What are ATR inhibitors and how do you quickly get the latest development progress?
ATR is a key protein in DNA Damage Response (DDR), a member of the Phosphoinositide 3-Kinase-like Kinases (PIKK) family, sharing the same family with ATM, which also participates in DDR.
In tumor cells, due to the activation of oncogenes and the loss of G1 checkpoint function, replication stress (RS) significantly increases. When DNA damage occurs, ATR primarily acts as a sensor for RS, participating in the repair of DNA single-strand breaks. When there is RS or DDR production within the cell, Replication Protein A (RPA) wraps single-strand DNA (ssDNA) to form RPA-ssDNA complexes, and recruits regulatory factors needed to activate ATR: ATRIP, 9-1-1 complex (Rad9-Rad1-Hus1), and Topoisomerase II Binding Protein 1 (TopBP1), etc. ATR and its ligand ATRIP bind and are recruited to RPA-ssDNA, forming an ATR-ATRIP complex. At the same time, ATR undergoes autophosphorylation at site T1989. Once ATR is activated, it prevents activation of CDK2 by phosphating CHK1, CHK2, and inactivating CDC25. These alterations also activate WEE1 directly or via CHK1, causing CDK1 and CDK2 to be phosphorylated and inactivated, thereby stalling the G1/S or G2/M cell cycle progression, giving cells more time for DNA damage repair before entering mitosis. If the damage is too extensive, the corresponding senescence or apoptosis pathway is activated.
Understanding the role of ATR is essential for developing targeted therapies and interventions in the pharmaceutical industry.
How do they work?
