Unleashing the Power of Torsemide: A Comprehensive Review on R&D Breakthroughs
Torsemide's R&D Progress
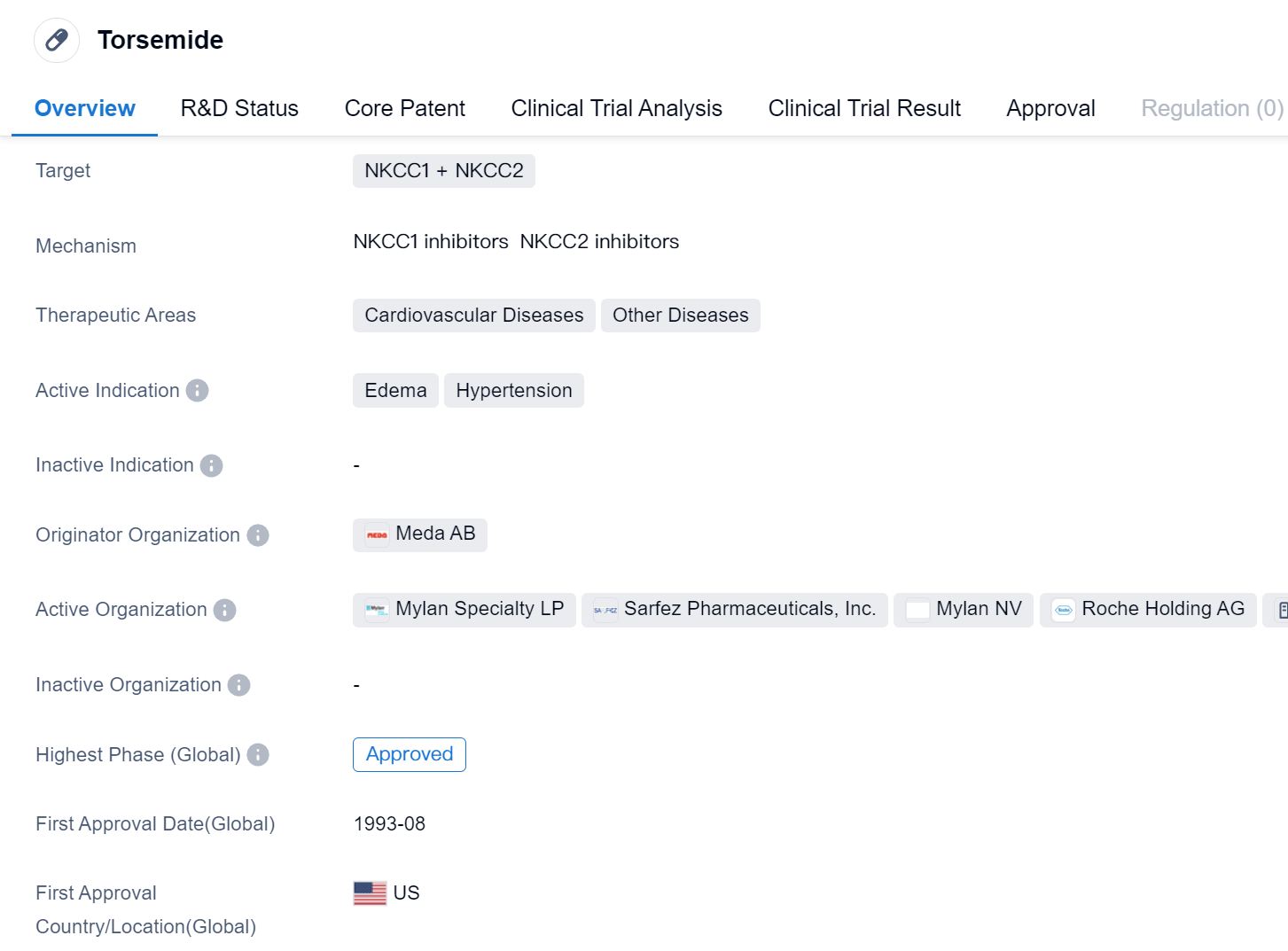
Torsemide is a small molecule drug that targets NKCC1 and NKCC2. It is primarily used in the treatment of cardiovascular diseases and other diseases. The active indications for Torsemide include edema and hypertension. The drug was developed by Meda AB and has received approval in multiple countries.
