Last update 19 Sep 2024
Lower respiratory tract infection bacterial
Last update 19 Sep 2024
Basic Info
Synonyms Bacterial lower respiratory tract infections, Lower respiratory tract infection bacterial, bacterial lower respiratory tract infection + [4] |
Introduction- |
Related
1
Drugs associated with Lower respiratory tract infection bacterialTarget- |
Mechanism- |
Active Org. |
Originator Org. |
Active Indication |
Inactive Indication- |
Drug Highest PhasePreclinical |
First Approval Ctry. / Loc.- |
First Approval Date20 Jan 1800 |
14
Clinical Trials associated with Lower respiratory tract infection bacterialA Phase I/IIa study to evaluate safety, biodistribution, dosimetry and preliminary diagnostic performance of [68Ga]Ga-Deferoxamine for PET imaging in patients with bacterial infections
Start Date23 Oct 2020 |
Sponsor / Collaborator- |
复方罗红霉素片治疗轻中度急性下呼吸道细菌感染伴有痰液粘稠的随机双盲双模拟阳性药平行对照多中心临床试验
[Translation] A randomized, double-blind, double-dummy, positive drug parallel-controlled multicenter clinical trial of compound roxithromycin tablets in the treatment of mild to moderate acute bacterial infection of the lower respiratory tract with thick sputum
以罗红霉素为对照,进一步评价复方罗红霉素片治疗轻、中度急性下呼吸道细菌感染伴有痰液粘稠的安全性和有效性
[Translation]
Taking roxithromycin as a control, the safety and efficacy of compound roxithromycin tablets in the treatment of mild to moderate acute lower respiratory tract bacterial infection with thick sputum were further evaluated
Start Date03 Jul 2014 |
Sponsor / Collaborator |
DOUBLE-BLIND, RANDOMIZED, PLACEBO-CONTROLLED STUDY TO EVALUATE THE SAFETY, TOLERABILITY AND PHARMACOKINETICS OF SINGLE ASCENDING DOSES AND THE EFFECT OF FOOD ON ORAL WCK 4873 IN HEALTHY ADULT VOLUNTEERS - WCK 4873 Phase 1 SAD FE Study
Start Date14 Mar 2013 |
Sponsor / Collaborator |
100 Clinical Results associated with Lower respiratory tract infection bacterial
Login to view more data
100 Translational Medicine associated with Lower respiratory tract infection bacterial
Login to view more data
0 Patents (Medical) associated with Lower respiratory tract infection bacterial
Login to view more data
232
Literatures (Medical) associated with Lower respiratory tract infection bacterial01 Jan 2024·International journal of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
ApoA1, ApoB, ApoA1/B for Pathogenic Prediction of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Complicated by Acute Lower Respiratory Tract Infection: A Cross-Sectional Study.
Article
Author: Jiaqi Meng ; Weichang Yang ; Ziyong Chen ; Caixia Pei ; Xinmin Peng ; Can Li ; Fengyuan Li
Purpose:
To investigate the value of apolipoprotein A1 (ApoA1), apolipoprotein B (ApoB), and ApoA1/B ratio in pathogenic diagnosis of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) complicated by acute lower respiratory tract infection, assisting comprehensive disease assessment.
Patients and Methods:
The study enrolled 171 COPD patients with acute lower respiratory tract infections, 35 COPD patients without acute lower respiratory tract infections, and 41 healthy controls. Correlation analysis and binary logistic regression were used to assess the roles of various factors in COPD with acute lower respiratory tract infections. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves were plotted and area under curves (AUC) values were calculated to evaluate the predictive performance.
Results:
Infections were the cause of alterations in ApoA1, ApoB and ApoA1/B index. In correlation analysis for pathogenic diagnosis of COPD complicated by acute lower respiratory infections, age, ApoA1, ApoA1/B ratio, lymphocyte count (LYMPH), neutrophil count (NEUT), C-reactive protein (CRP), erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) and endotoxin were significantly correlated. For predicting COPD complicated by acute lower respiratory tract bacterial infection, ApoA1 had the highest area under the ROC curve (AUC: 0.889), with sensitivity and specificity of 82.9% and 83.9%, respectively. The combination of NEUT and ApoA1 improved the prediction efficacy (AUC: 0.909; sensitivity/specificity: 85.1%/85.7%).
Conclusion:
ApoA1, ApoB, and ApoA1/B ratio are good indicators for predicting pathogens in COPD complicated by acute lower respiratory tract infection, especially ApoA1 which has high predictive value.
