What are CDK7 inhibitors and how do you quickly get the latest development progress?
CDK7, also known as cyclin-dependent kinase 7, plays a crucial role in the regulation of cell cycle progression and transcriptional control in the human body. It is a key component of the CDK-activating kinase (CAK) complex, which phosphorylates and activates other cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs). CDK7 is involved in the initiation of transcription by phosphorylating the C-terminal domain of RNA polymerase II, enabling the recruitment of transcription factors. Additionally, CDK7 is essential for the progression of the cell cycle by phosphorylating proteins involved in DNA replication and cell division. Understanding the role of CDK7 provides valuable insights for the development of targeted therapies in the pharmaceutical industry.
The quest to identify CDK7 as a potential therapeutic target has been unrelenting for roughly ten years, with considerable strides made especially in recent years. The realm of CDK7 inhibitors is steadily expanding, encompassing a vast range of chemical types while exhibiting potential for kinase selectivity. Moreover, the currently available agents have distinct inhibition methods, inclusive of traditional competition, irreversible association, and specific triggering of CDK7 breakdown by heterobifunctional agents. The fresh agents revealed in 58 patents submissions published within the reviewed duration, from 2018 to 2022, cover beyond 15 chemotypes. We categorized and encapsulated the chemical formations and their biochemical and biological attributes, offering scientists a thorough briefing of the field, including thrilling clinical contenders.
