Tune Therapeutics Launches TUNE-401: An Epigenetic Approach to Hepatitis B
Tune Therapeutics, a prominent company in the field of epigenome editing, has announced that it has secured approval for a clinical trial application (CTA) from the New Zealand Medicines and Medical Devices Safety Authority (Medsafe). This approval allows the company to commence a Phase 1b clinical trial for TUNE-401, an experimental epigenetic silencing treatment aimed at addressing chronic Hepatitis B (HBV).
👇Explore more about this drug by clicking the image below. Gain detailed insights into its R&D Status, Core Patent, Clinical Trials and Global Approval Status. Stay informed and updated.
With this recent endorsement, TUNE-401 is poised to become the first epigenetic treatment to advance to clinical trials for a prevalent infectious illness. Over 250 million individuals are currently affected by chronic HBV infection, which is the primary cause of hepatocellular carcinoma, or liver cancer, representing roughly 56% of global cases.
The initial human clinical trial will assess the safety, tolerability, pharmacokinetics (PK), and pharmacodynamics (PD) of TUNE-401 in adults suffering from chronic HBV. The first trial location will be in Auckland, New Zealand, under the direction of Principal Investigator Dr. Ed Gane.
“TUNE-401 is crafted to replicate and enhance the body's natural immune response to HBV,” stated Derek Jantz, Chief Scientific Officer at Tune Therapeutics. “While the impact of epigenetics on viral management is well-documented, Tune-401 is distinguished as the first therapy to utilize direct epigenetic silencing to deactivate a virus. We are optimistic that this innovative mechanism will offer long-awaited advantages to HBV patients and reignite interest and activity within the broader field of genetic medicine.”
TUNE-401 utilizes lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) to transport RNA that encodes the active HBV-targeting construct directly into liver cells. Within these cells, the construct is converted into an epigenetic silencing protein aimed at both integrated HBV DNA and cccDNA episomes—looped structures of HBV DNA that produce new viral particles and perpetuate chronic infection for long durations. Medical experts emphasize that disabling these cccDNA 'viral factories' is crucial for achieving a functional cure for HBV.
Importantly, TUNE-401 is the first therapeutic agent to enter the clinical phase with the goal of silencing both integrated HBV and HBV cccDNA at the epigenetic level, without the need for DNA cutting or modification. Its active epigenetic silencing protein attaches to the DNA without cleaving it, adding methyl groups that repress or deactivate viral genes while preserving the integrity of the human genome. This protein is also highly specific, focusing on a DNA sequence unique to HBV and conserved among HBV strains.
“Hepatitis B continues to pose a major global health challenge, affecting millions who require effective long-term treatment options,” remarked Dr. Ed Gane, Professor of Medicine at the University of Auckland. “Epigenetic silencing could fulfill a long-held aspiration in the medical community: the potential for lasting disease remission following a limited treatment period.”
Tune Therapeutics will share data supporting its clinical trial initiation at the upcoming AASLD Liver Meeting on Monday, November 18th.
👇Explore the most recent advancements in drug research, indications, organizations, clinical trials, results, and patents related to this target by clicking the image link below. Dive in to gain deeper insights!
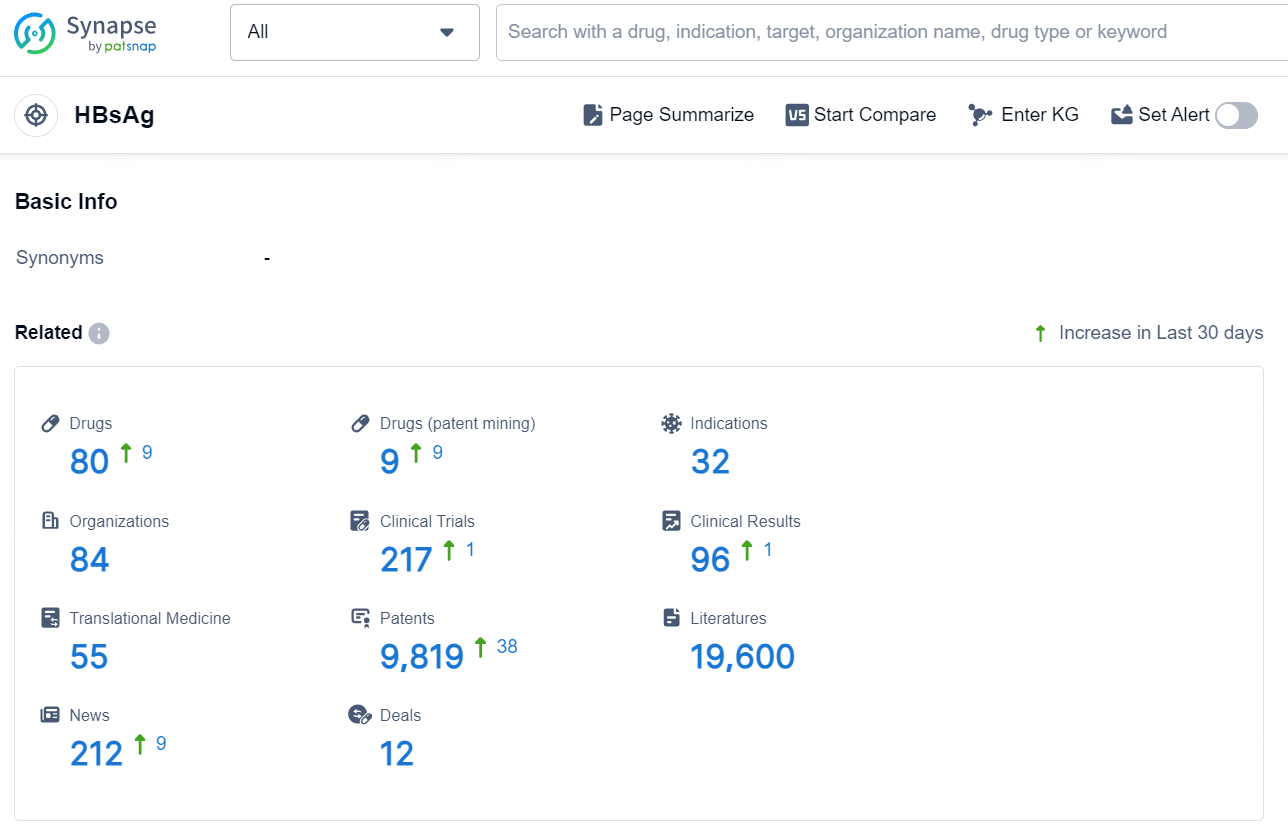
According to the data provided by the Synapse Database, As of November 18, 2024, there are 80 investigational drugs for the HBsAg target, including 32 indication, 84 R&D institutions involved, with related clinical trial reaching 217, and as many as 9819 patents.
