suspected to have activity in the brain, in limited studies, its over-activity is associated with neurodegenerative diseases such as multiple sclerosis, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, Parkinson's disease, and Alzheimer's disease.
Cox-2 Competitive Landscape
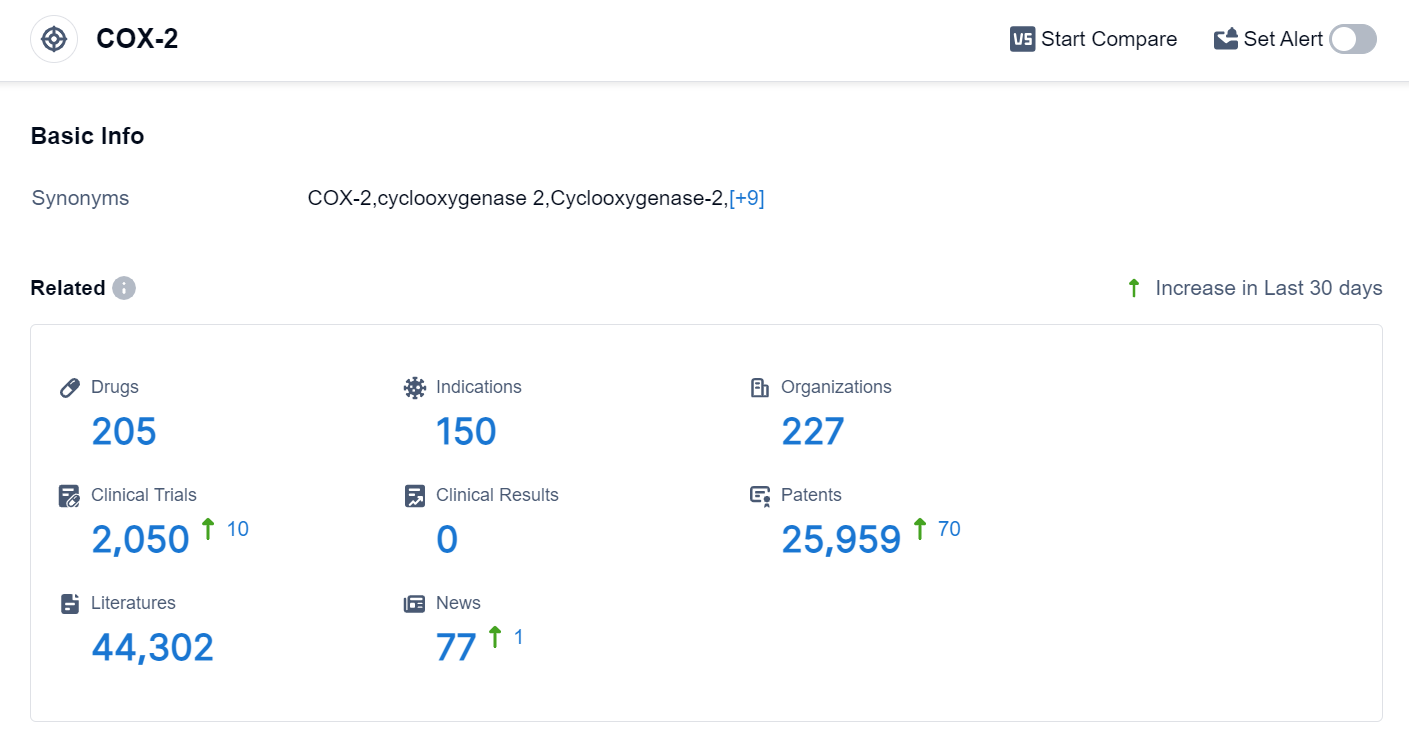
According to the data provided by Patsnap Synapse-Global Drug Intelligence Database: the following figure shows that as of 24 Sep 2023, there are a total of 205 COX-2 drugs worldwide, from 227 organizations, covering 150 indications, and conducting 2050 clinical trials.
