Unveiling the Veil of JAK Inhibitors
JAK is one of the hot spots for global drug R&D. JAK inhibitors can inhibit JAK kinases, block the JAK-STAT signaling pathway, and have great therapeutic potential for a variety of diseases including tumors, immune & inflammation, hematopoietic system diseases, COVID-19 infections, etc.
The potential of JAK inhibitors is tremendous
The full name of JAK kinase is Janus kinase, which consists of seven homology domains (JH). Starting from the carboxyl terminus, the JH1 domain is the kinase domain responsible for regulating JAK kinase activity; JH2 is a pseudokinase domain that regulates JH1 kinase activity; JH3~JH5 domains are homologous to the Src-homology-2 domain (SH2 domain); The amino terminal JH6~JH7 domain is termed the FERM domain and participates in the binding of JAK to cytokine receptors and/or other kinases.
JAK kinases are a type of cytoplasmic non-receptor tyrosine kinase, with four subtypes: JAK1, JAK2, JAK3, TYK2. As the core of the JAK-STAT signaling pathway, JAK kinases are involved in many important biological processes including stem cell proliferation, differentiation, apoptosis, and immune regulation et al.
JAK1 plays a crucial role in signal transduction of IL-4, IL-13, IL-9, IL-22, IL-31, and TSLP; JAK2 is involved in erythrocyte production, thrombocyte activation, and bone marrow hematopoiesis; JAK3 is implicated in the immune function of CD8+ T lymphocytes and NK cell activity; TYK2 is involved in the immune function of interferon and multiple ILs.
With further research, scientists have found that tumors, myelofibrosis, thrombocytosis, vitiligo, atopic dermatitis, psoriasis and other autoimmune diseases are all related to the abnormal activation of the JAK-STAT pathway. Therefore, JAK inhibitors can serve as important therapeutic targets for these diseases.
JAK Competitive Landscape
According to the data provided by Patsnap Synapse-Global Drug Intelligence Database: the following figure shows that as of 3 Sep 2023, there are a total of 217 JAK drugs worldwide, from 254 organizations, covering 214 indications, and conducting 2138 clinical trials.
👇Please click on the picture link below for free registration or login directly if you have freemium accounts, you can browse the latest research progress on drugs , indications, organizations, clinical trials, clinical results, and drug patents related to this target.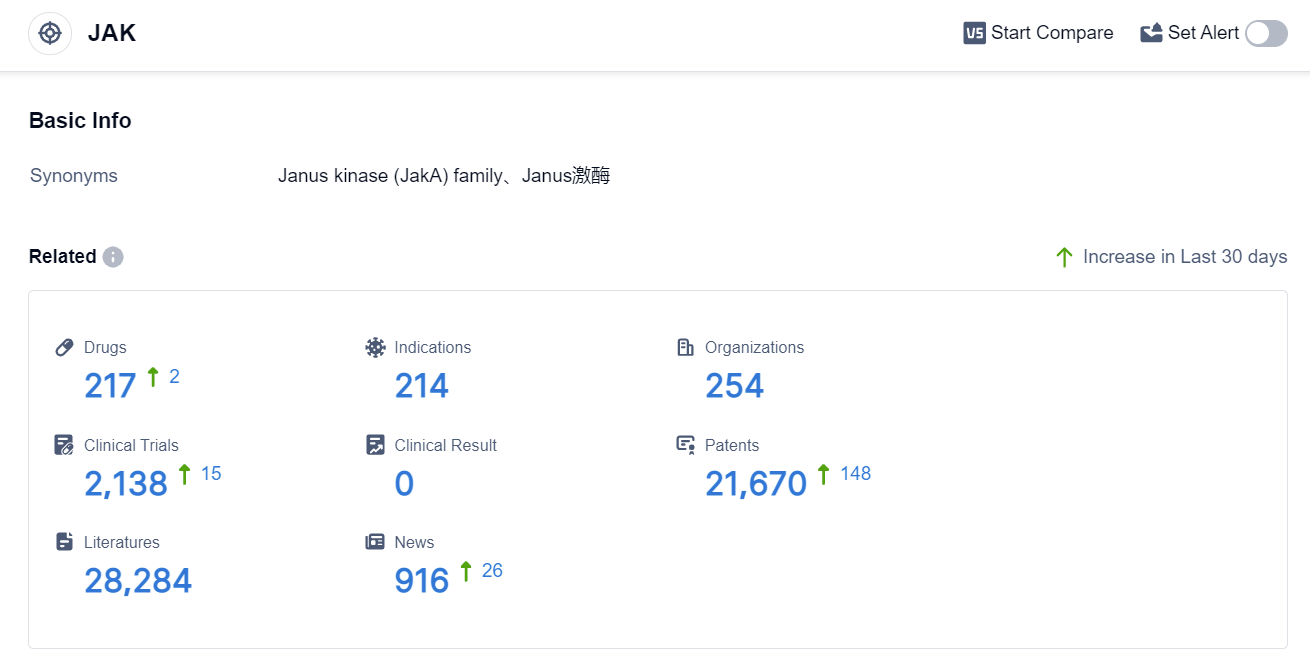
The analysis of the target JAK from various perspectives provides valuable insights into the current competitive landscape and future development. Pfizer Inc. emerges as the leading company in terms of drug count and development phases. Rheumatoid Arthritis, Dermatitis, Atopic, Colitis, Ulcerative, and Primary Myelofibrosis are the most common indications for approved drugs. Small molecule drugs dominate the development phases, indicating intense competition. The United States, Japan, European Union, and China are the leading countries/locations in drug development. Overall, the target JAK presents a competitive landscape with multiple companies, indications, drug types, and countries/locations actively involved in research and development.