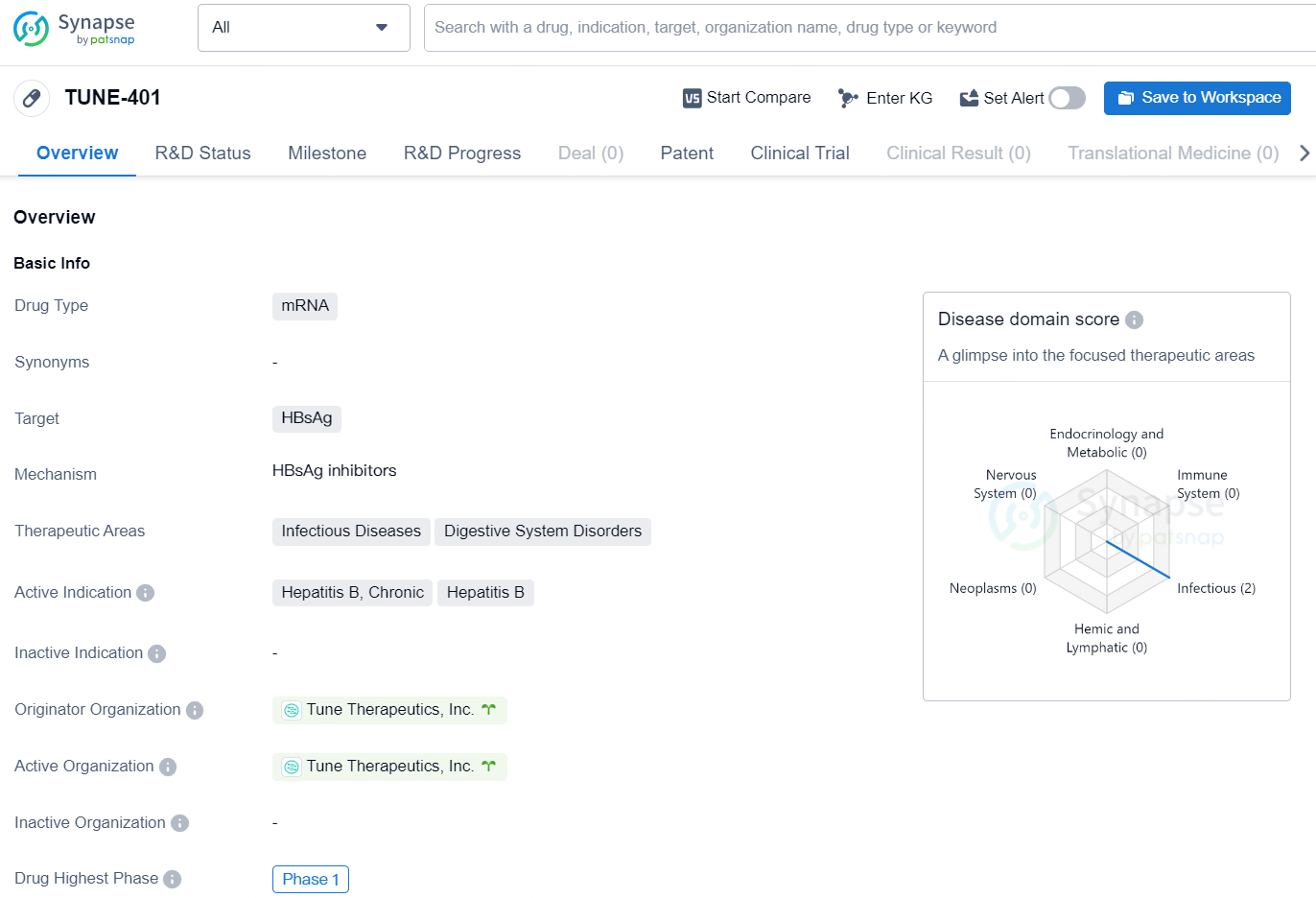
TUNE-401 is a mRNA-based drug developed by Tune Therapeutics, Inc. The drug targets HBsAg and is intended for the treatment of Chronic Hepatitis B. It falls within the therapeutic areas of Infectious Diseases and Digestive System Disorders. As of the latest available information, TUNE-401 has reached phase 1 of clinical development on a global scale.