12 Dec 2023·Healthcare (Basel, Switzerland)
Common Bacterial Infections during the 3-Month Period after SARS-CoV-2 Infection: A Retrospective Cohort Study.
Article
Author: Bar Cohen ; Shirley Shapiro Ben David ; Daniella Rahamim-Cohen ; Afif Nakhleh ; Arnon Shahar ; Ilan Yehoshua ; Avital Bilitzky-Kopit ; Joseph Azuri ; Miri Mizrahi Reuveni ; Limor Adler
INTRODUCTION:
Correlations between SARS-CoV-2 and bacterial infections have mainly been studied in hospitals, and these studies have shown that such interactions may be lethal for many. In the context of community flora, less is known of the trends and consequences of viral infections relative to subsequent bacterial infections.
PURPOSE:
This study aims to explore the prevalence and characteristics of bacterial infections in the three months following SARS-CoV-2 infections, in a community, real-world setting.
METHODS:
In this retrospective cohort study, we compared patients who completed a polymerase chain reaction (PCR) test or an antigen test for SARS-CoV-2 during January 2022, the peak of the Omicron wave, and examined bacterial infections following the test. We searched these cases for diagnoses of the following four bacterial infections for three months following the test: Group A Streptococcus (GAS) pharyngitis, pneumonia, cellulitis, and urinary tract infections (UTI).
RESULTS:
During January 2022, 267,931 patients tested positive and 261,909 tested negative for SARS-CoV-2. Test-positive compared to test-negative patients were significantly younger (42.5 years old vs. 48.5 years old, p < 0.001), smoked less, and had fewer comorbidities (including ischemic heart disease, diabetes mellitus, hypertension, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, and chronic renal failure). In the multivariable analysis, test-positive patients had an increased risk for GAS pharyngitis (adjusted odds ratio [aOR] = 1.25, 95% CI 1.14-1.38, p-value < 0.001) and pneumonia (aOR = 1.25, 95% CI 1.15-1.35, p-value < 0.001), a trend towards an increased prevalence of UTI (aOR = 1.05, 95% CI 0.99-1.12, p-value = 0.092), and lower risk for cellulitis (aOR = 0.92, 95% CI 0.86-0.99, p-value < 0.05).
CONCLUSIONS:
A history of SARS-CoV-2 infection in the past three months increased susceptibility to respiratory tract bacterial infections and the prevalence of UTI.
30 Oct 2023·The Pediatric infectious disease journal
Impact of Respiratory Bacterial Codetection on Outcomes in Ventilated Infants With Bronchiolitis.
Article
Author: Manzilat Akande ; Sandra P Spencer ; Melissa Moore-Clingenpeel ; Nathan Jamieson ; Todd Karsies
BACKGROUND:
Viral bronchiolitis is a common cause of acute respiratory failure requiring intubation for infants. Bacterial respiratory tract infections can occur with bronchiolitis, although their prevalence and impact on outcomes are unclear, especially with increased use of noninvasive respiratory support.
METHODS:
This was a single-center retrospective cohort study of children <2 years old requiring intubation in the emergency department for bronchiolitis from 2012 to 2017 who had viral testing plus a lower respiratory culture obtained. We evaluated the impact of bacterial codetection (positive respiratory culture plus moderate or many polymorphonuclear neutrophils on Gram stain) on mechanical ventilation (MV) duration and intensive care unit length of stay using multivariable gamma regression.
RESULTS:
Of 149 patients enrolled, 52% had bacterial codetection. In adjusted analysis, patients with codetection had shorter MV duration [adjusted relative risk (aRR) 0.819, 95% confidence interval (CI): 0.69-0.98; marginal mean duration of 5.31 days (4.71-5.99) compared to 6.48 days (5.72-7.35) without codetection]. Patients with codetection had a shorter intensive care unit stay [aRR 0.806 (0.69-0.94); marginal mean length of stay 6.9 days (6.21-7.68) vs. 8.57 days (7.68-9.56) without codetection]. The association between codetection and duration of ventilation appears confined to those receiving earlier antibiotics (less than the median time) rather than later antibiotics [aRR 0.738 (0.56-0.95) for earlier vs. aRR 0.92 (0.70-1.18) for later].
CONCLUSIONS:
Respiratory bacterial codetection is common and associated with shorter MV duration in infants requiring early intubation for bronchiolitis. Early antibiotics may contribute to these outcomes, but further multicenter studies are needed to understand the role of codetection and antibiotics on bronchiolitis outcomes.