The first-generation JAK inhibitors are generally not high in selectivity.
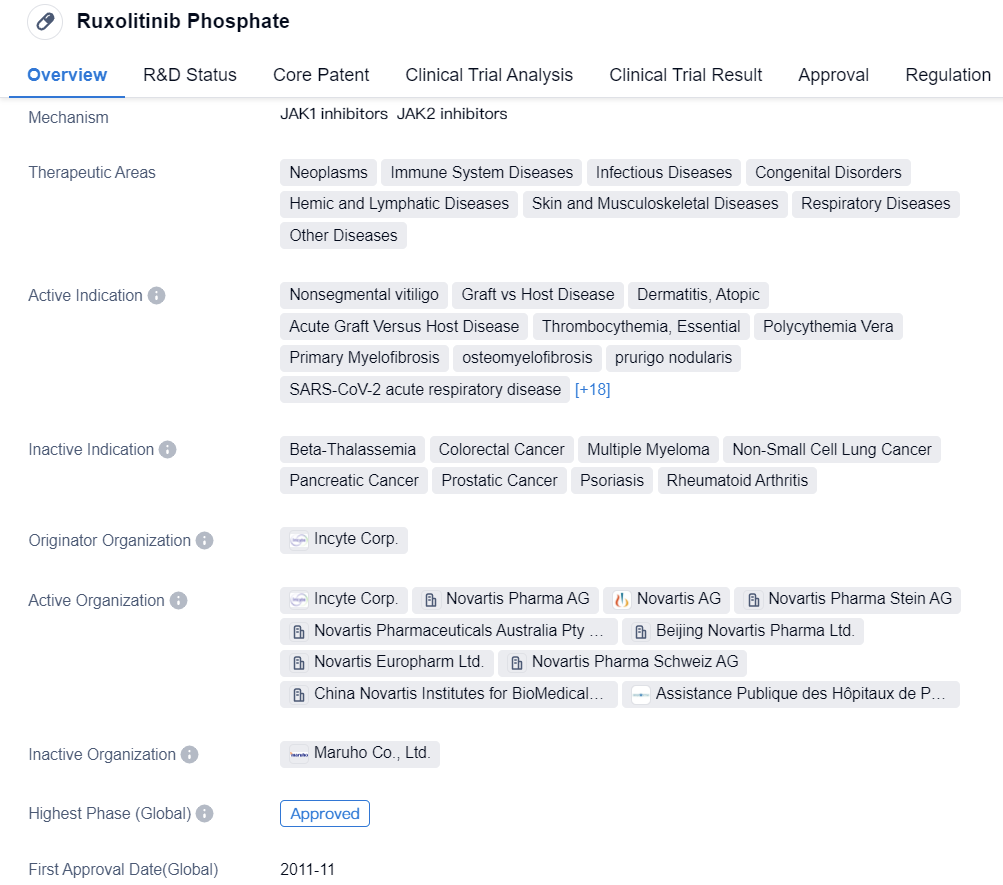
Novartis's Ruxolitinib Phosphate, a reversible JAK1/2 inhibitor, was approved by the FDA in 2011 for the treatment of myelofibrosis and entered the Chinese market in 2017. Besides myelofibrosis, it has also been approved for the treatment of polycythemia vera, graft-versus-host disease, and its ointment formulation has been approved for the treatment of vitiligo and atopic dermatitis.
