Exploring Diflunisal's Revolutionary R&D Successes and its Mechanism of Action on Drug Target
Diflunisal's R&D Progress
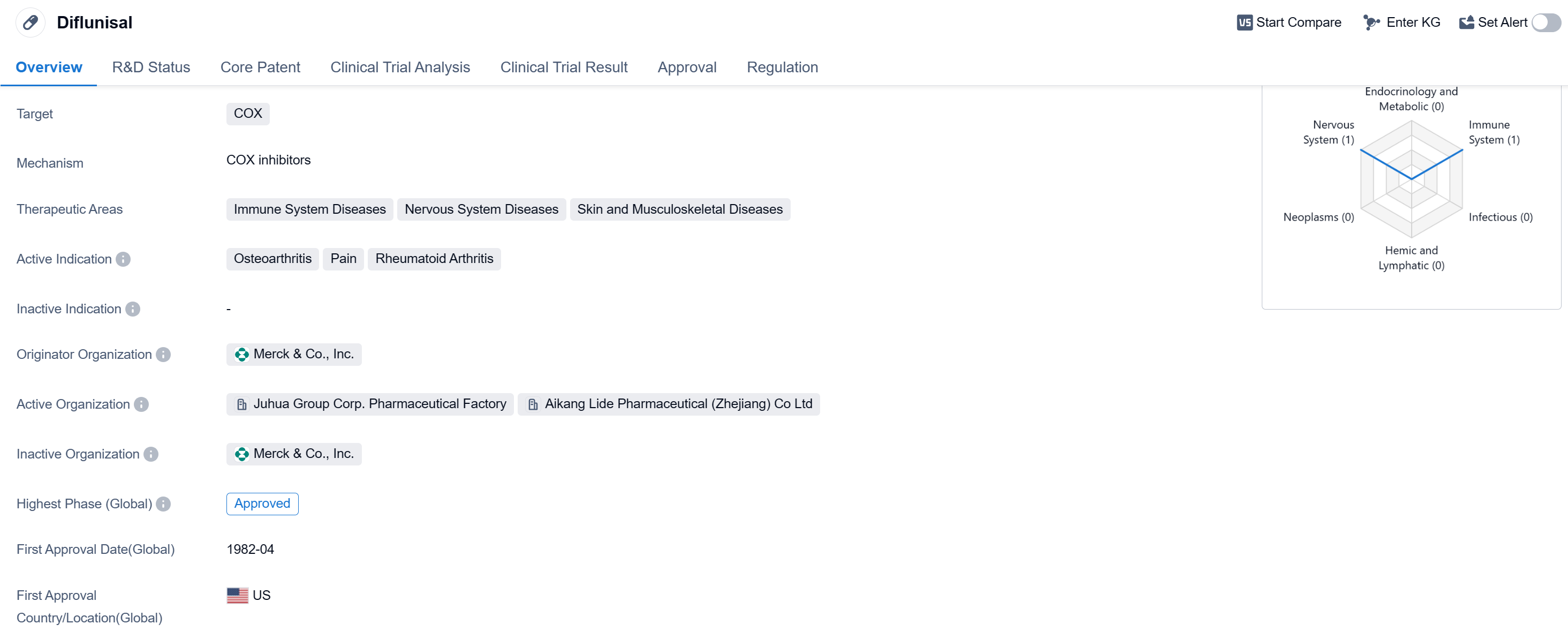
Diflunisalis a small molecule drug that belongs to the class of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). It primarily targets the enzyme cyclooxygenase (COX), which is involved in the production of prostaglandins, substances that play a role in inflammation and pain. By inhibiting COX, diflunisal helps reduce inflammation and alleviate pain associated with various conditions.
The therapeutic areas in which diflunisal is used include immune system diseases, nervous system diseases, and skin and musculoskeletal diseases. Specifically, it is indicated for the treatment of osteoarthritis, pain, and rheumatoid arthritis. These conditions are characterized by joint inflammation, stiffness, and pain, and diflunisal helps manage these symptoms.
Diflunisal was originally developed by Merck & Co., Inc., a renowned pharmaceutical company. It has received approval for use in multiple countries, including the United States, where it was first approved in April 1982. The drug has also obtained regulatory status as an orphan drug, indicating its potential to treat rare diseases or conditions.
In terms of clinical development, diflunisal has reached the highest phase of approval globally. Being approved in both regions further highlights its potential as a therapeutic option for patients.
👇Please click on the image below to directly access the latest data (R&D Status | Core Patent | Clinical Trial | Approval status in Global countries) of this drug.
Mechanism of Action for Diflunisal: COX inhibitors
COX inhibitors are a class of drugs that work by inhibiting the activity of cyclooxygenase (COX) enzymes. These enzymes play a crucial role in the production of prostaglandins, which are hormone-like substances involved in inflammation, pain, and fever. By blocking the action of COX enzymes, COX inhibitors reduce the production of prostaglandins, leading to anti-inflammatory, analgesic (pain-relieving), and antipyretic (fever-reducing) effects.
