Decoding Chlortetracycline: A Comprehensive Study of its R&D Trends
Chlortetracycline's R&D Progress
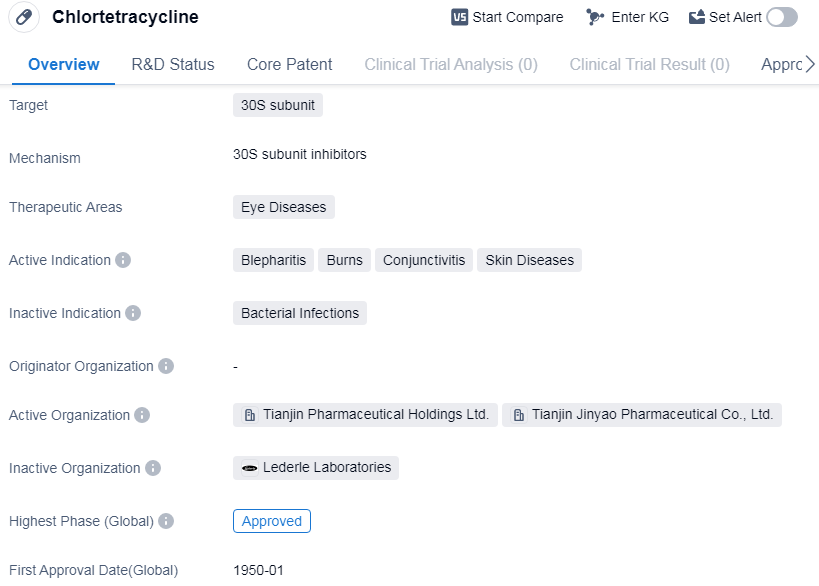
Chlortetracyclineis a small molecule drug that belongs to the class of antibiotics known as tetracyclines. It primarily targets the 30S subunit of bacterial ribosomes, inhibiting protein synthesis and thereby exerting its antimicrobial effects.
In terms of therapeutic areas, Chlortetracycline is primarily used in the treatment of eye diseases. It has been found to be effective in managing conditions such as blepharitis, burns, conjunctivitis, and certain skin diseases. These indications highlight the drug's potential in addressing various inflammatory and infectious conditions affecting the eyes and surrounding tissues.
Chlortetracycline has a long history in the pharmaceutical industry, with its first approval dating back to January 1950 in the United States. It has since gained approval in China and several other countries, making it a globally recognized drug.
As a small molecule drug, Chlortetracycline offers advantages such as ease of synthesis, oral bioavailability, and the ability to penetrate various tissues. These characteristics contribute to its effectiveness in treating eye diseases, as it can reach the target site and exert its therapeutic effects.
The approval of Chlortetracycline in multiple countries suggests its established safety and efficacy profile. Its long history of use further supports its reliability and potential benefits in the treatment of eye diseases. However, it is important to note that the information provided does not specify the current status of the drug in terms of ongoing clinical trials or any recent developments.
👇Please click on the image below to directly access the latest data (R&D Status | Core Patent | Clinical Trial | Approval status in Global countries) of this drug.
Mechanism of Action for Chlortetracycline: 30S subunit inhibitors
30S subunit inhibitors are a type of drugs that target the 30S subunit of the bacterial ribosome. The ribosome is a complex molecular machine responsible for protein synthesis in cells. It consists of two subunits, the 30S subunit and the 50S subunit. The 30S subunit plays a crucial role in the initiation of protein synthesis by binding to the messenger RNA (mRNA) and the transfer RNA (tRNA) carrying the amino acids.
Inhibitors of the 30S subunit interfere with the normal functioning of the ribosome, preventing the synthesis of proteins essential for bacterial growth and survival. These inhibitors can bind to specific sites on the 30S subunit, disrupting the decoding of the genetic information carried by the mRNA and inhibiting the formation of peptide bonds between amino acids.
By targeting the bacterial ribosome, 30S subunit inhibitors exhibit antibacterial activity and are used as antibiotics to treat various bacterial infections. Examples of 30S subunit inhibitors include tetracyclines and aminoglycosides. These drugs are effective against a wide range of bacteria but may have side effects and limitations in their use due to the potential for resistance development and adverse reactions in humans.
From a biomedical perspective, understanding the mechanism of action of 30S subunit inhibitors is crucial for developing new antibiotics and combating antibiotic resistance. Researchers study the structure and function of the bacterial ribosome to design more effective drugs that selectively target bacterial protein synthesis while minimizing harm to human cells.
Drug Target R&D Trends for Chlortetracycline
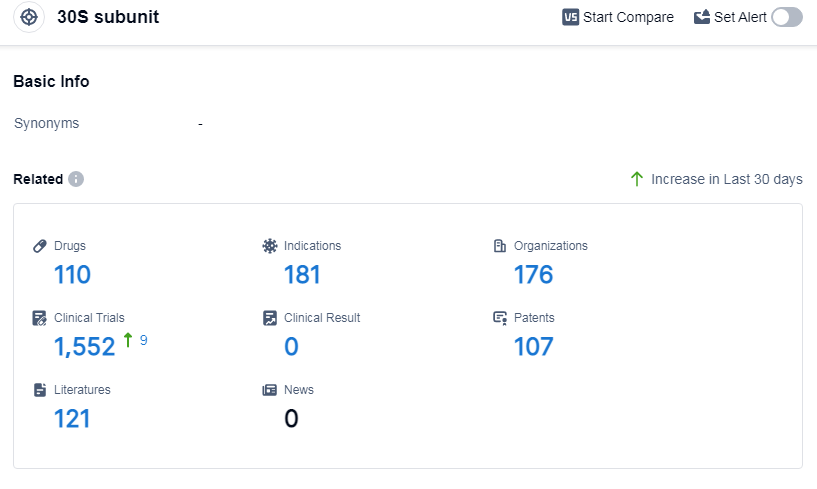
According to Patsnap Synapse, as of 8 Sep 2023, there are a total of 110 30S subunit drugs worldwide, from 176 organizations, covering 181 indications, and conducting 1552 clinical trials.
The analysis of the target 30S subunit reveals a competitive landscape with multiple companies focusing on research and development. Pfizer Inc. has the highest stage of development with 6 approved drugs. Bacterial infections are the most targeted indication, with a significant number of approved drugs. Small molecule drugs are progressing rapidly, indicating intense competition in this area. China is leading in terms of the number of approved drugs, followed by the United States and Japan. The future development of the target 30S subunit is promising, with ongoing research and development efforts focused on addressing various indications and drug types.
👇Please click on the picture link below for free registration or log in directly if you have a freemium account, you can browse the latest research progress on drugs, indications, organizations, clinical trials, clinical results, and drug patents related to this target
Conclusion
In summary, Chlortetracycline is a small molecule drug that targets the 30S subunit and is primarily used in the treatment of eye diseases. It has been approved in multiple countries, including the United States and China, with its first approval dating back to 1950. The drug's indications include blepharitis, burns, conjunctivitis, and certain skin diseases. Its long history and global approvals indicate its established safety and efficacy profile in the field of biomedicine.