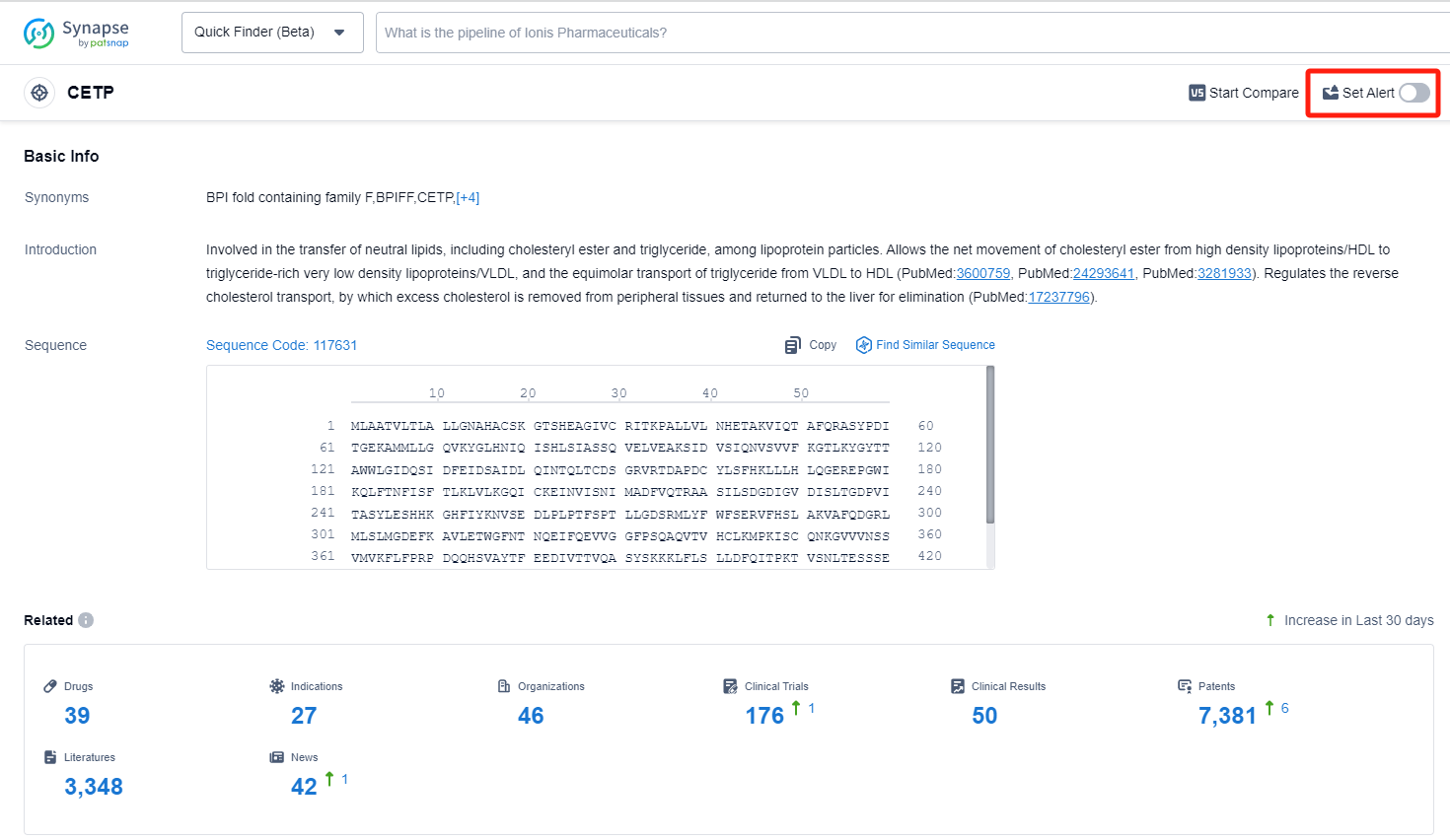
What are CETP inhibitors and how do you quickly get the latest development progress?
CETP, or Cholesteryl Ester Transfer Protein, plays a crucial role in lipid metabolism within the human body. It facilitates the transfer of cholesteryl esters (CE) and triglycerides (TG) between high-density lipoproteins (HDL) and low-density lipoproteins (LDL). By promoting the exchange of lipids, CETP contributes to the redistribution of cholesterol and triglycerides among lipoprotein particles. This process is essential for maintaining a healthy lipid profile and preventing the accumulation of cholesterol in the arteries. Understanding the function of CETP has led to the development of pharmaceutical interventions aimed at modulating its activity to improve cardiovascular health.