ATR inhibitors are a type of drug that target and inhibit the activity of the Ataxia Telangiectasia and Rad3-related (ATR) protein. ATR is a key enzyme involved in the DNA damage response pathway, which helps to maintain genomic stability and prevent the replication of damaged DNA. By inhibiting ATR, these inhibitors can disrupt the DNA damage repair process in cancer cells, leading to their death.
From a biomedical perspective, ATR inhibitors have gained significant attention in the field of cancer research and therapy. Cancer cells often have high levels of DNA damage due to their rapid and uncontrolled growth. ATR inhibitors can selectively target cancer cells by exploiting their increased reliance on the DNA damage response pathway. By blocking ATR, these inhibitors can enhance the effectiveness of DNA-damaging treatments, such as chemotherapy or radiation therapy, as cancer cells become more vulnerable to DNA damage-induced cell death.
ATR inhibitors have shown promise as potential anti-cancer agents and are currently being investigated in preclinical and clinical trials. They hold potential for the treatment of various types of cancer, including those with DNA repair defects or resistance to conventional therapies. However, further research is needed to fully understand their mechanisms of action, optimize their efficacy, and minimize potential side effects.
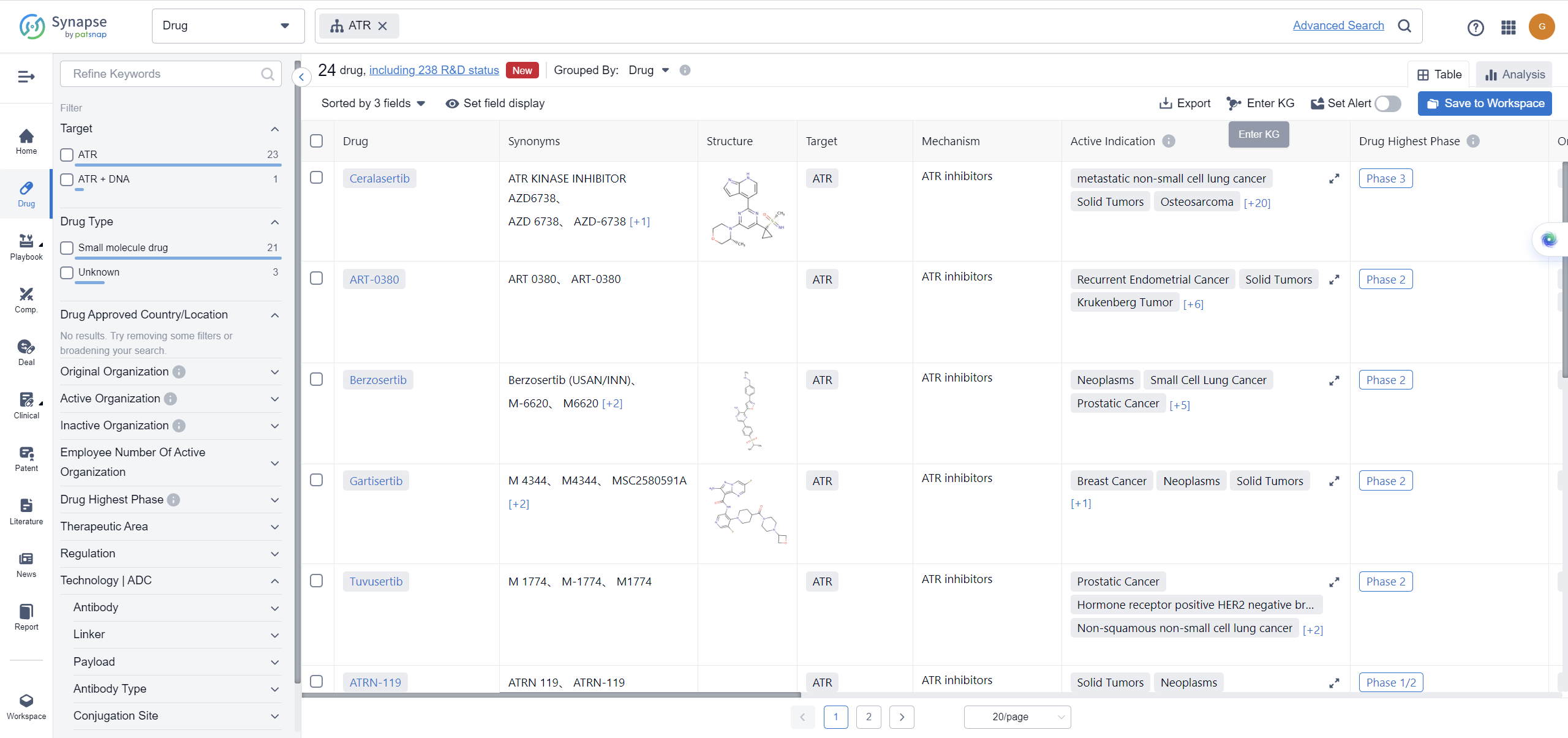
List of ATR Inhibitors
The currently marketed ATR inhibitors include:
For more information, please click on the image below.
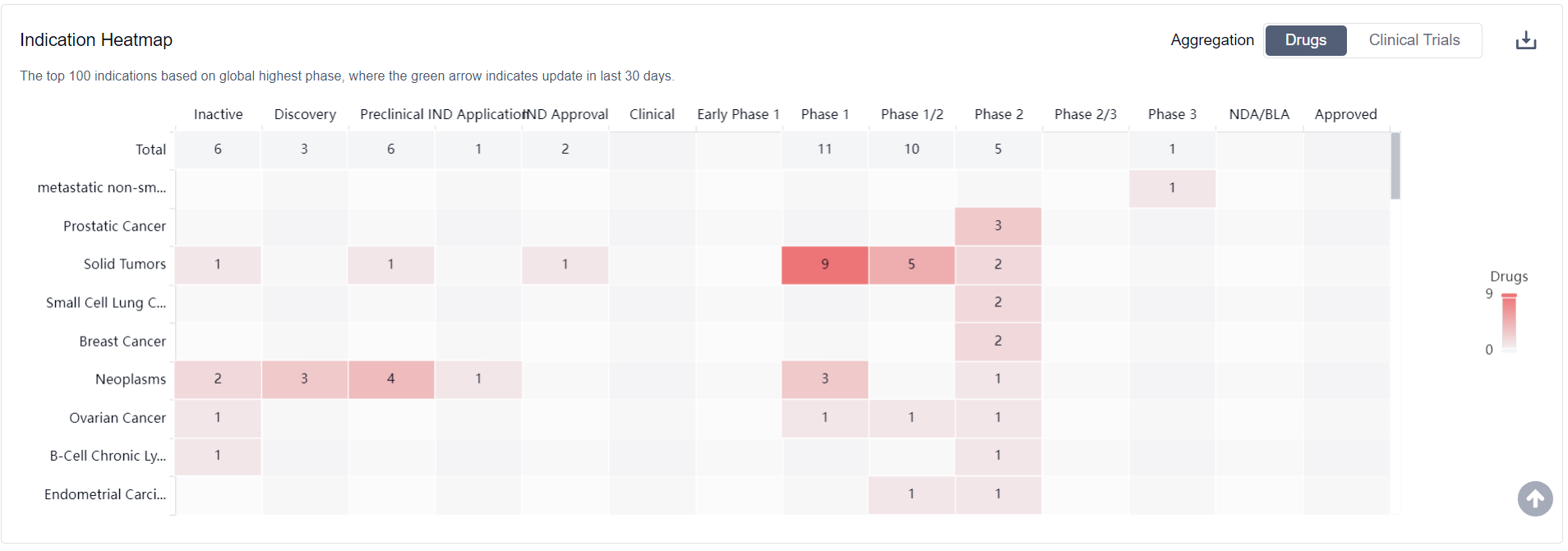
What are ATR inhibitors used for?