How do they work?
CDK7 inhibitors are a type of drug that specifically target and inhibit the activity of the cyclin-dependent kinase 7 (CDK7) enzyme. CDK7 is a protein kinase that plays a crucial role in regulating the cell cycle and gene transcription. By inhibiting CDK7, these inhibitors can disrupt the cell cycle progression and inhibit the transcription of certain genes involved in cell proliferation.
From a biomedical perspective, CDK7 inhibitors have shown potential as therapeutic agents in the field of cancer research. Cancer cells often exhibit dysregulated cell cycle control and increased transcription of genes involved in cell growth and survival. By targeting CDK7, these inhibitors can potentially halt cancer cell proliferation and induce cell death.
CDK7 inhibitors have been investigated in preclinical and clinical studies for various types of cancer, including breast cancer, lung cancer, and hematological malignancies. They are being explored as a potential treatment strategy either as standalone therapies or in combination with other anticancer drugs. The development of CDK7 inhibitors represents a promising avenue in the quest for more effective and targeted cancer treatments
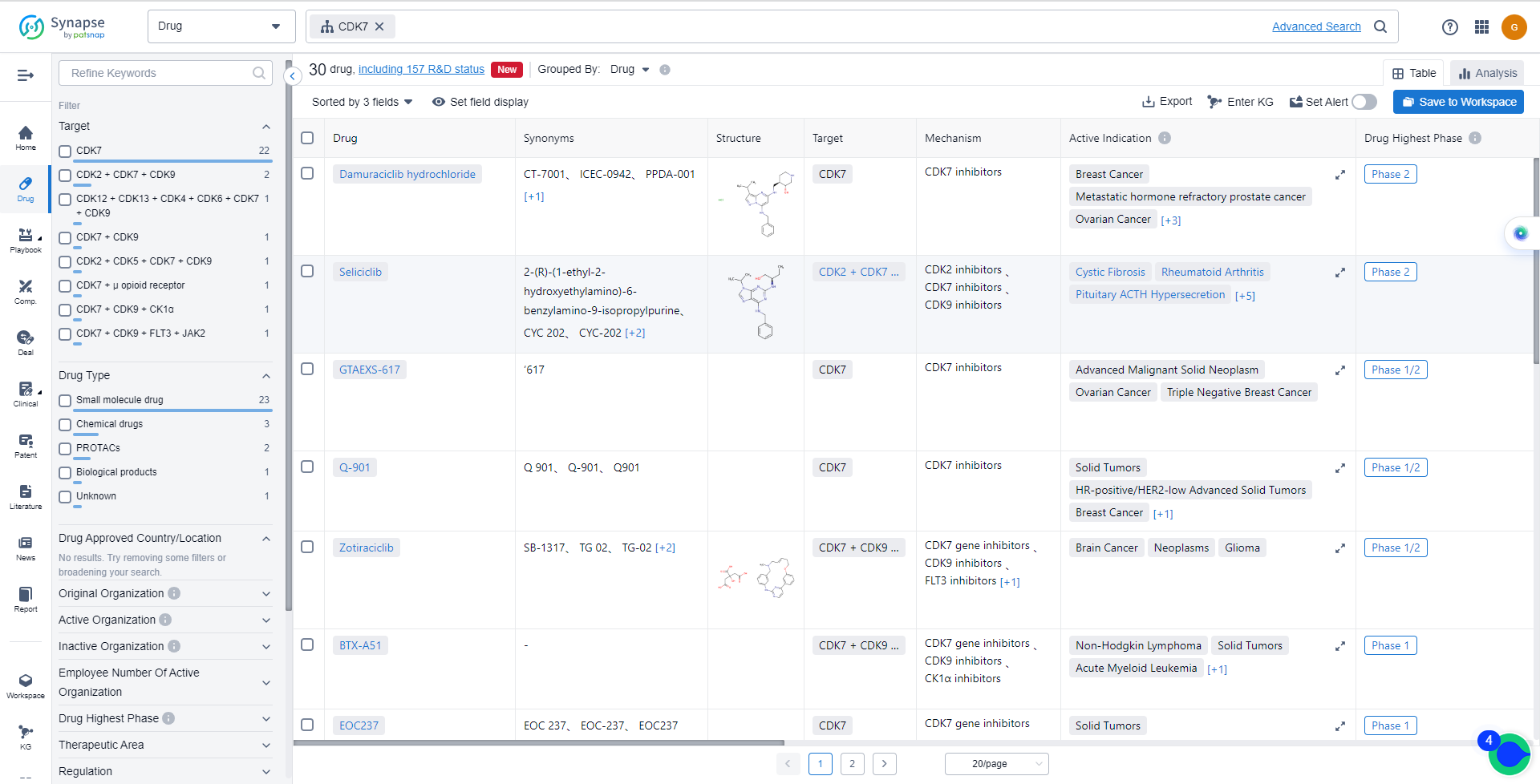
List of CDK7 Inhibitors
The currently marketed CDK7 inhibitors include:
- Damuraciclib hydrochloride
- Seliciclib
- GTAEXS-617
- Q-901
- Zotiraciclib
- BTX-A51
- EOC237
- LY-3405105
- SY-5609
- TY-2699a
For more information, please click on the image below.
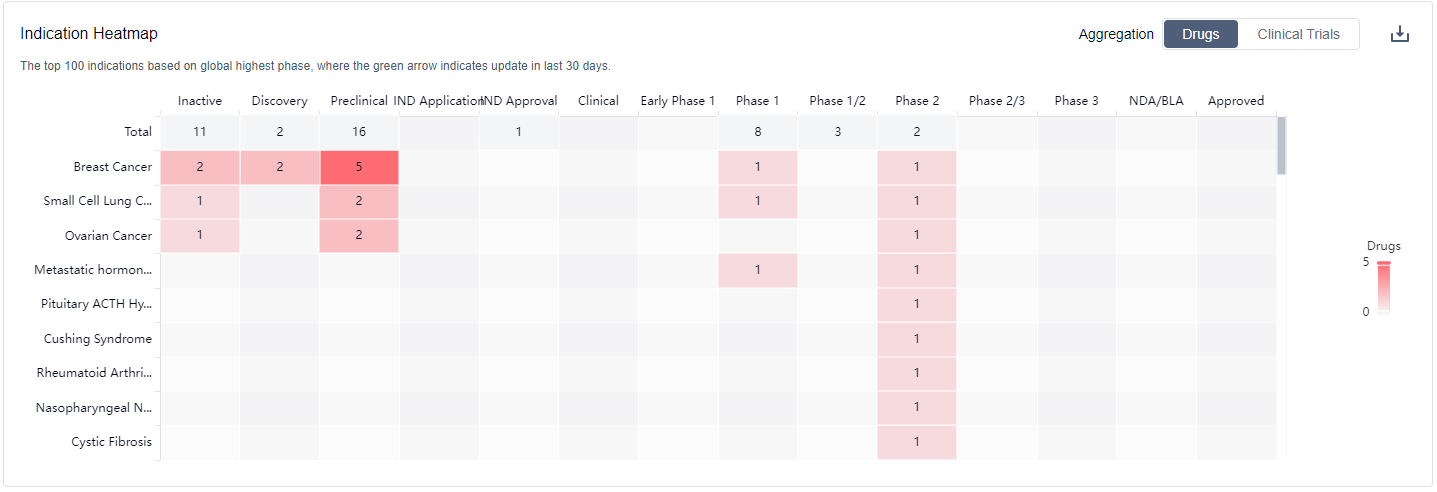
What are CDK7 inhibitors used for?
