Request Demo
Last update 07 Mar 2026
Ipilimumab
Last update 07 Mar 2026
Overview
Basic Info
Drug Type Monoclonal antibody |
Synonyms Anti CTLA-4 monoclonal antibody, Anti-CTLA-4 Mab, Ipilimumab (Genetical Recombination) + [17] |
Target |
Action inhibitors |
Mechanism CTLA4 inhibitors(Cytotoxic T-Lymphocyte-Associated Antigen 4 inhibitors) |
Therapeutic Areas |
Inactive Indication |
Originator Organization |
Active Organization |
License Organization |
Drug Highest PhaseApproved |
First Approval Date United States (25 Mar 2011), |
RegulationPriority Review (United States), Breakthrough Therapy (United States), Accelerated Approval (United States), Orphan Drug (United States), Priority Review (China), Breakthrough Therapy (China), Conditional marketing approval (China), Orphan Drug (Japan), Orphan Drug (South Korea), Priority Review (Australia), Fast Track (United States) |
Login to view timeline
Structure/Sequence
Sequence Code 143797L

Source: *****
Sequence Code 9060585H

Source: *****
External Link
| KEGG | Wiki | ATC | Drug Bank |
|---|---|---|---|
| D04603 | Ipilimumab |
R&D Status
Approved
10 top approved records. to view more data
Login
| Indication | Country/Location | Organization | Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| Microsatellite instability-high Rectal Cancer | Japan | 25 Aug 2025 | |
| PD-L1 positive Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer | China | 22 Jul 2025 | |
| Metastatic hepatocellular carcinoma | Australia | 27 Jun 2025 | |
| Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma | European Union | 08 Mar 2025 | |
| Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma | Iceland | 08 Mar 2025 | |
| Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma | Liechtenstein | 08 Mar 2025 | |
| Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma | Norway | 08 Mar 2025 | |
| Unresectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma | European Union | 08 Mar 2025 | |
| Unresectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma | Iceland | 08 Mar 2025 | |
| Unresectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma | Liechtenstein | 08 Mar 2025 | |
| Unresectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma | Norway | 08 Mar 2025 | |
| Mismatch repair-deficient Colonic Cancer | European Union | 13 Jan 2025 | |
| Mismatch repair-deficient Colonic Cancer | Iceland | 13 Jan 2025 | |
| Mismatch repair-deficient Colonic Cancer | Liechtenstein | 13 Jan 2025 | |
| Mismatch repair-deficient Colonic Cancer | Norway | 13 Jan 2025 | |
| Unresectable Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma | United States | 27 May 2022 | |
| Esophageal Carcinoma | Japan | 26 May 2022 | |
| Hepatocellular Carcinoma | United States | 10 Mar 2020 | |
| Melanoma, Cutaneous Malignant | United States | 10 Jul 2018 | |
| Colorectal Cancer | United States | 16 Apr 2018 |
Developing
10 top R&D records. to view more data
Login
| Indication | Highest Phase | Country/Location | Organization | Date |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bladder Cancer | Phase 3 | United States | 30 Jan 2022 | |
| Bladder Cancer | Phase 3 | United States | 30 Jan 2022 | |
| HER2 negative Gastric Cancer | Phase 3 | Japan | 05 Nov 2021 | |
| HER2 negative Gastric Cancer | Phase 3 | South Korea | 05 Nov 2021 | |
| HER2 negative Gastric Cancer | Phase 3 | Taiwan Province | 05 Nov 2021 | |
| Sarcoma | Phase 3 | France | 24 Dec 2020 | |
| Glioblastoma | Phase 3 | United States | 01 Sep 2020 | |
| Gliosarcoma | Phase 3 | United States | 01 Sep 2020 | |
| Locally Advanced Lung Non-Small Cell Carcinoma | Phase 3 | United States | 08 Oct 2019 | |
| Locally Advanced Lung Non-Small Cell Carcinoma | Phase 3 | China | 08 Oct 2019 |
Login to view more data
Clinical Result
Clinical Result
Indication
Phase
Evaluation
View All Results
Phase 2 | 50 | btrmvqkjek(hhqgdvihmm) = ghcmfthqjf vvmdqmqmeo (yqhirudefv, 0.67 - 0.9) View more | Positive | 27 Feb 2026 | |||
Not Applicable | 514 | (Total) | gomfqznvmk(todwqlctuf) = bivbysatxa rpycqerace (cueygxmmxg, 4.5 - 7.7) | Negative | 26 Feb 2026 | ||
(ISUP Grade ≤3) | gomfqznvmk(todwqlctuf) = nfalfxfskl rpycqerace (cueygxmmxg, 2.0 - 3.8) | ||||||
Not Applicable | 514 | (<70 years) | yfdmckfuzo(fwjxcyqfbw) = nwsyoqxlcp pyhqxyihpd (tomlnrznkf ) View more | Positive | 26 Feb 2026 | ||
(≥70 years) | yfdmckfuzo(fwjxcyqfbw) = xtxkasgysx pyhqxyihpd (tomlnrznkf ) View more | ||||||
Not Applicable | 426 | 4 doses of Ipilimumab and Nivolumab | uaanoosoxl(fgvnsshbut) = ejvzrntciw uuwnljpwpo (qlhberaclx ) View more | Positive | 26 Feb 2026 | ||
uaanoosoxl(fgvnsshbut) = oueucjozwb uuwnljpwpo (qlhberaclx ) View more | |||||||
Phase 1/2 | 48 | xaspghpksp(flovplqsjj) = acmxwcfbju glqzaumqlp (uwqzkcmcku ) | Positive | 26 Feb 2026 | |||
xaspghpksp(flovplqsjj) = wexdpmbmkl glqzaumqlp (uwqzkcmcku ) | |||||||
Phase 2 | Urothelial Carcinoma of the Urinary Bladder Consolidation | 50 | Induction ipilimumab plus nivolumab followed by consolidating chemoradiotherapy | unsokkkplq(cexixjwith) = jmwmoiwcla pfctlrlqyh (kpfromacza, 0.65 - 0.89) View more | Positive | 26 Feb 2026 | |
Not Applicable | 56 | cinlrtxhpi(fqykngwxeu) = khmviporfh btomfalbtx (fkpifsegfw, 4.8 - 21.2) View more | Positive | 26 Feb 2026 | |||
cinlrtxhpi(fqykngwxeu) = covvnkypfl btomfalbtx (fkpifsegfw, 9.1 - 15.8) View more | |||||||
Phase 2 | Kidney Neoplasms First line | 67 | Ipilimumab/nivolumab + SBRT | bolvrahfgn(hcwvcufclo) = gfhecryxbj bjcdxvqbce (hhetenwgbz, 21 - 49) View more | Negative | 26 Feb 2026 | |
Ipilimumab/nivolumab alone | bolvrahfgn(hcwvcufclo) = nlczcutyrf bjcdxvqbce (hhetenwgbz, 27 - 66) View more | ||||||
Phase 2 | 11 | xcszkjhegx(rbkvnnhdlt) = ttckibtmtx xanktvgbwm (pigtfhlfkn ) View more | Positive | 26 Feb 2026 | |||
Phase 2 | 43 | eeykgjgrmy(slraqpdaqn) = iiisdeyozd jsvpehbyfw (kndzyzsaks ) View more | Positive | 26 Feb 2026 | |||
(chromophobe RCC) | eeykgjgrmy(slraqpdaqn) = oxddjedzhf jsvpehbyfw (kndzyzsaks ) View more |
Login to view more data
Translational Medicine
Boost your research with our translational medicine data.
login
or