Currently, the main drugs for increasing HDL-C include fibrates, niacin, and Cholesteryl Ester Transfer Protein (CETP) inhibitors. Among them, CETP inhibitors are the most potent in elevating HDL-C levels, making them a recent focus of major pharmaceutical companies. CETP is a plasma glycoprotein synthesized by the liver, most of which circulates in combination with HDL. The primary function of CETP is to mediate the transfer of cholesterol from HDL to VLDL and LDL during the process of triacylglycerol exchange, and CETP inhibitors can block this transfer process, theoretically possessing anti-atherosclerosis effects and the ability to reduce cardiovascular risks. The first CETP inhibitor developed by Pfizer in 2006, Torcetrapib, significantly increased HDL-C in coronary disease patients by 72.1%, but paradoxically, this increase led to a rise in cardiovascular events and mortality risk. In 2012, Dalcetrapib, a CETP inhibitor developed by Roche, significantly increased HDL-C levels by 31% to 40% compared to baseline in acute coronary syndrome patients during the dal-OUTCOMES phase III trial with an average follow-up of 31 months. However, the benefits in the primary endpoint (a composite of coronary death, nonfatal myocardial infarction, ischemic stroke, unstable angina, or cardiac arrest revival) were no better than the placebo group, and its development was also terminated. Lilly ceased development of its CETP inhibitor evacetrapib on October 12, 2015, and the prospects for Merck's anacetrapib are similarly bleak. However, research and development of CETP inhibitors have not stopped, with drugs such as BAY60-5521, JNJ-28545595, TA8895, and CKD519 gradually entering the preclinical development phase. Recent studies regarding the safety, tolerability, and pharmacodynamics of CKD-519 in a single ascending dose study with 40 healthy volunteers demonstrated that a single dose of CKD-519 (25 mg to 400 mg) significantly increased HDL-C levels without causing severe adverse events, nor causing an increase in blood pressure similar to that caused by Torcetrapib. Therefore, the issue that increasing HDL-C does not decrease cardiovascular events and mortality risk, as well as the future research direction for CETP inhibitors, have become recent points of discussion and research focus.
How do they work?
CETP inhibitors are a type of drug that target the cholesteryl ester transfer protein (CETP). CETP is a protein involved in the transfer of cholesterol esters between lipoproteins, such as high-density lipoprotein (HDL) and low-density lipoprotein (LDL).
From a biomedical perspective, CETP inhibitors are designed to block the activity of CETP, thereby increasing the levels of HDL cholesterol and reducing the levels of LDL cholesterol. This mechanism is based on the understanding that higher levels of HDL cholesterol are associated with a lower risk of cardiovascular diseases, while elevated levels of LDL cholesterol are linked to an increased risk.
By inhibiting CETP, these drugs aim to promote a favorable lipid profile and potentially reduce the risk of conditions like atherosclerosis, heart attacks, and strokes. However, it is important to note that the clinical efficacy and safety of CETP inhibitors are still being evaluated, and more research is needed to fully understand their potential benefits and risks.
List of CETP Inhibitors
The currently marketed CETP inhibitors include:
- Ezetimibe/Pitavastatin Calcium
- Dalcetrapib
- Evacetrapib
- Obicetrapib
- Obicetrapib/Ezetimibe
- DRL-17822
- Icosabutate
- NST-1024
- CKD-508
- Anacetrapib
For more information, please click on the image below.