👇Please click on the image below to directly access the latest data (R&D Status | Core Patent | Clinical Trial | Approval status in Global countries) of this drug.
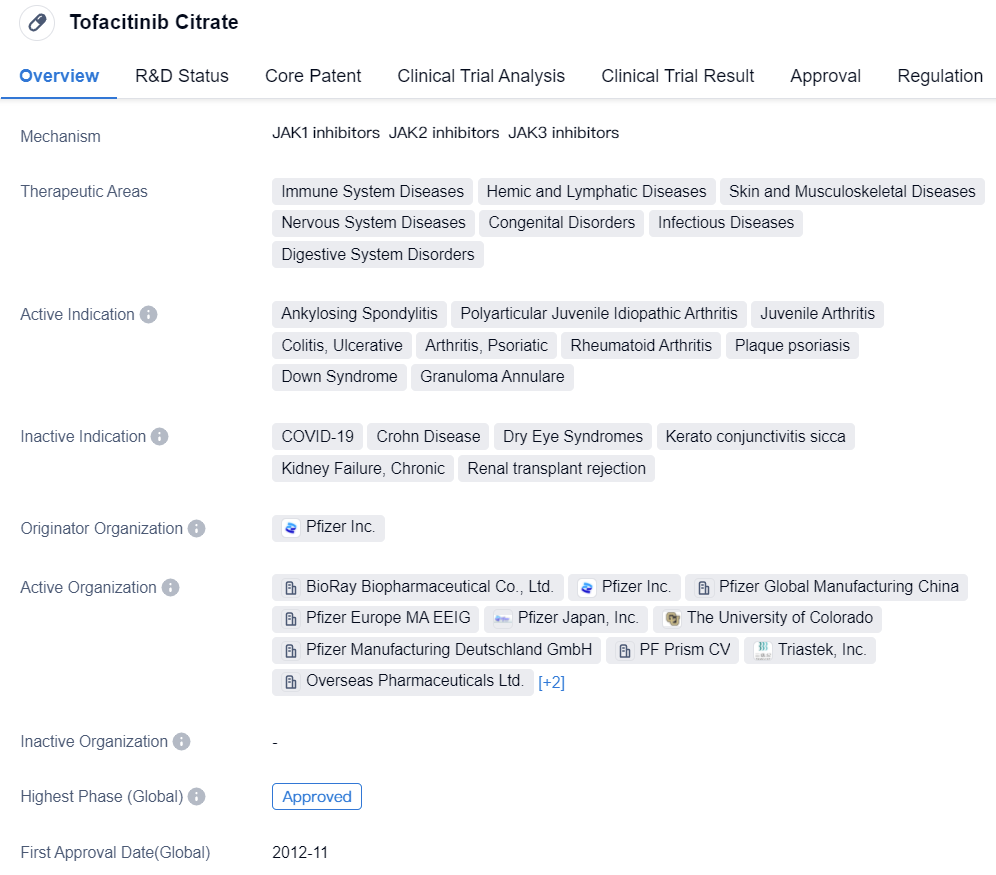
Pfizer's Tofacitinib Citrate is the second JAK inhibitor globally, targeting JAK1/JAK2/JAK3. In 2012, Tofacitinib was approved by the FDA for the treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA), becoming the first JAK inhibitor in the field of autoimmune diseases. In 2017, Tofacitinib Citrate tablets were approved for marketing in China for the treatment of moderate to severe active rheumatoid adults who respond inadequately to Methotrexate (MTX) or are intolerant to it. Today, the indications for Tofacitinib cover diseases like ankylosing spondylitis, juvenile idiopathic arthritis, and ulcerative colitis.
👇Please click on the image below to directly access the latest data (R&D Status | Core Patent | Clinical Trial | Approval status in Global countries) of this drug.
