A Comprehensive Review of erythromycin stearate's R&D Innovations and Drug Target Mechanism
Erythromycin stearate's R&D Progress
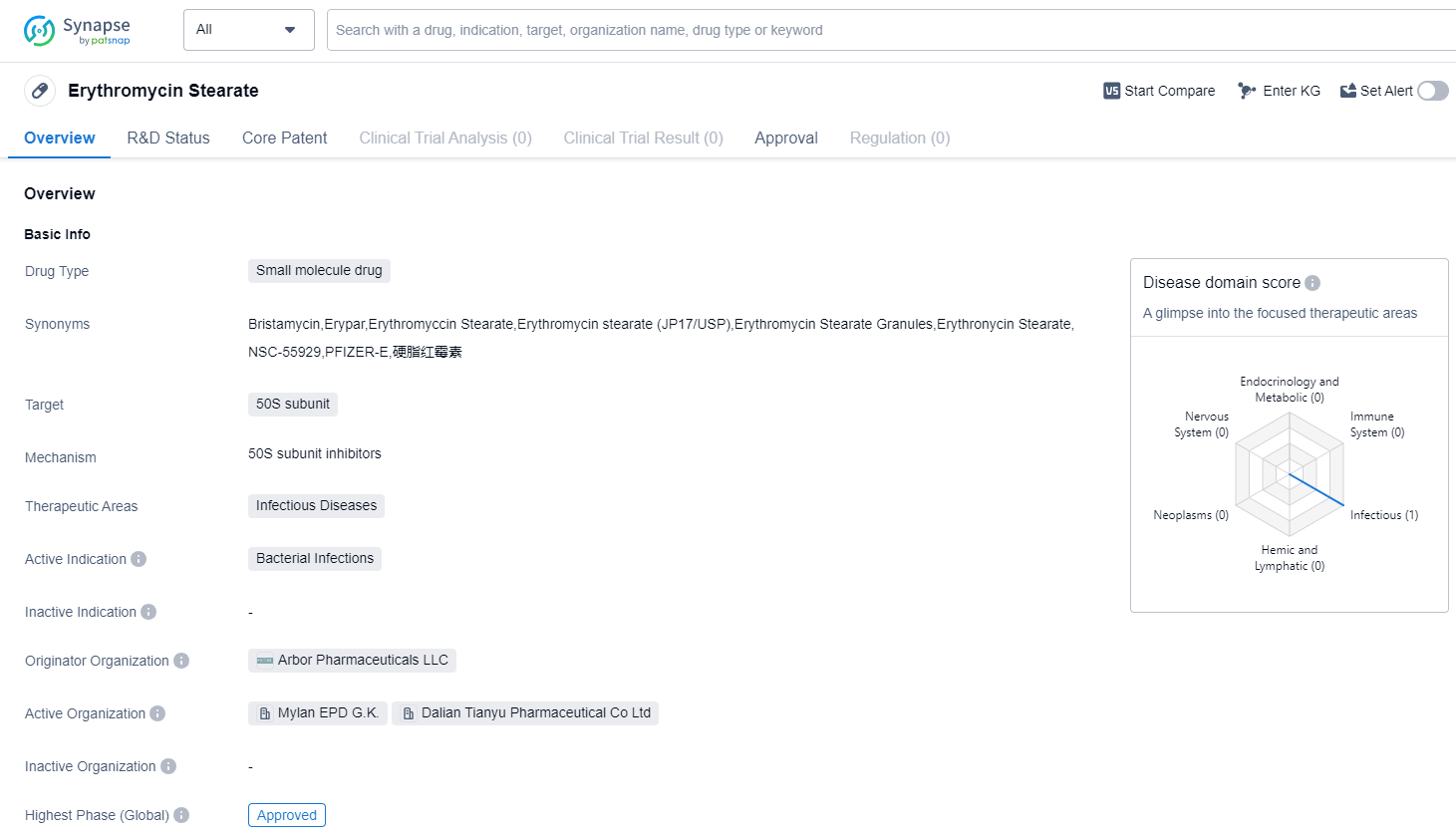
Erythromycin Stearate is a small molecule drug that belongs to the therapeutic area of infectious diseases. It specifically targets the 50S subunit, making it effective against bacterial infections. The drug has reached the highest phase of development which is approved globally.
The originator organization of Erythromycin Stearate is Arbor Pharmaceuticals LLC. This pharmaceutical company played a crucial role in the development and commercialization of the drug. With its expertise and resources, Arbor Pharmaceuticals LLC successfully brought Erythromycin Stearate to market.
Erythromycin Stearate received its first approval in Japan in September 1955. This approval marked the drug's entry into the global market. Since then, it has gained approval in various countries worldwide, highlighting its widespread recognition and acceptance.
As a small molecule drug, Erythromycin Stearate offers several advantages. Its small size allows for easy absorption and distribution within the body, enhancing its therapeutic effects. Additionally, small molecule drugs often have well-established manufacturing processes, making them more cost-effective to produce.
The primary therapeutic application of Erythromycin Stearate is in the treatment of bacterial infections. Its mechanism of action, targeting the 50S subunit, disrupts bacterial protein synthesis, ultimately leading to bacterial cell death. This makes Erythromycin Stearate an effective option for a wide range of infectious diseases caused by susceptible bacteria.