👇Please click on the picture link below for free registration or login directly if you have freemium accounts, you can browse the latest research progress on drugs , indications, organizations, clinical trials, clinical results, and drug patents related to this target.
The analysis of the target COX-2 reveals a competitive landscape with multiple companies involved in the development of drugs. Viatris Inc. is leading in terms of the highest stage of development, with 3 approved drugs. Pain is the most common indication for approved drugs under the target COX-2. Small molecule drugs are progressing rapidly, indicating intense competition. China is showing significant progress in the development of drugs under the target COX-2. Overall, the target COX-2 presents opportunities for further research and development, with potential for innovative drugs and competition in the pharmaceutical industry.
The globally approved COX-2 inhibitor on the market: Polmacoxib
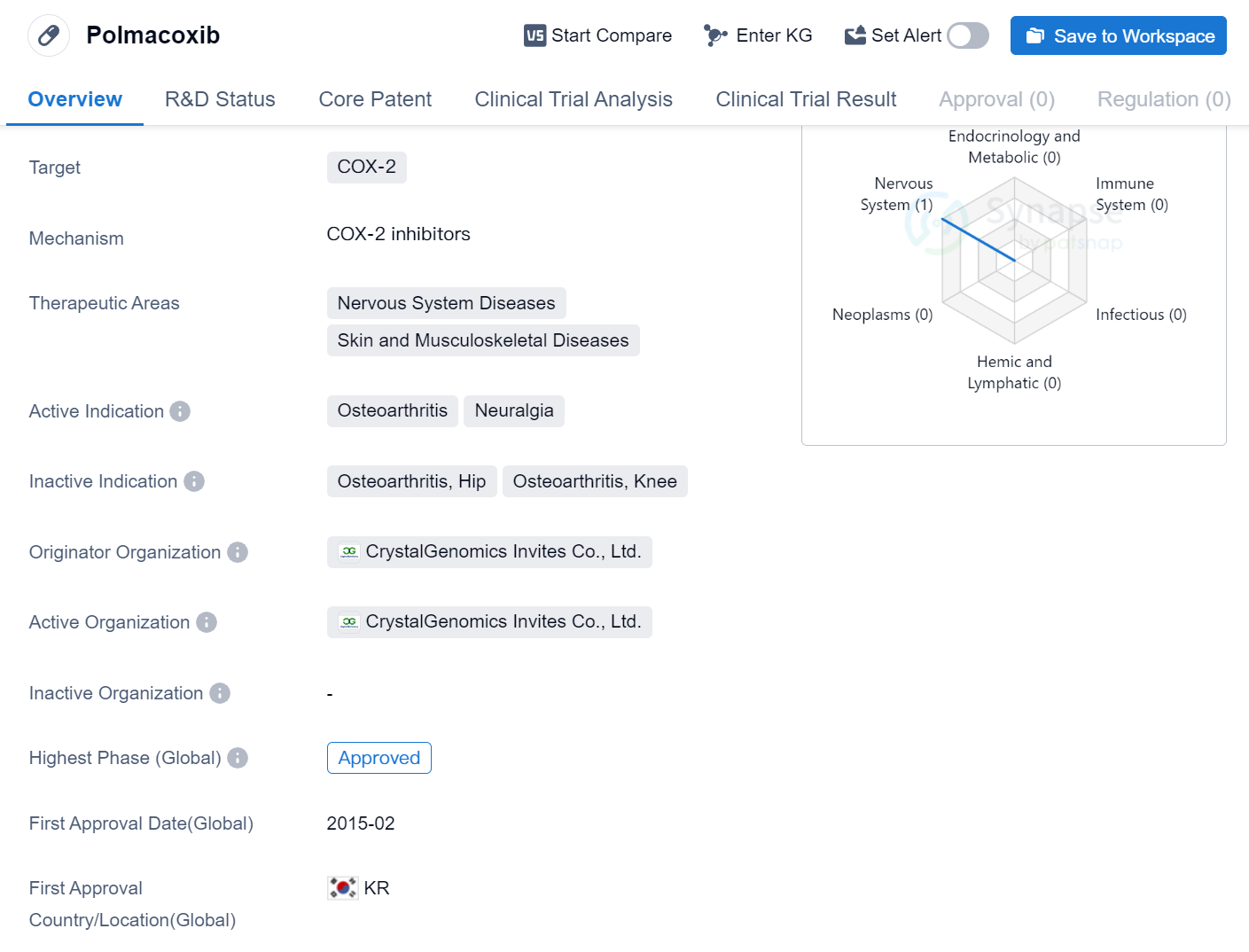
Polmacoxib is a small molecule drug that targets COX-2, making it suitable for the treatment of various nervous system diseases, as well as skin and musculoskeletal diseases. The drug has been specifically approved for the treatment of osteoarthritis and neuralgia.