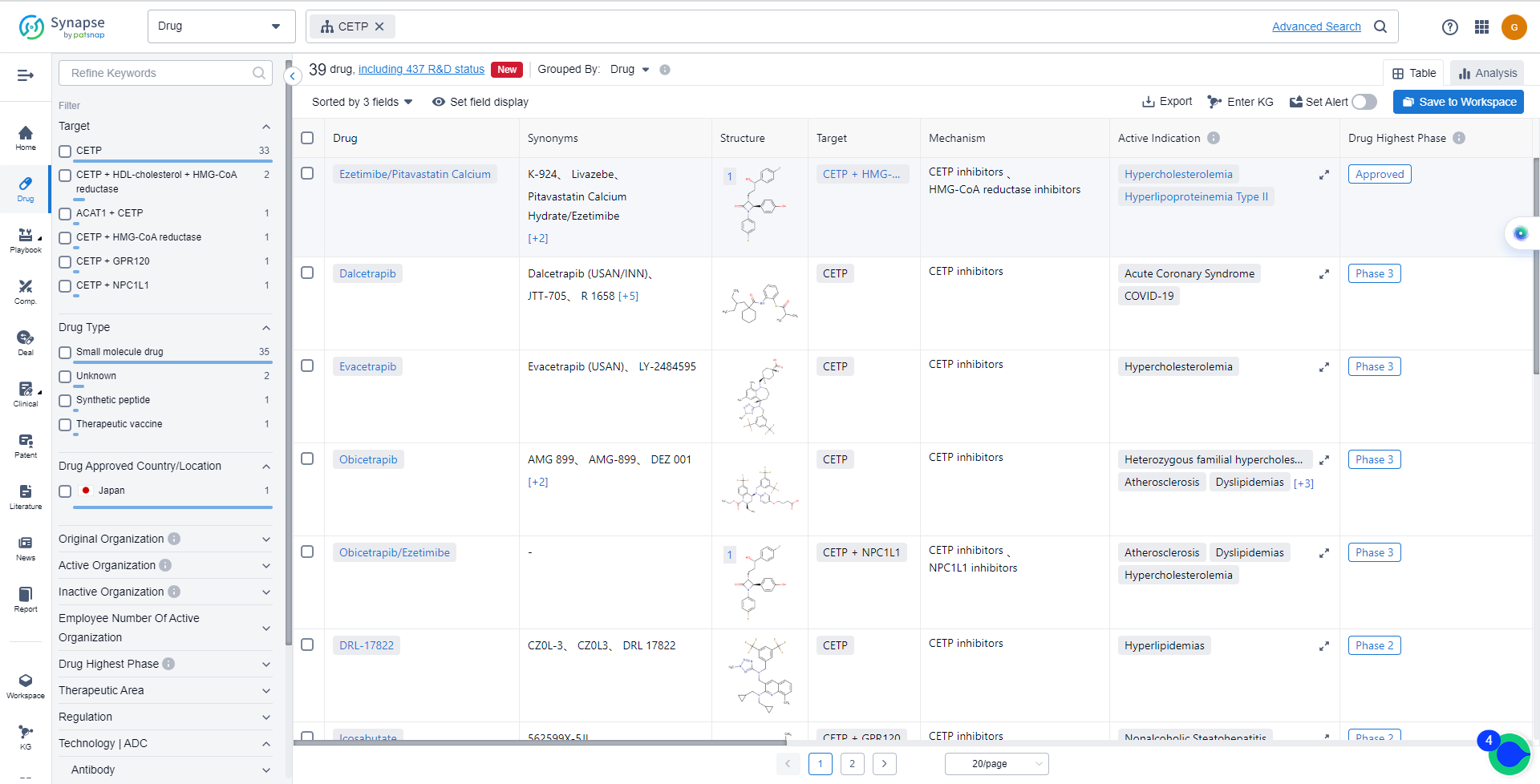 What are CETP inhibitors used for?
What are CETP inhibitors used for?
CETP inhibitors are approved indications include Hypercholesterolemia and Hyperlipoproteinemia Type II. For more information, please click on the image below to log in and search.
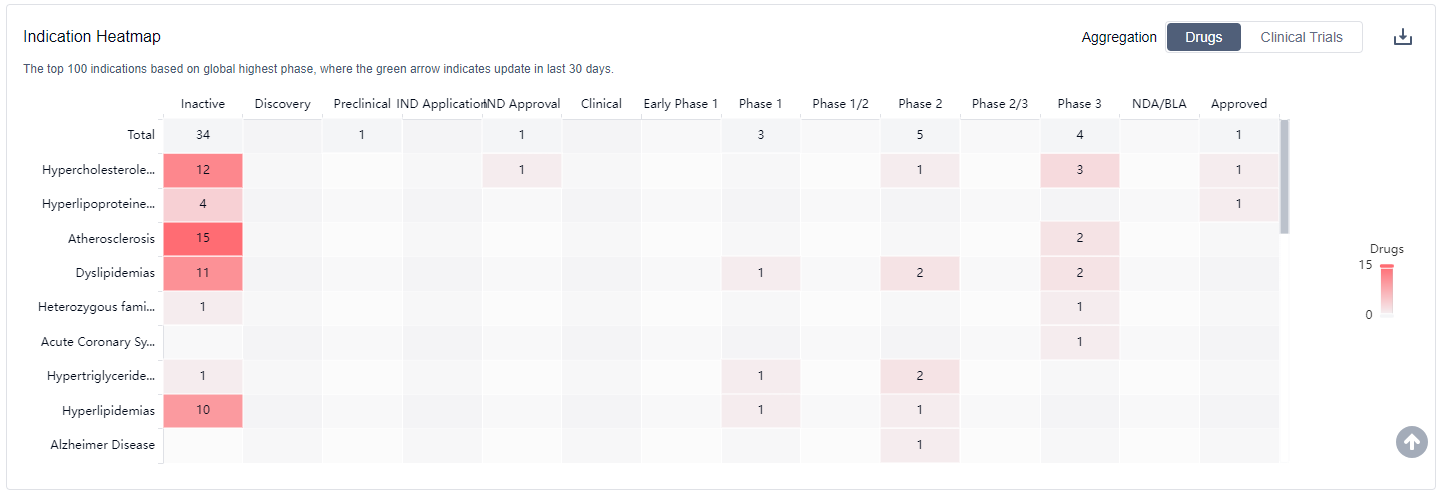 How to obtain the latest development progress of CETP inhibitors?