There are two isoforms of COX enzymes: COX-1 and COX-2. COX-1 is constitutively expressed in many tissues and is involved in maintaining normal physiological functions, such as protecting the stomach lining and promoting kidney function. COX-2, on the other hand, is primarily induced during inflammation and is responsible for the production of prostaglandins that contribute to pain and inflammation.
COX inhibitors can be further classified into two main types: non-selective COX inhibitors and selective COX-2 inhibitors. Non-selective COX inhibitors, such as aspirin and ibuprofen, inhibit both COX-1 and COX-2 enzymes, resulting in a broader range of effects. Selective COX-2 inhibitors, like celecoxib, specifically target the COX-2 enzyme, aiming to minimize the gastrointestinal side effects associated with non-selective COX inhibitors.
These drugs are commonly used in the treatment of various conditions involving inflammation and pain, such as arthritis, menstrual cramps, and acute injuries. However, it's important to note that COX inhibitors can have potential side effects, particularly on the gastrointestinal system, cardiovascular system, and renal function. Therefore, their use should be carefully considered, and patients should follow the prescribed dosage and duration of treatment as advised by healthcare professionals.
Drug Target R&D Trends for Diflunisal
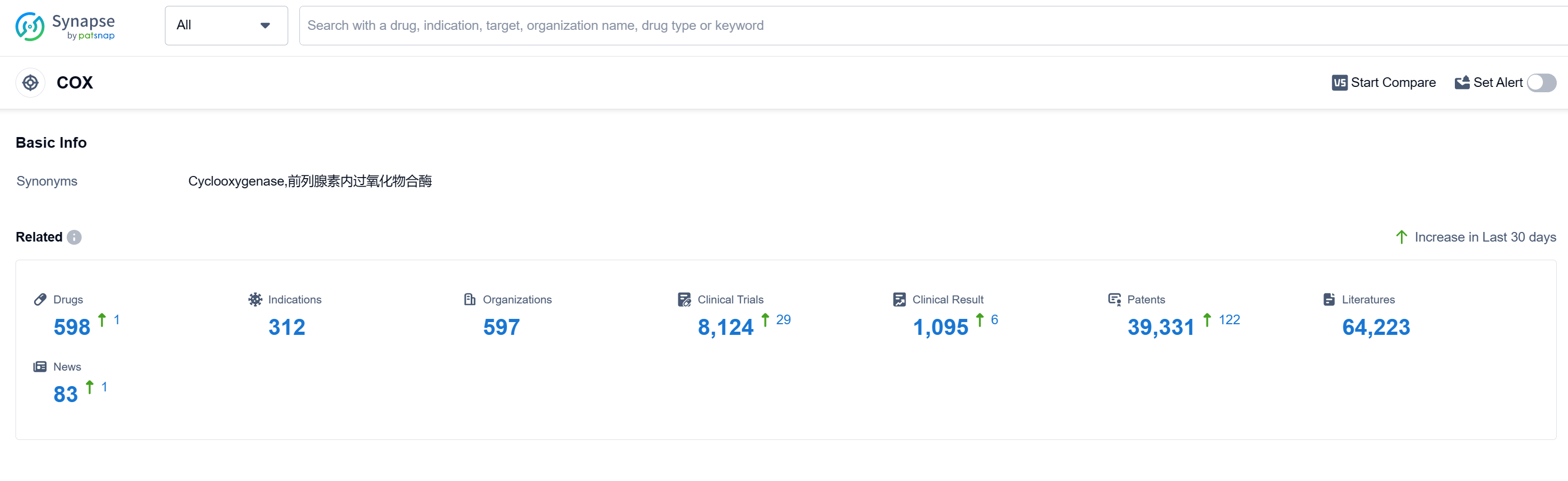
According to Patsnap Synapse, as of 15 Sep 2023, there are a total of 598 COX drugs worldwide, from 597 organizations, covering 312 indications, and conducting 8124 clinical trials.
The analysis of the target COX reveals a competitive landscape with multiple companies actively involved in the development of COX inhibitors. GSK Plc, Viatris Inc., and Pfizer Inc. are the companies growing the fastest, with significant drug counts in various phases of development. Pain is the most common indication for approved drugs, followed by indications such as common cold, rheumatoid arthritis, and osteoarthritis. Small molecule drugs dominate the drug types progressing rapidly, indicating intense competition and potential for biosimilars. China is the country developing the fastest under the target COX, with a high number of drugs in the approved phase. This analysis highlights the current competitive landscape and future development potential of target COX in the pharmaceutical industry.
👇Please click on the picture link below for free registration or log in directly if you have a freemium account, you can browse the latest research progress on drugs, indications, organizations, clinical trials, clinical results, and drug patents related to this target
Conclusion
In summary, diflunisal is a small molecule drug that targets COX and is used in the treatment of immune system diseases, nervous system diseases, and skin and musculoskeletal diseases. It is indicated for osteoarthritis, pain, and rheumatoid arthritis. Developed by Merck & Co., Inc., diflunisal has obtained regulatory approval in multiple countries, including the United States. Its orphan drug status signifies its potential to address rare diseases or conditions. Overall, diflunisal represents a valuable option in the pharmaceutical industry for managing inflammation and pain associated with various medical conditions.