👇Please click on the image below to directly access the latest data (R&D Status | Core Patent | Clinical Trial | Approval status in Global countries) of this drug.
Polmacoxib was developed by CrystalGenomics Invites Co., Ltd., an originator organization based in South Korea. It received its first approval in February 2015, making it available for use in the South Korean market.
As a small molecule drug, Polmacoxib is designed to interact with specific enzymes or receptors in the body, in this case, COX-2. By targeting COX-2, the drug aims to reduce inflammation and alleviate pain associated with conditions such as osteoarthritis and neuralgia.
The therapeutic areas of nervous system diseases, skin, and musculoskeletal diseases highlight the potential versatility of Polmacoxib in treating a range of conditions. Nervous system diseases encompass a wide range of disorders affecting the brain, spinal cord, and nerves, while skin and musculoskeletal diseases refer to conditions affecting the skin, muscles, bones, and joints.
Osteoarthritis, one of the approved indications for Polmacoxib, is a degenerative joint disease characterized by the breakdown of cartilage and the underlying bone. It is a common condition that causes pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility in affected joints. Neuralgia, another approved indication, refers to severe, shooting pain that occurs along the course of a nerve.
The approval of Polmacoxib in South Korea and its indication for osteoarthritis and neuralgia suggest that it may be a valuable treatment option for patients suffering from these conditions. However, further research and clinical trials may be necessary to explore its potential benefits in other therapeutic areas and indications.
Imrecoxib
Imrecoxib is a small molecule drug that targets COX-2, making it suitable for the treatment of various infectious diseases, as well as skin and musculoskeletal diseases. The drug has been specifically indicated for osteoarthritis and ankylosing spondylitis. Imrecoxib was developed by Jiangsu Hengrui Pharmaceuticals Co., Ltd., a pharmaceutical organization based in China.
