A Comprehensive Review of Cyanamide's R&D Innovations and Drug Target Mechanism
Cyanamide's R&D Progress
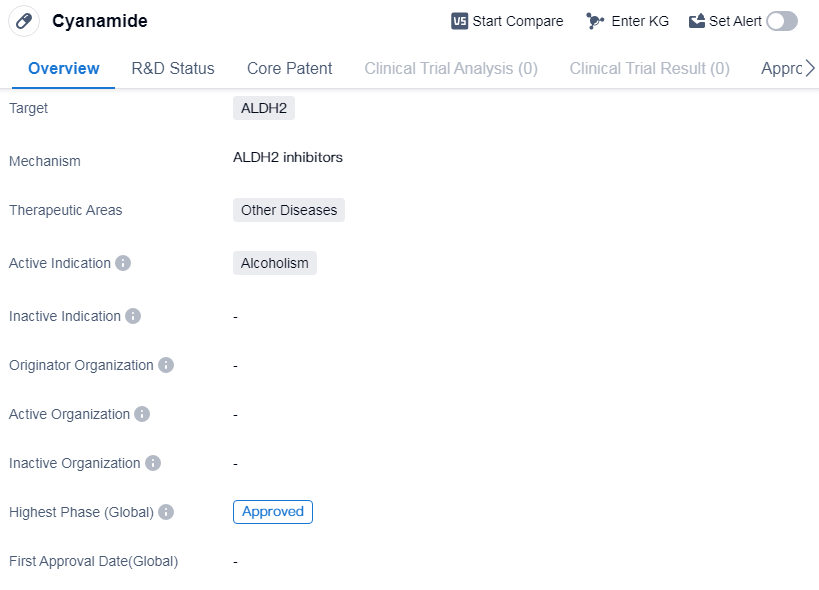
Cyanamide is a small molecule drug that targets ALDH2 and is primarily used in the treatment of alcoholism. It falls under the therapeutic area of other diseases. The drug has reached the highest phase of development, which is approved globally.
Cyanamide is classified as a small molecule drug, these drugs are typically orally administered and can easily penetrate cell membranes, allowing them to interact with specific targets within the body.
Cyanamide specifically targets ALDH2, which stands for aldehyde dehydrogenase 2. ALDH2 is an enzyme involved in the metabolism of alcohol, and its inhibition can help reduce the desire to consume alcohol. By targeting ALDH2, Cyanamide aims to provide a therapeutic effect in individuals suffering from alcoholism.Alcoholism is a chronic disease, it can lead to various physical and mental health problems and is a significant public health concern worldwide.
Cyanamide has successfully completed its development process and has reached the highest phase, which is approval. This means that it has undergone rigorous testing and evaluation, demonstrating its safety and efficacy in treating alcoholism. It has received regulatory approval for use in multiple countries globally.
👇Please click on the image below to directly access the latest data (R&D Status | Core Patent | Clinical Trial | Approval status in Global countries) of this drug.
Mechanism of Action for Cyanamide: ALDH2 inhibitors
ALDH2 inhibitors are a type of medication that specifically target and inhibit the activity of the enzyme ALDH2 (aldehyde dehydrogenase 2). ALDH2 is an important enzyme involved in the metabolism of alcohol and other aldehydes in the body.
From a biomedical perspective, ALDH2 inhibitors are of particular interest in the field of alcohol research and addiction medicine. ALDH2 plays a crucial role in the breakdown of acetaldehyde, a toxic byproduct of alcohol metabolism. Individuals with a genetic variant that leads to reduced ALDH2 activity may experience adverse reactions when consuming alcohol, such as facial flushing, nausea, and increased heart rate. ALDH2 inhibitors can potentially be used to modulate the effects of alcohol by reducing the metabolism of acetaldehyde, thereby decreasing the unpleasant symptoms associated with alcohol consumption.
Furthermore, ALDH2 inhibitors have shown potential therapeutic applications beyond alcohol metabolism. They have been investigated for their potential in the treatment of certain types of cancer, as ALDH2 is involved in the detoxification of chemotherapeutic agents. By inhibiting ALDH2, these inhibitors can potentially enhance the effectiveness of chemotherapy drugs by preventing the breakdown of the drugs within cancer cells.
In summary, ALDH2 inhibitors are a class of drugs that target the ALDH2 enzyme, primarily known for their potential in alcohol research and addiction medicine, as well as their potential in cancer treatment.
Drug Target R&D Trends for Cyanamide
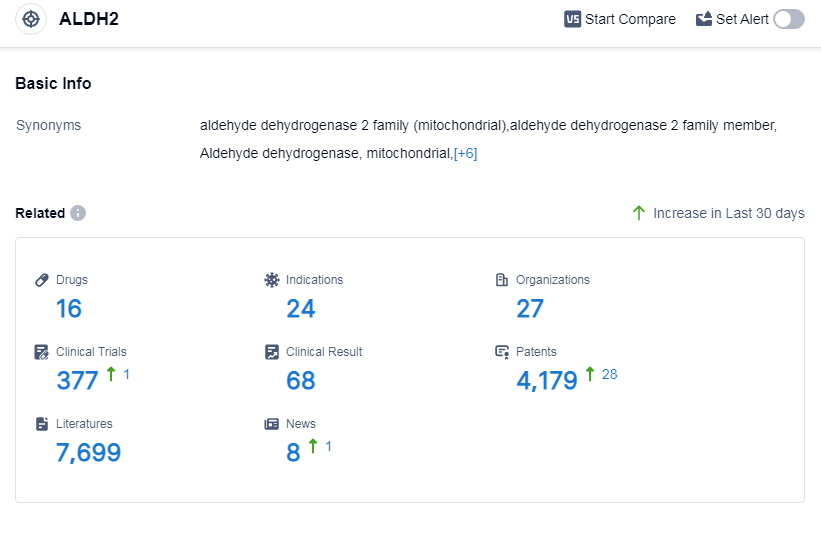
According to Patsnap Synapse, as of 9 Sep 2023, there are a total of 16 ALDH2 drugs worldwide, from 27 organizations, covering 24 indications, and conducting 377 clinical trials.
The analysis of target ALDH2 reveals a competitive landscape with multiple companies focusing on its development. Small molecule drugs are progressing rapidly, indicating intense competition in the market. China is one of the countries/locations with the fastest development and has shown progress with drugs in the approved and inactive phases. Overall, the analysis suggests a promising future for the development of target ALDH2 in the pharmaceutical industry.
👇Please click on the picture link below for free registration or log in directly if you have a freemium account, you can browse the latest research progress on drugs, indications, organizations, clinical trials, clinical results, and drug patents related to this target
Conclusion
In summary, Cyanamide is a small molecule drug that targets ALDH2 and is indicated for the treatment of alcoholism. It has reached the highest phase of development and is approved globally. This drug holds promise in addressing the significant health and societal challenges associated with alcoholism.