ATR inhibitors are under investigation for indications that include metastatic non-small cell lung cancer, prostatic cancer, pancreatic cancer, triple negative breast cancer, metastatic renal cell carcinoma, locally advanced pancreatic adenocarcinoma, cholangiocarcinoma, and secondary malignant neoplasm of pancreas For more information, please click on the image below to log in and search.
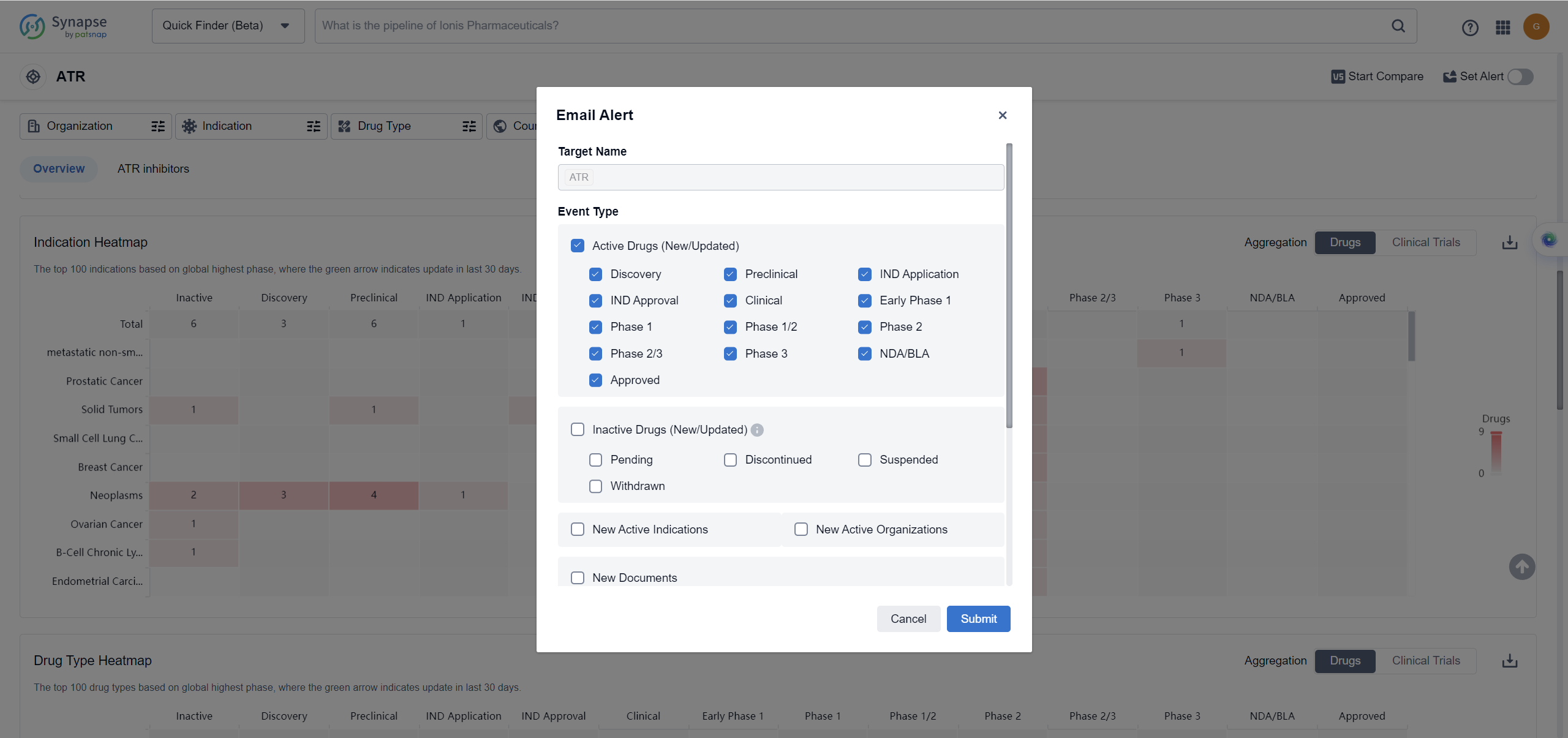
How to obtain the latest development progress of ATR inhibitors?
In the Synapse database, you can keep abreast of the latest research and development advances of ATR inhibitors anywhere and anytime, daily or weekly, through the "Set Alert" function. Click on the image below to embark on a brand new journey of drug discovery!