👇Please click on the image below to directly access the latest data (R&D Status | Core Patent | Clinical Trial | Approval status in Global countries) of this drug.
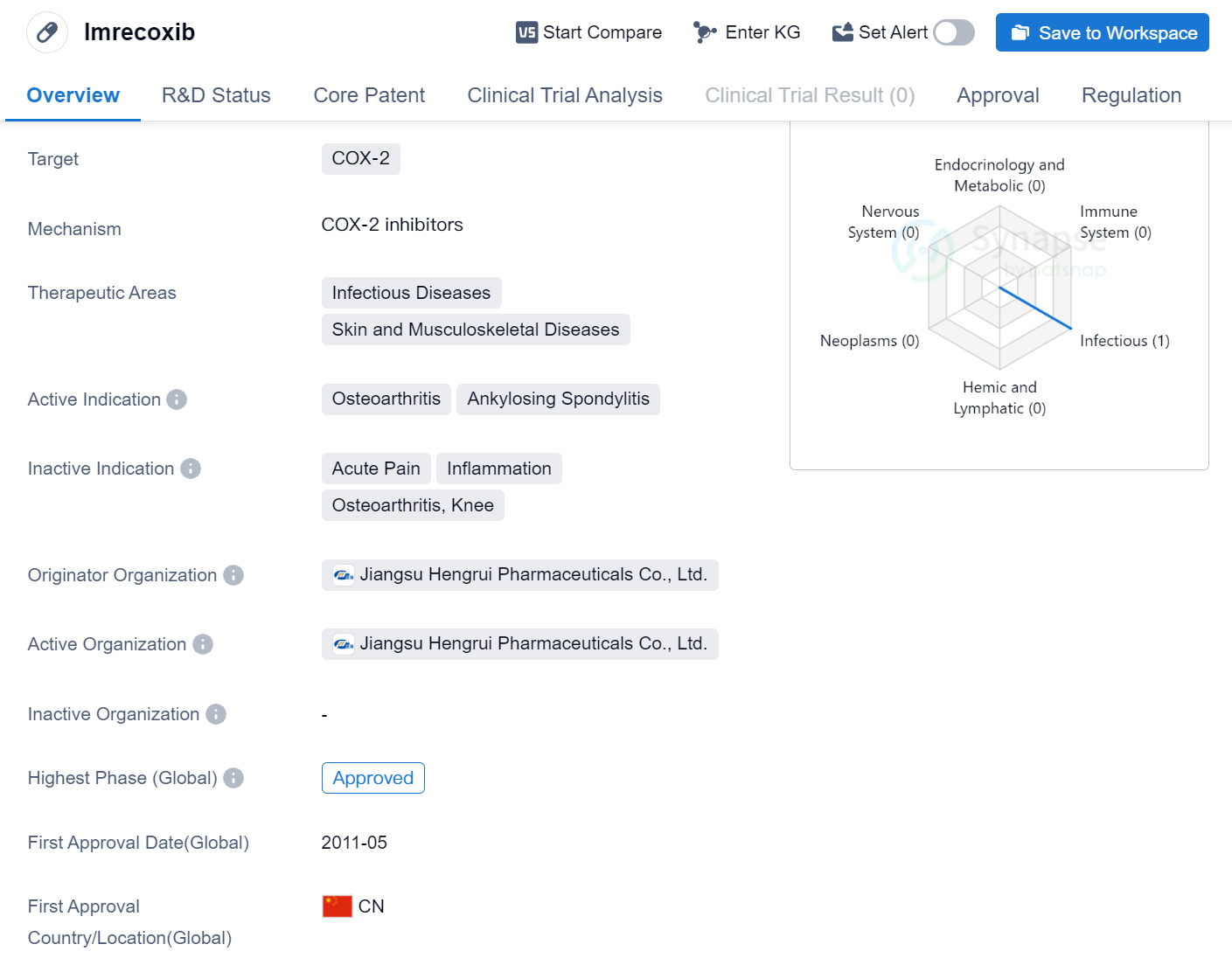
Imrecoxib has successfully completed the highest phase of clinical trials and has received approval globally. The drug was first approved in China in May 2011, marking its initial entry into the market. It is important to note that Imrecoxib falls under the Special Review Project regulation, which suggests that it may have undergone a more rigorous evaluation process due to its unique characteristics or potential risks.
Osteoarthritis is a degenerative joint disease that affects millions of people worldwide, causing pain and reduced mobility. Ankylosing spondylitis, on the other hand, is a chronic inflammatory condition primarily affecting the spine, leading to stiffness and discomfort. By targeting COX-2, Imrecoxib aims to alleviate the symptoms associated with these conditions, providing relief to patients.
As a small molecule drug, Imrecoxib offers advantages such as ease of formulation, administration, and potential cost-effectiveness. Its approval in China suggests that it has met the necessary regulatory requirements and demonstrated its therapeutic benefits. However, further information regarding the drug's efficacy, safety profile, and potential side effects would be valuable in assessing its overall potential and market competitiveness.
In summary, Imrecoxib is a small molecule drug developed by Jiangsu Hengrui Pharmaceuticals Co., Ltd. It targets COX-2 and has been approved for the treatment of osteoarthritis and ankylosing spondylitis. As a small molecule drug, Imrecoxib offers potential advantages in formulation and administration. However, additional information is needed to fully evaluate its therapeutic potential and market viability.