Torsemide is classified as a small molecule drug, which means it is composed of low molecular weight compounds. It specifically targets NKCC1 and NKCC2, which are transport proteins involved in the regulation of sodium and chloride ions in the body. By inhibiting these proteins, Torsemide helps to reduce fluid retention and lower blood pressure.
The therapeutic areas for Torsemide include cardiovascular diseases, such as congestive heart failure and hypertension, as well as other diseases where fluid retention is a concern. Edema, which is the accumulation of fluid in the body's tissues, and hypertension, which is high blood pressure, are the active indications for this drug.
Meda AB is the originator organization of Torsemide. They developed and obtained approval for the drug, which was first approved in the United States in August 1993. Since then, Torsemide has received approval in other countries as well.
In terms of its development phase, Torsemide has reached the highest phase of development which is approved globally. This indicates that it has successfully completed clinical trials and has been deemed safe and effective for use in patients.
👇Please click on the image below to directly access the latest data (R&D Status | Core Patent | Clinical Trial | Approval status in Global countries) of this drug.
Mechanism of Action for Torsemide: NKCC1 inhibitors and NKCC2 inhibitors
NKCC1 inhibitors and NKCC2 inhibitors are two different types of drugs that target specific transporters in the body.
From a biomedical perspective, NKCC1 inhibitors are drugs that inhibit the activity of the sodium-potassium-chloride cotransporter 1 (NKCC1). This cotransporter is responsible for transporting sodium, potassium, and chloride ions across cell membranes. By inhibiting NKCC1, these drugs can reduce the movement of these ions, which can have various effects on different tissues and organs. For example, in the central nervous system, NKCC1 inhibitors can reduce neuronal excitability and have potential applications in the treatment of epilepsy and other neurological disorders.
On the other hand, NKCC2 inhibitors target the sodium-potassium-chloride cotransporter 2 (NKCC2), which is primarily found in the kidneys. NKCC2 plays a crucial role in reabsorbing sodium, potassium, and chloride ions from the urine back into the bloodstream. By inhibiting NKCC2, these drugs can reduce the reabsorption of these ions, leading to increased excretion of sodium and water. This mechanism of action is utilized in diuretic medications, which are commonly prescribed to treat conditions such as hypertension and edema.
In summary, NKCC1 inhibitors and NKCC2 inhibitors are drugs that target specific transporters in the body, with NKCC1 inhibitors affecting neuronal excitability and NKCC2 inhibitors primarily used as diuretics to increase sodium and water excretion.
Drug Target R&D Trends for Torsemide
NKCC1 and NKCC2 are two isoforms of the sodium-potassium-chloride cotransporter found in the human body. NKCC1 is widely expressed in various tissues and plays a crucial role in maintaining cell volume, ion homeostasis, and cell migration. It is involved in processes such as neuronal excitability, fluid secretion, and regulation of blood pressure. On the other hand, NKCC2 is primarily found in the kidney and is responsible for reabsorbing sodium, potassium, and chloride ions from the urine, thereby regulating electrolyte balance and blood pressure. Dysfunction or dysregulation of NKCC1 and NKCC2 can lead to various disorders, highlighting their importance in human physiology.
