A Comprehensive Review of Efavirenz's R&D Innovations and Drug Target Mechanism
Efavirenz's R&D Progress
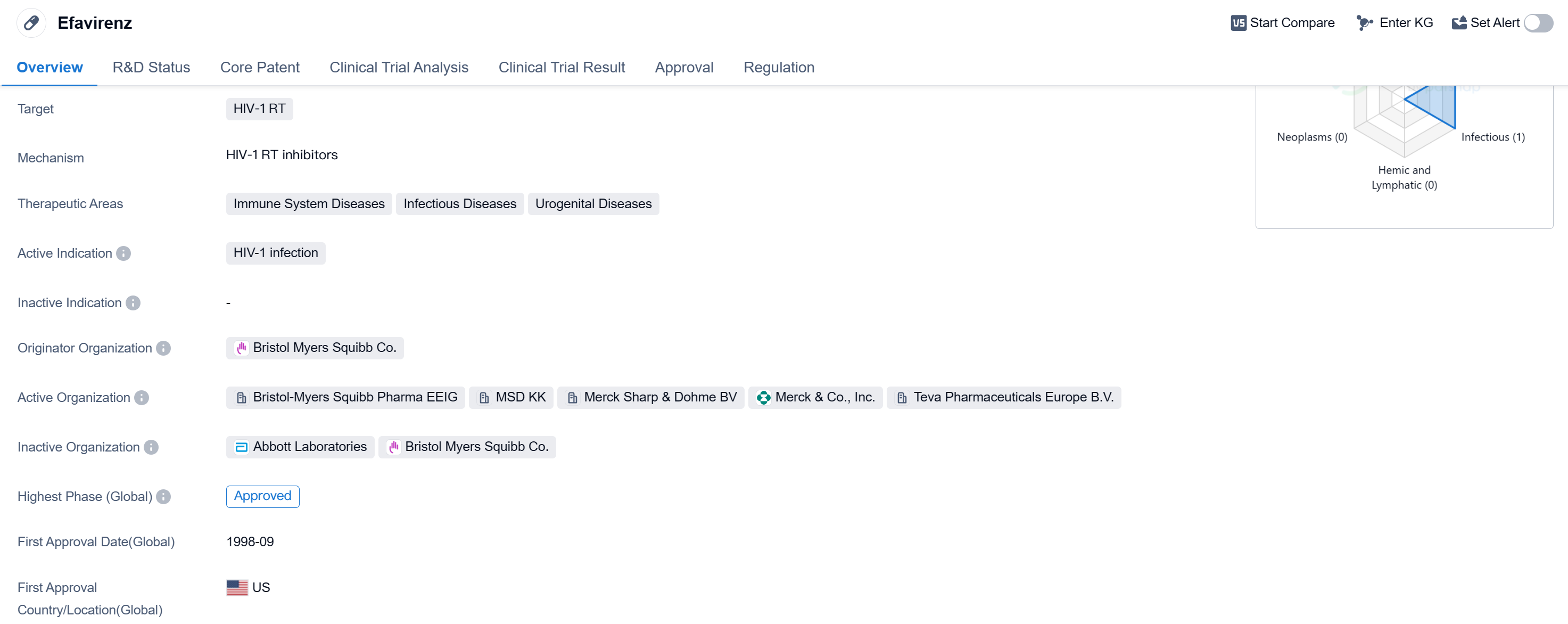
Efavirenz is a small molecule drug that is primarily used for the treatment of HIV-1 infection. It targets the HIV-1 reverse transcriptase (RT), an enzyme essential for the replication of the virus. The drug falls under the therapeutic areas of immune system diseases, infectious diseases, and urogenital diseases.
The originator organization of Efavirenz is Bristol Myers Squibb Co., a renowned pharmaceutical company. The drug has achieved the highest phase of approval globally. It received its first approval in the United States in September 1998, making it one of the early drugs in the fight against HIV.
Efavirenz has been granted accelerated approval and orphan drug status, highlighting its importance in addressing a significant medical need. Accelerated approval is a regulatory pathway that allows for the expedited approval of drugs that treat serious conditions and provide a meaningful advantage over existing therapies. Orphan drug designation is granted to drugs that target rare diseases, providing incentives for their development.
The objective presentation of this information allows for a clear understanding of Efavirenz's key characteristics and its significance in the pharmaceutical industry. As a small molecule drug, it specifically targets the HIV-1 RT enzyme, making it effective in combating HIV-1 infection. Its therapeutic areas encompass immune system diseases, infectious diseases, and urogenital diseases, reflecting its broad applicability in treating various conditions.
The drug's approval in the global markets demonstrates its widespread acceptance and recognition by regulatory authorities. Its first approval in the United States in 1998 signifies its early entry into the market and its contribution to the treatment of HIV. The regulatory designations of accelerated approval and orphan drug status further emphasize its importance in addressing unmet medical needs.
👇Please click on the image below to directly access the latest data (R&D Status | Core Patent | Clinical Trial | Approval status in Global countries) of this drug.