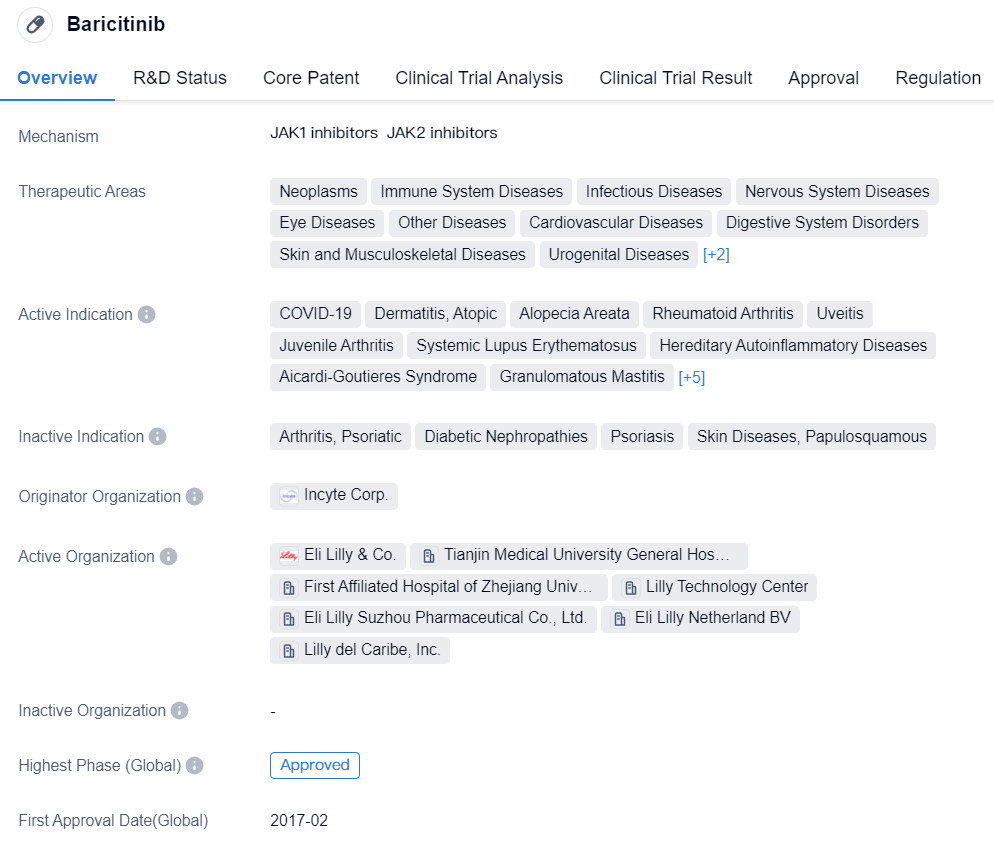
Baricitinib, developed by Eli Lilly and Incyte, is a JAK1/2 inhibitor. It was approved by the European Union in 2017 for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis (RA), and in 2020 for the treatment of atopic dermatitis. In May and June of 2022, the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved it for supplemental oxygen therapy in adult COVID-19 patients and for the systemic treatment of alopecia areata, respectively. Currently, its expanded indication trials also include uveitis and juvenile arthritis.
👇Please click on the image below to directly access the latest data (R&D Status | Core Patent | Clinical Trial | Approval status in Global countries) of this drug.
However, the selectivity of the previously approved JAK inhibitors is relatively low. Given that the JAK family mediates the signal transduction of multiple cytokines, and different receptors are associated with different JAKs, the comprehensive inhibition of the JAK family can lead to various side effects. For example, the erroneous inhibition of JAK2 may result in thrombocytopenia and anemia, while the erroneous inhibition of JAK3 could lead to the lack of active T cells and B cells, thereby causing immune deficiencies and infections, etc. Therefore, this is the biggest safety risk of the first-generation JAK inhibitors. In order to reduce the occurrence of side effects, the development of highly selective second-generation inhibitors has become a focus.