Deal
Boost your decision using our deal data.
login
or

Core Patent
Boost your research with our Core Patent data.
login
or

Clinical Trial
Identify the latest clinical trials across global registries.
login
or

Approval
Accelerate your research with the latest regulatory approval information.
login
or

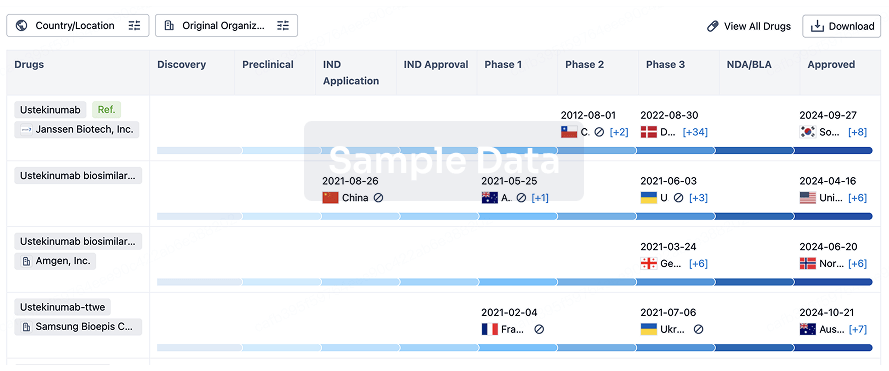
Biosimilar
Competitive landscape of biosimilars in different countries/locations. Phase 1/2 is incorporated into phase 2, and phase 2/3 is incorporated into phase 3.
login
or
Regulation
Understand key drug designations in just a few clicks with Synapse.
login
or

AI Agents Built for Biopharma Breakthroughs
Accelerate discovery. Empower decisions. Transform outcomes.
Get started for free today!
Accelerate Strategic R&D decision making with Synapse, PatSnap’s AI-powered Connected Innovation Intelligence Platform Built for Life Sciences Professionals.
Start your data trial now!
Synapse data is also accessible to external entities via APIs or data packages. Empower better decisions with the latest in pharmaceutical intelligence.
Bio
Bio Sequences Search & Analysis
Sign up for free
Chemical
Chemical Structures Search & Analysis
Sign up for free