How to obtain the latest development progress of CETP inhibitors?
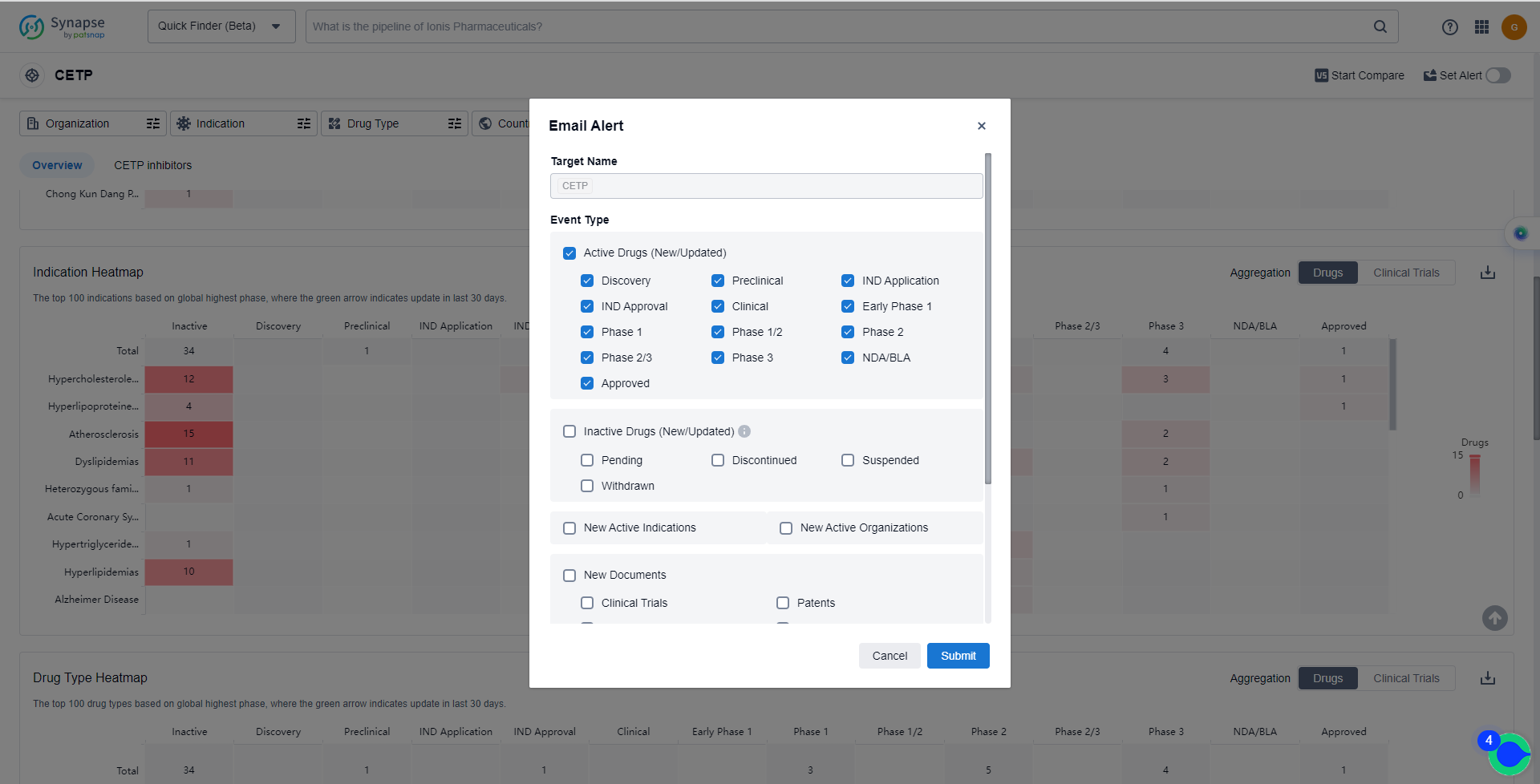
In the Synapse database, you can keep abreast of the latest research and development advances of CETP inhibitors anywhere and anytime, daily or weekly, through the "Set Alert" function. Click on the image below to embark on a brand new journey of drug discovery!