Second-generation JAK inhibitors: a new game in a changing field
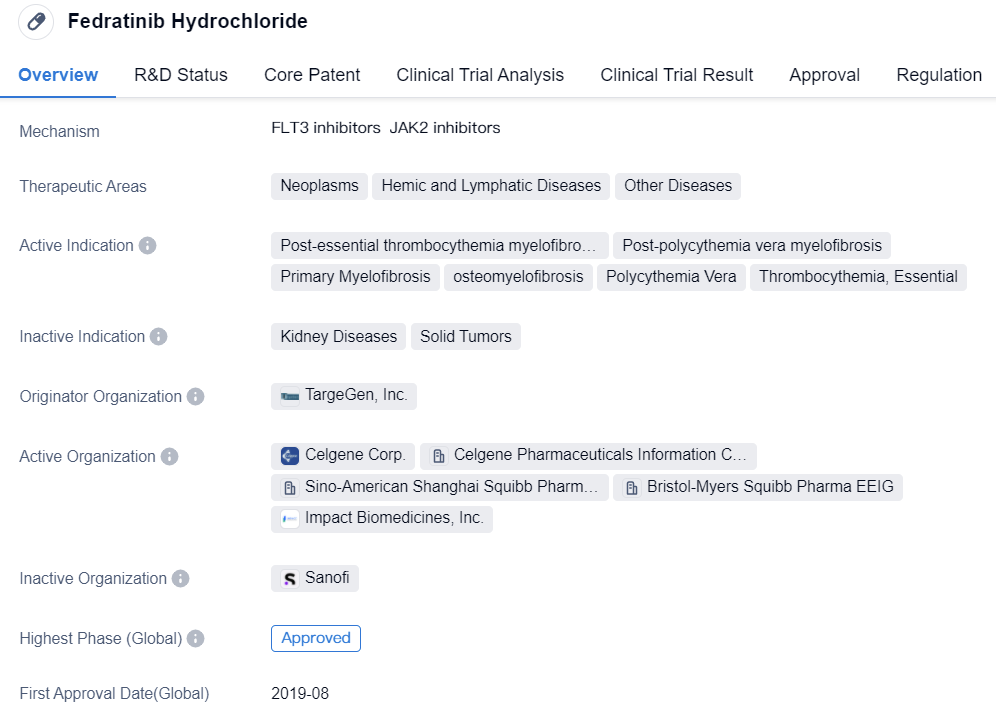
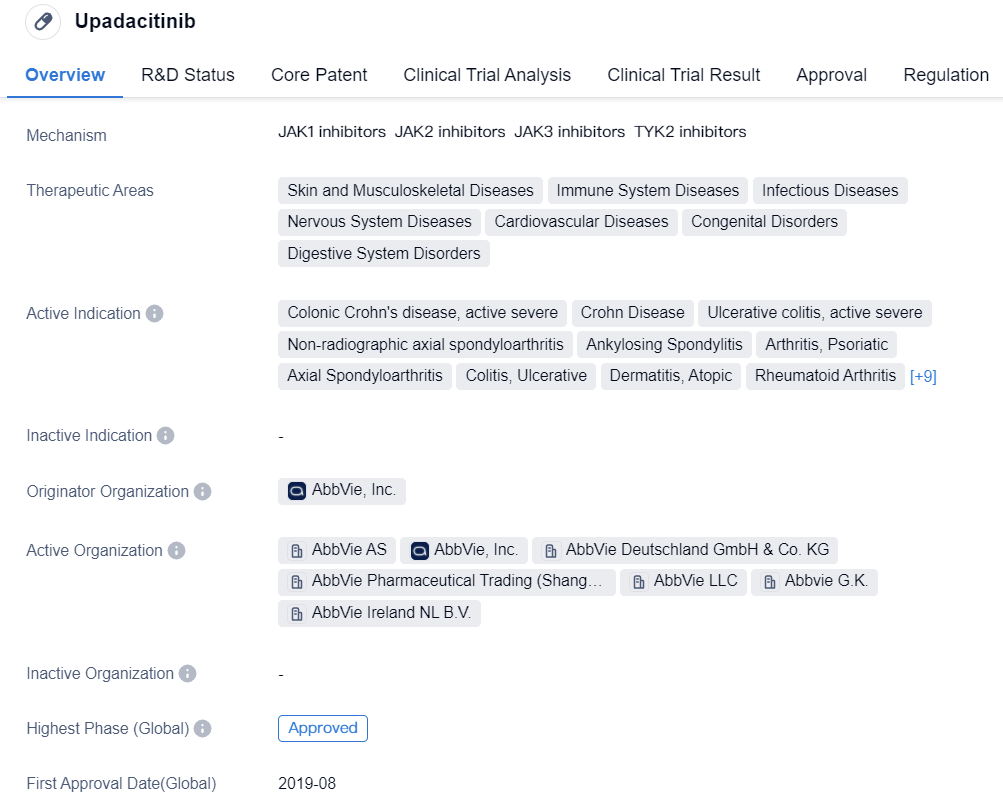
In August 2019, both BMS's Fedratinib Hydrochloride and AbbVie's Upadacitinib received FDA approval on the same day, marking the official arrival of the selective second-generation JAK inhibitors for the JAK family. Among them, Fedratinib Hydrochloride is a highly specific JAK2 inhibitor, its inhibitory effect on JAK2 is stronger than on JAK1, JAK3, and TYK2. It received FDA approval for the treatment of myelofibrosis.
👇Please click on the image below to directly access the latest data (R&D Status | Core Patent | Clinical Trial | Approval status in Global countries) of this drug.
