Doxepin Hydrochloride Unveiled: A Detailed Overview of its Revolutionary R&D Breakthroughs
Doxepin Hydrochloride's R&D Progress
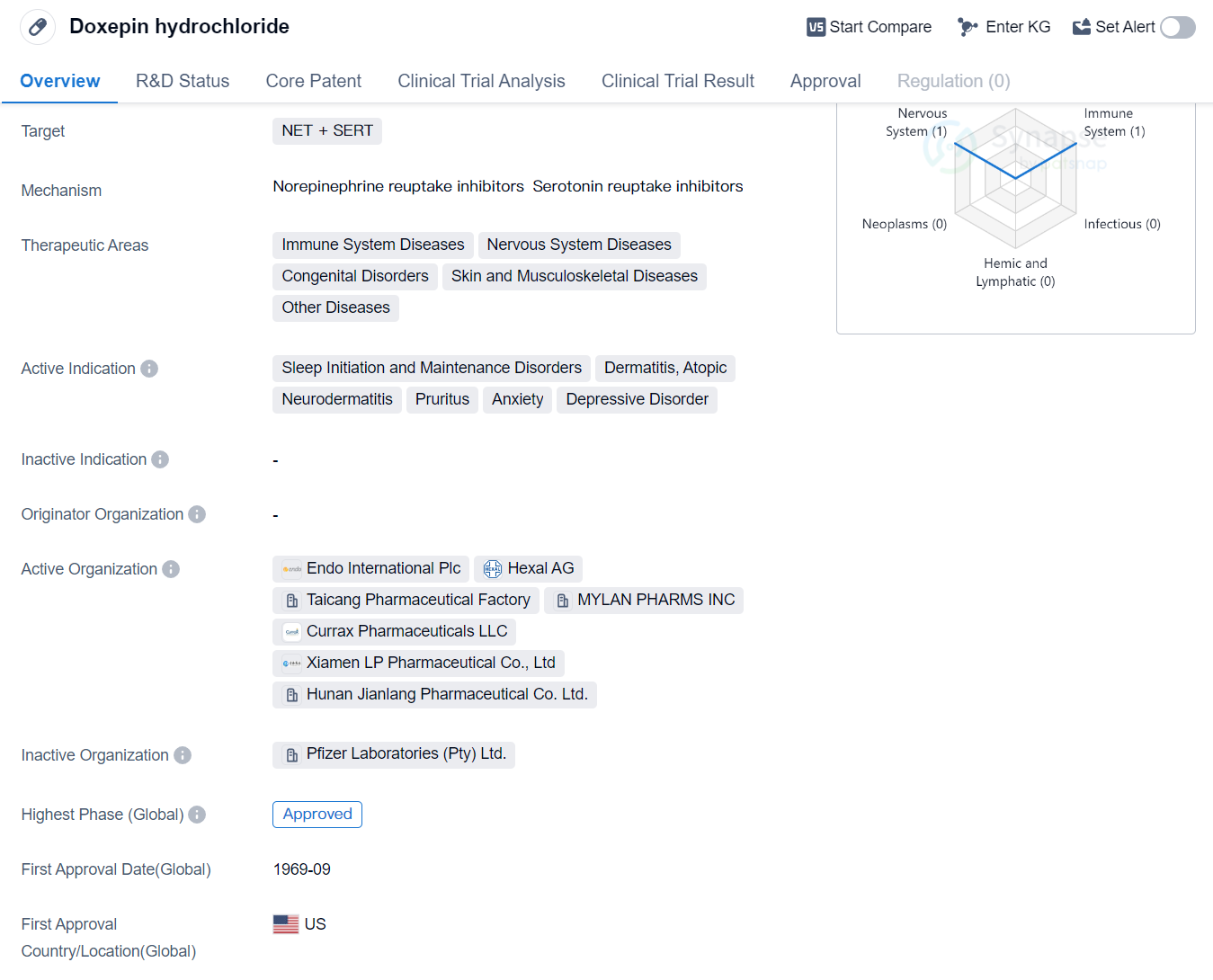
Doxepin hydrochloride is a small molecule drug that targets the NET (norepinephrine transporter) and SERT (serotonin transporter). It has been approved for use in various therapeutic areas including immune system diseases, nervous system diseases, congenital disorders, skin and musculoskeletal diseases, and other diseases. The drug has shown efficacy in treating sleep initiation and maintenance disorders, dermatitis (specifically atopic dermatitis and neurodermatitis), pruritus, anxiety, and depressive disorder.
Doxepin hydrochloride was first approved in the United States in September 1969, making it a well-established drug in the pharmaceutical market. It has also received approval in China, indicating its global recognition and acceptance. The drug's approval in multiple countries suggests its effectiveness and safety profile.
Sleep initiation and maintenance disorders are a common indication for Doxepin hydrochloride. These disorders refer to difficulties in falling asleep or staying asleep, leading to inadequate rest and daytime fatigue. Dermatitis, including atopic dermatitis and neurodermatitis, is another active indication for the drug. These conditions involve inflammation of the skin, resulting in itching, redness, and discomfort. Pruritus, which is severe itching, is also effectively treated with Doxepin hydrochloride.