👇Please click on the image below to directly access the latest data (R&D Status | Core Patent | Clinical Trial | Approval status in Global countries) of this drug.
Mechanism of Action for erythromycin stearate: 50S subunit inhibitors
From a biomedical perspective, 50S subunit inhibitors are a type of drugs that specifically target the 50S subunit of bacterial ribosomes. Ribosomes are essential cellular structures responsible for protein synthesis. In bacteria, the ribosome is composed of two subunits, the 30S and the 50S subunits. The 50S subunit is larger and contains the peptidyl transferase center, which is responsible for catalyzing the formation of peptide bonds between amino acids during protein synthesis.
By inhibiting the 50S subunit, these inhibitors interfere with the bacterial ribosome's ability to synthesize proteins, ultimately leading to the inhibition of bacterial growth and reproduction. This class of drugs is commonly used as antibiotics to treat bacterial infections. Examples of 50S subunit inhibitors include macrolides (such as erythromycin and azithromycin) and lincosamides (such as clindamycin).
It is important to note that 50S subunit inhibitors specifically target bacterial ribosomes and are not effective against eukaryotic ribosomes found in human cells. This selective targeting makes them valuable in the treatment of bacterial infections while minimizing harm to human cells.
Drug Target R&D Trends for erythromycin stearate
The 50S subunit is a crucial component of the ribosome, which is responsible for protein synthesis in the human body. It plays a vital role in the translation of genetic information from mRNA into functional proteins. The 50S subunit, along with the 30S subunit, forms the complete ribosome structure. It provides the catalytic site for peptide bond formation during protein synthesis. Additionally, the 50S subunit is involved in the binding of tRNA molecules and the translocation of the ribosome along the mRNA strand. Overall, the 50S subunit is essential for the accurate and efficient production of proteins, which are essential for various biological processes in the human body.
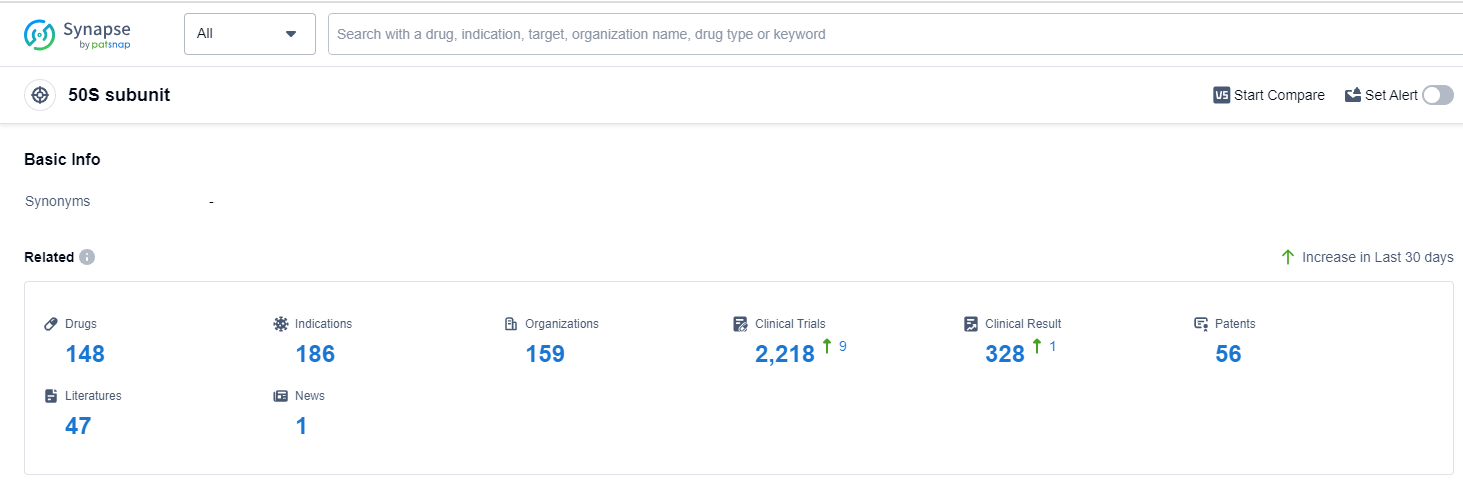
According to Patsnap Synapse, as of 13 Sep 2023, there are a total of 148 50S subunit drugs worldwide, from 159 organizations, covering 186 indications, and conducting 2218 clinical trials.
Overall, the target 50S subunit shows promising development potential in the pharmaceutical industry, with a focus on addressing bacterial infections and other related indications. The competition among companies, the diversity of drug types, and the involvement of various countries/locations indicate a dynamic and evolving landscape for the future development of drugs targeting the 50S subunit.
👇Please click on the picture link below for free registration or log in directly if you have a freemium account, you can browse the latest research progress on drugs, indications, organizations, clinical trials, clinical results, and drug patents related to this target
Conclusion
Overall, Erythromycin Stearate is a well-established drug in the field of biomedicine. The drug's global approval and long history since 1955 in Japan demonstrate its safety and effectiveness.As a small molecule drug, it offers advantages in terms of absorption, distribution, and cost-effectiveness. With its ability to target the 50S subunit, Erythromycin Stearate is a valuable therapeutic option for the treatment of bacterial infections.