Upadacitinib is a JAK1 selective inhibitor developed by AbbVie, which has been approved by the FDA for the treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) and entered the Chinese market in 2022. The approved indications for Upadacitinib, besides RA, also include non-radiographic axial spondyloarthritis, ulcerative colitis, atopic dermatitis, ankylosing spondylitis, and psoriatic arthritis, among others. Clarivate has predicted that Upadacitinib will become a blockbuster drug.
👇Please click on the image below to directly access the latest data (R&D Status | Core Patent | Clinical Trial | Approval status in Global countries) of this drug.
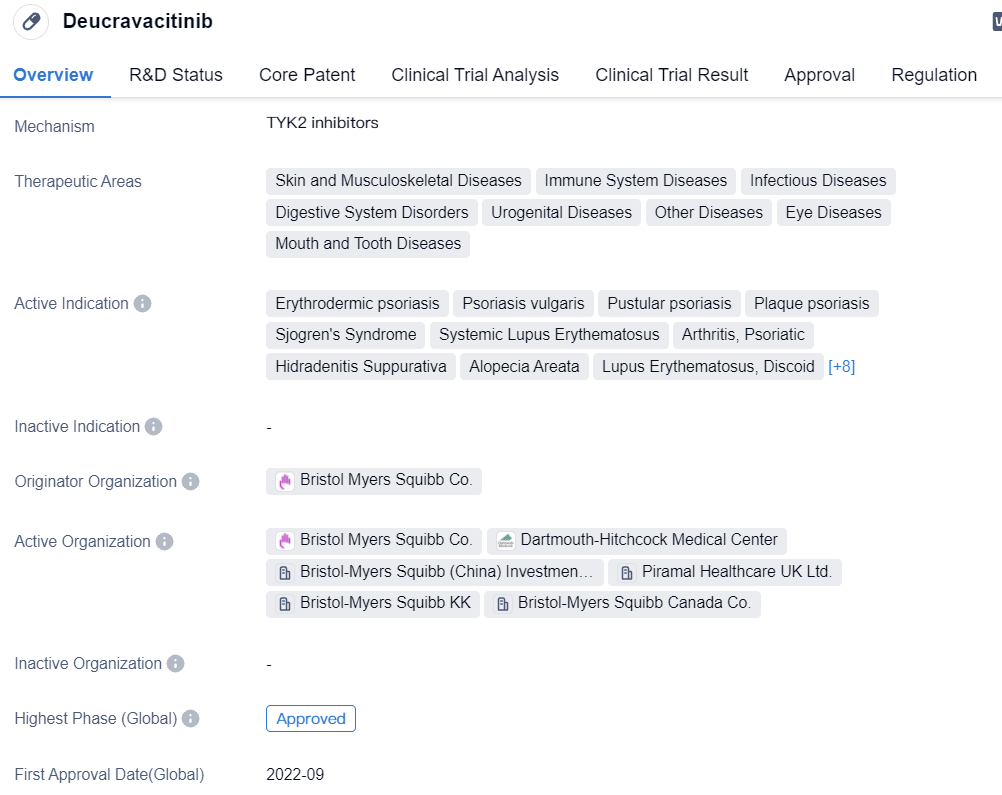
Deucravacitinib, a TYK2 inhibitor developed by BMS, was approved by the FDA in September 2022 for the treatment of plaque psoriasis. It is also the first TYK2 inhibitor to be approved worldwide. In terms of selectivity, Deucravacitinib stands out. It does not bind to the kinase domain (JH1) like other JAK inhibitors, but binds to the pseudokinase domain (JH2) to induce conformational changes, thereby blocking the signal transduction of key cytokines (such as IL-23, etc.) that drive the pathogenesis of various immune-mediated diseases. Within the physiological concentration range, Deucravacitinib selectively inhibits TYK2 and does not inhibit JAK1, JAK2, or JAK3 under therapeutic doses. In addition to psoriasis, Deucravacitinib is also being developed for the treatment of various immunological diseases, including psoriatic arthritis, scalp psoriasis, and inflammatory bowel disease.
👇Please click on the image below to directly access the latest data (R&D Status | Core Patent | Clinical Trial | Approval status in Global countries) of this drug.
In summary, the design principle of the second-generation JAK inhibitors is to improve the selective inhibition of specific JAK kinase subtypes, to avoid the toxic side effects caused by the inhibition of other subtypes' kinases, and to reduce adverse reactions while maintaining the efficacy of the drug for specific diseases. However, the second-generation JAK inhibitors still have not escaped safety risks.