Mechanism of Action for Efavirenz: HIV-1 RT inhibitors
HIV-1 RT inhibitors are a type of medication used in the treatment of HIV/AIDS. HIV-1 refers to the human immunodeficiency virus type 1, which is the most common and widespread strain of the virus. RT stands for reverse transcriptase, which is an enzyme produced by the virus that plays a crucial role in its replication process.
HIV-1 RT inhibitors specifically target the reverse transcriptase enzyme, inhibiting its activity and preventing the virus from replicating and spreading in the body. By blocking this enzyme, these inhibitors help to reduce the viral load in HIV-infected individuals, slow down the progression of the disease, and improve the immune system's ability to fight off infections.
There are different classes of HIV-1 RT inhibitors, including nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NRTIs) and non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NNRTIs). NRTIs work by mimicking the building blocks of DNA and RNA, which are necessary for viral replication. Once incorporated into the viral DNA chain, NRTIs terminate the replication process. On the other hand, NNRTIs bind to a different site on the reverse transcriptase enzyme, causing a conformational change that inhibits its activity.
HIV-1 RT inhibitors are typically used in combination with other antiretroviral drugs as part of highly active antiretroviral therapy (HAART). This multidrug approach helps to suppress viral replication, reduce the risk of drug resistance, and improve treatment outcomes for individuals living with HIV/AIDS. It is important to note that HIV-1 RT inhibitors are not a cure for HIV/AIDS, but they can effectively manage the infection and improve the quality of life for patients.
Drug Target R&D Trends for Efavirenz
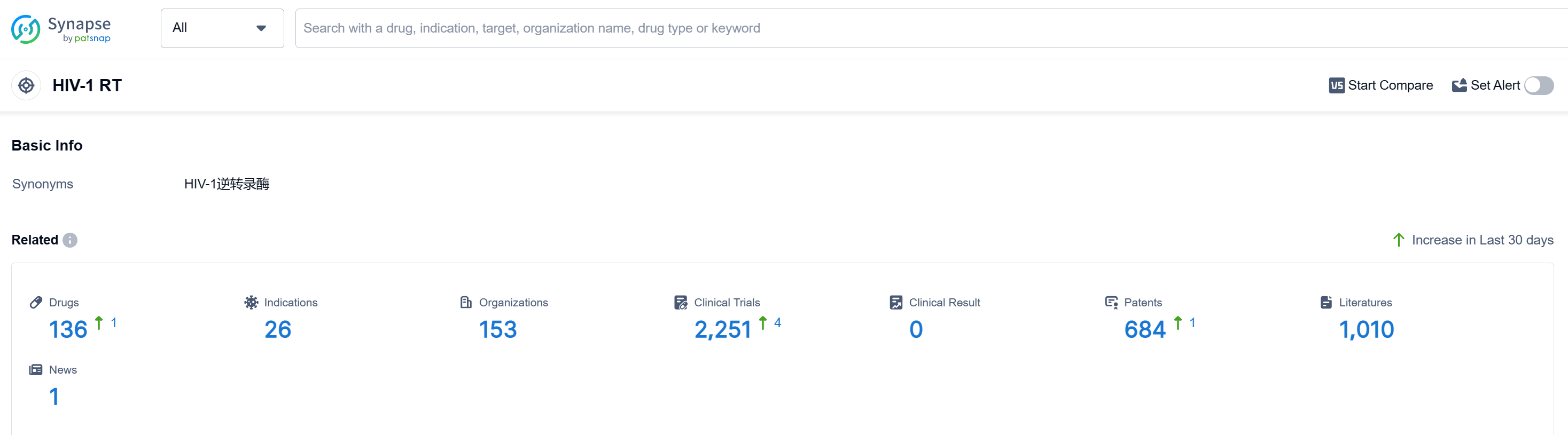
According to Patsnap Synapse, as of 10 Sep 2023, there are a total of 136 HIV-1 RT drugs worldwide, from 153 organizations, covering 26 indications, and conducting 2251 clinical trials. Based on the analysis, Gilead Sciences, Inc., GSK Plc, and Johnson & Johnson are the companies growing fastest under the target HIV-1 RT. The primary indications for approved drugs are HIV Infections, HIV-1 infection, Hepatitis B, and Chronic Hepatitis B. Small molecule drugs dominate the development pipeline, with biosimilars like synthetic peptides also showing progress. The European Union, the United States, China, and Japan are the countries/locations developing fastest under the target, with China showing significant progress. Overall, the competitive landscape for target HIV-1 RT is dynamic, with ongoing R&D efforts and potential for future development in various countries and companies.
👇Please click on the picture link below for free registration or log in directly if you have a freemium account, you can browse the latest research progress on drugs, indications, organizations, clinical trials, clinical results, and drug patents related to this target
Conclusion
Overall, Efavirenz's objective information showcases its role as a significant drug in the field of biomedicine, particularly in the treatment of HIV-1 infection. Its originator organization, Bristol Myers Squibb Co., has successfully developed and brought this drug to market, benefiting patients worldwide.