Anxiety and depressive disorders are prevalent mental health conditions that can significantly impact a person's quality of life. Doxepin hydrochloride has been found to be effective in managing symptoms associated with these disorders, providing relief to patients.
The approval of Doxepin hydrochloride in the late 1960s highlights its long-standing presence in the pharmaceutical market. Its continued approval in both the United States and China suggests its ongoing relevance and importance in the treatment of various diseases.
👇Please click on the image below to directly access the latest data (R&D Status | Core Patent | Clinical Trial | Approval status in Global countries) of this drug.
Mechanism of Action for Doxepin Hydrochloride: Norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor and Serotonin reuptake inhibitor
Norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors and serotonin reuptake inhibitors are two different classes of drugs used in biomedicine to treat various conditions.
Norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (NRIs) are medications that primarily work by blocking the reuptake of norepinephrine, a neurotransmitter in the brain. By inhibiting the reuptake process, NRIs increase the levels of norepinephrine in the synaptic cleft, which can help improve mood, attention, and focus. NRIs are commonly prescribed for the treatment of depression, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), and certain anxiety disorders.
Serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SRIs), also known as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), are a class of drugs that primarily target the reuptake of serotonin, another neurotransmitter in the brain. By blocking the reuptake of serotonin, SRIs increase the availability of serotonin in the synaptic cleft, leading to improved mood and reduced symptoms of depression and anxiety. SSRIs are widely used in the treatment of major depressive disorder, generalized anxiety disorder, obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD), and other related conditions.
Both NRI and SRI medications play a crucial role in managing mental health disorders by modulating the levels of specific neurotransmitters in the brain. However, it's important to note that the specific mechanisms of action and clinical applications may vary between different drugs within these classes. It is always recommended to consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice and treatment options.
Drug Target R&D Trends for Doxepin Hydrochloride
Based on the analysis of the provided data, the current competitive landscape of the target NET + SERT in the pharmaceutical industry is characterized by the presence of multiple companies with varying levels of R&D progress. The highest stage of development is the "Approved" phase, with a focus on indications such as Depressive Disorder, Depressive Disorder, Major, and Anxiety Disorders. Small molecule drugs are progressing most rapidly, indicating intense competition in this area. The countries developing fastest include the United States, China, and Japan. China has shown significant progress in the development of drugs under the target NET + SERT. Overall, the future development of this target is promising, with a strong pipeline of drugs and active research in various countries.
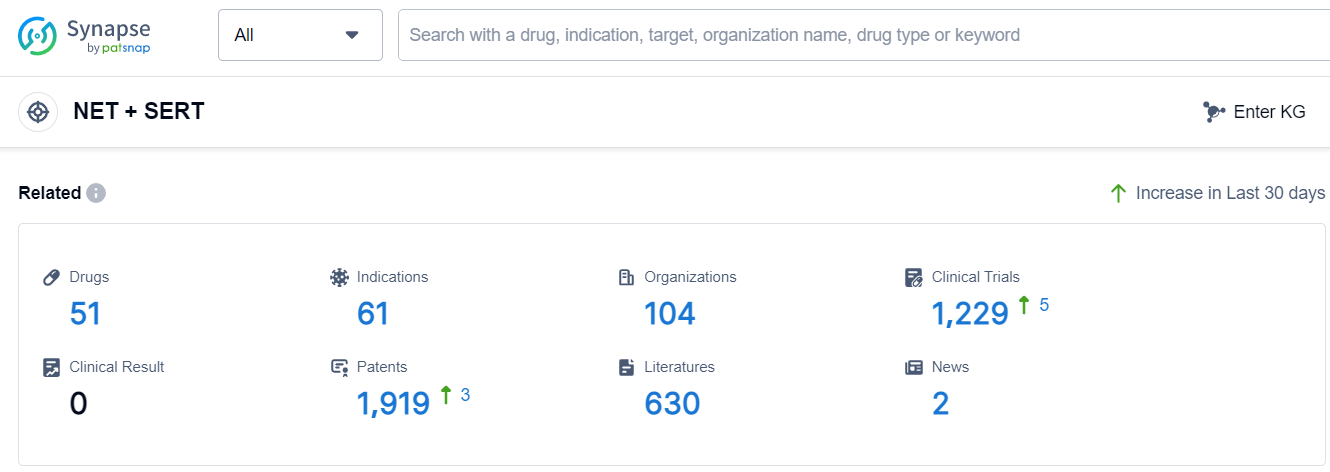
According to Patsnap Synapse, as of 18 Sep 2023, there are a total of 51 NET + SERT drugs worldwide, from 104 organizations, covering 61 indications, and conducting 1229 clinical trials.
Please click on the picture link below for free registration or log in directly if you have a freemium account, you can browse the latest research progress on drugs, indications, organizations, clinical trials, clinical results, and drug patents related to this target
Conclusion
In summary, Doxepin hydrochloride is a small molecule drug that targets the NET and SERT. It has been approved for use in multiple therapeutic areas, including immune system diseases, nervous system diseases, congenital disorders, skin and musculoskeletal diseases, and other diseases. The drug is indicated for sleep initiation and maintenance disorders, dermatitis (atopic and neurodermatitis), pruritus, anxiety, and depressive disorder. Its approval in the United States in 1969 and subsequent approval in China demonstrate its established presence in the pharmaceutical market.