CDK7 inhibitors are under investigation for indications that include multiple autoimmune diseases such as Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML), Prostate Cancer, Hepatocellular Carcinoma (Liver Cancer), Gastric Cancer, Cervical Cancer, Pancreatic Cancer, Colorectal Cancer, Neuroblastoma, Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC), and SOX-2 amplified Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Lung. For more information, please click on the image below to log in and search.
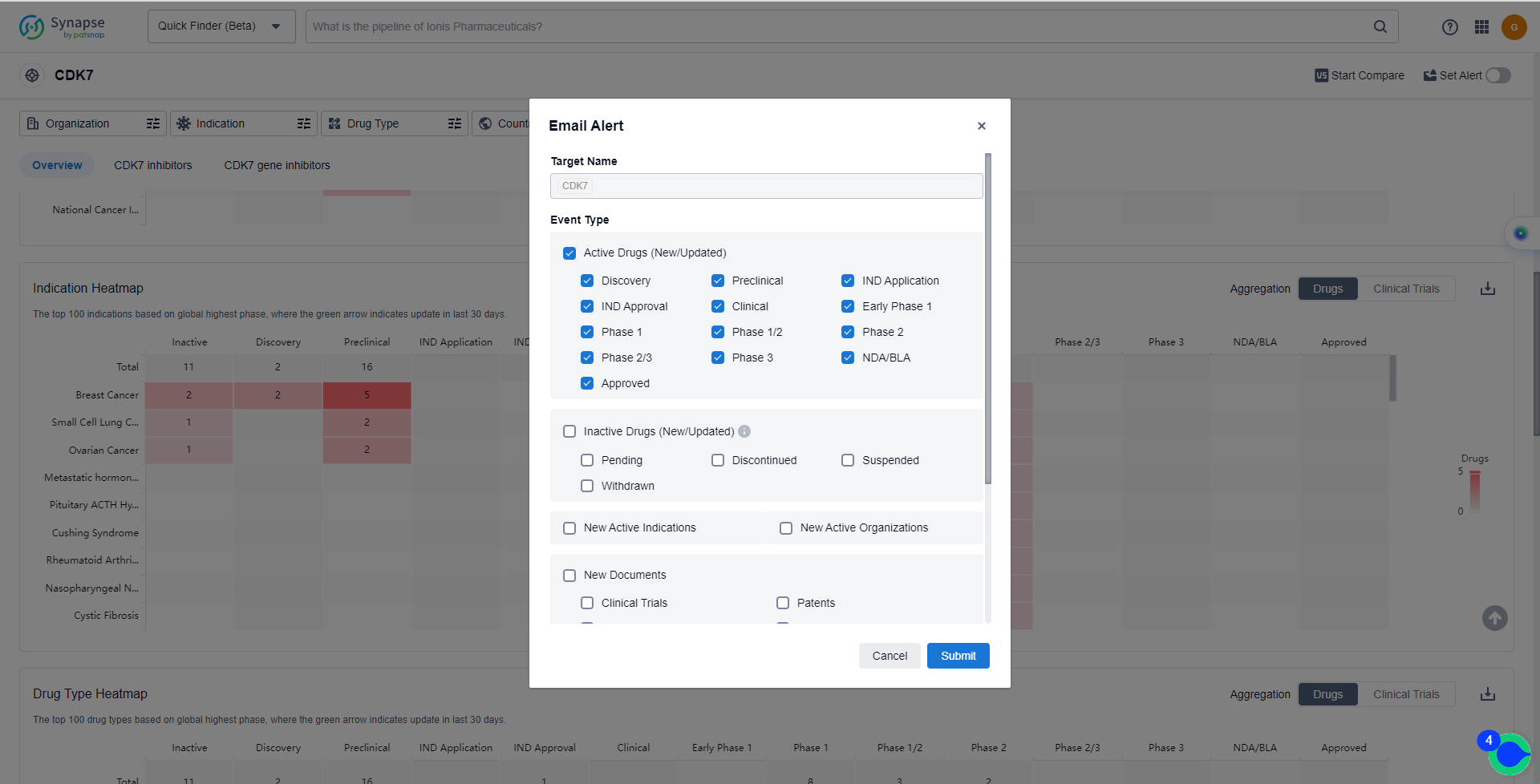
How to obtain the latest development progress of CDK7 inhibitors?
In the Synapse database, you can keep abreast of the latest research and development advances of CDK7 inhibitors anywhere and anytime, daily or weekly, through the "Set Alert" function. Click on the image below to embark on a brand new journey of drug discovery!