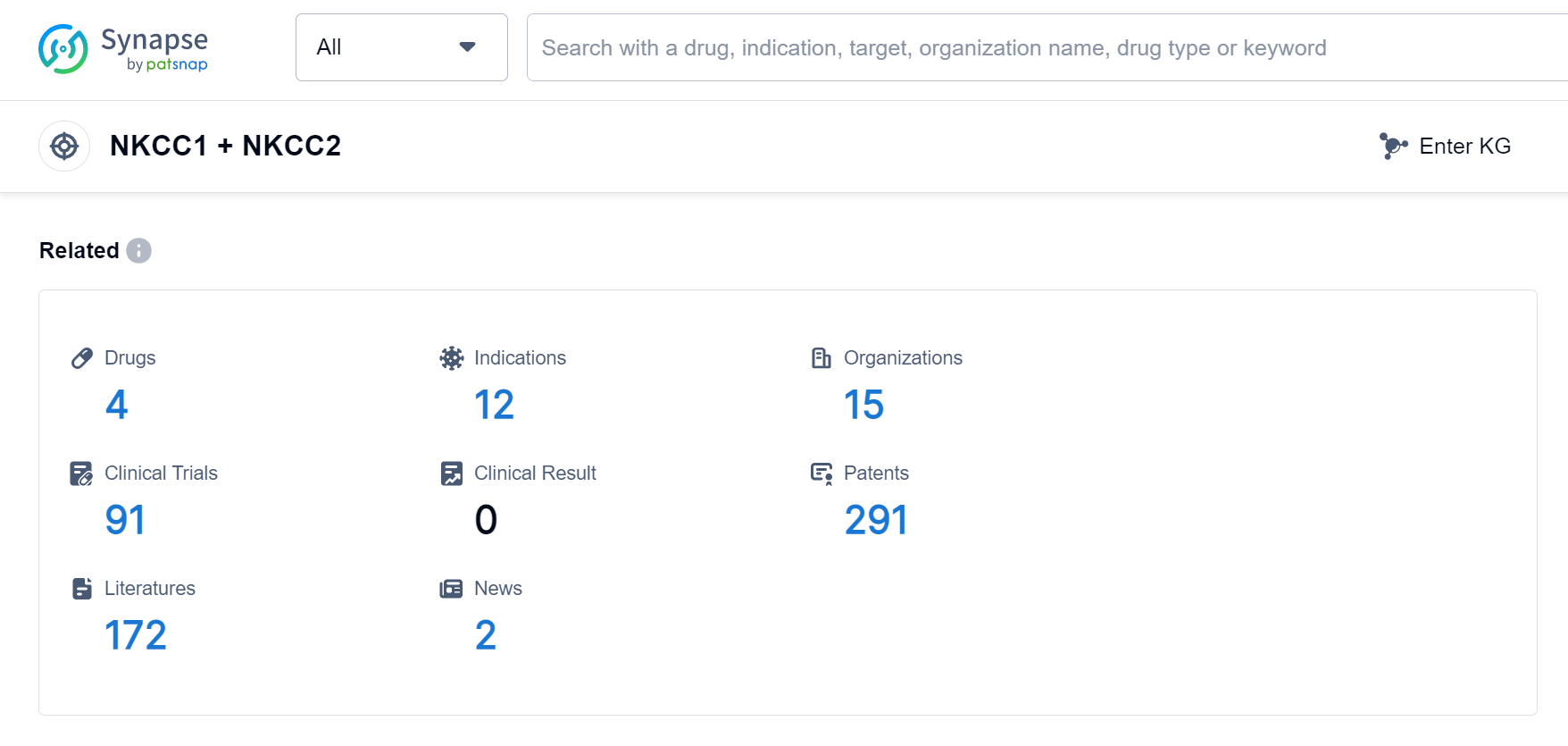
According to Patsnap Synapse, as of 6 Sep 2023, there are a total of 4 NKCC1 + NKCC2 drugs worldwide, from 15 organizations, covering 12 indications, and conducting 91 clinical trials.
👇Please click on the picture link below for free registration or log in directly if you have a freemium account, you can browse the latest research progress on drugs, indications, organizations, clinical trials, clinical results, and drug patents related to this target.
Conclusion
In summary, Torsemide is a small molecule drug developed by Meda AB. It targets NKCC1 and NKCC2 and is used in the treatment of cardiovascular diseases and other conditions. Its active indications include edema and hypertension. Torsemide has received approval in multiple countries, with its first approval in the United States in 1993.