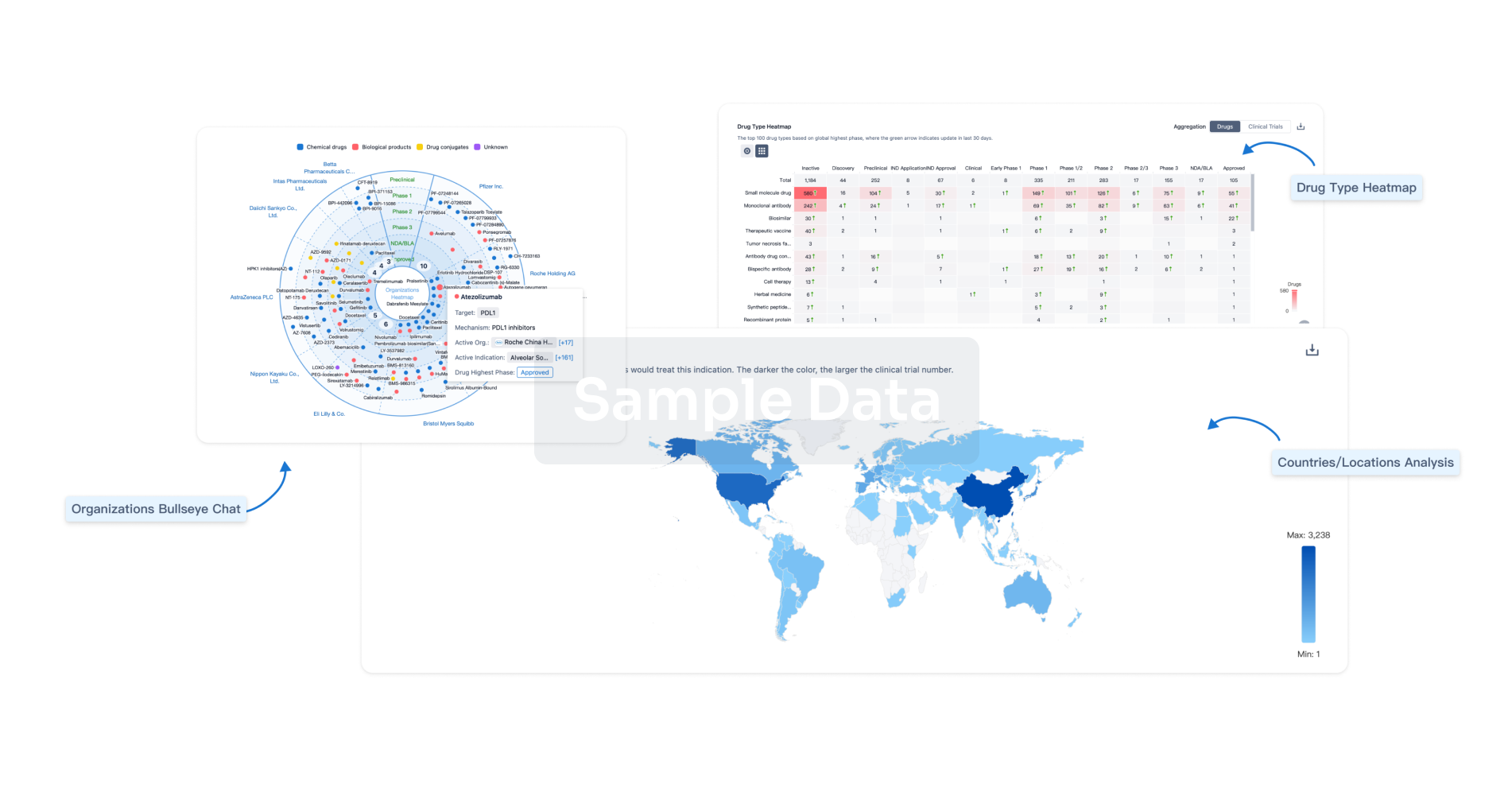
Analysis
Perform a panoramic analysis of this field.
login
or
Chat with Hiro
Get started for free today!
Accelerate Strategic R&D decision making with Synapse, PatSnap’s AI-powered Connected Innovation Intelligence Platform Built for Life Sciences Professionals.
Start your data trial now!
Synapse data is also accessible to external entities via APIs or data packages. Empower better decisions with the latest in pharmaceutical intelligence.
Bio
Bio Sequences Search & Analysis
Sign up for free
Chemical
Chemical Structures Search & Analysis
Sign up for free
