A Comprehensive Review of Ganaxolone's R&D Innovations and Drug Target Mechanism
Ganaxolone's R&D Progress
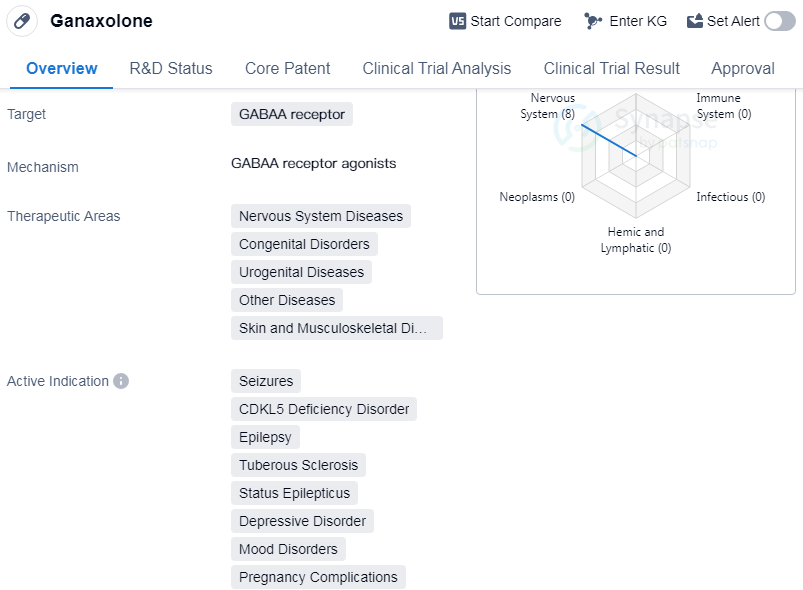
Ganaxoloneis a small molecule drug that targets the GABAA receptor. It is primarily used in the treatment of various nervous system diseases, congenital disorders, urogenital diseases, skin and musculoskeletal diseases, and other diseases. The drug has shown efficacy in treating seizures, CDKL5 deficiency disorder, epilepsy, tuberous sclerosis, status epilepticus, etc.
The originator of Ganaxolone is Purdue Pharma LP. The drug received its first approval in the United States in March 2022. It has reached the highest phase of development, which is approved globally. In China, it is currently in phase 3 of development.
Ganaxolone is regulated under priority review, rare pediatric disease, and orphan drug designations. Priority review status indicates that the drug has the potential to provide significant improvements in the treatment of serious conditions. The rare pediatric disease designation is given to drugs that target diseases affecting fewer than 200,000 individuals in the United States and have the potential to provide substantial benefits to patients. The orphan drug designation is granted to drugs intended to treat rare diseases.
👇Please click on the image below to directly access the latest data (R&D Status | Core Patent | Clinical Trial | Approval status in Global countries) of this drug.
Mechanism of Action for Ganaxolone: GABAA receptor agonists
GABAA receptor agonists are a type of drugs that bind to and activate the GABAA receptors in the brain. GABAA receptors are a type of neurotransmitter receptor that respond to the neurotransmitter gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), which is the main inhibitory neurotransmitter in the central nervous system. When GABAA receptors are activated by agonists, such as certain drugs, they increase the inhibitory effects of GABA, leading to a decrease in neuronal excitability and overall calming and sedative effects.
From a biomedical perspective, GABAA receptor agonists are used to treat various conditions related to excessive neuronal activity or overexcitability in the brain. They can be prescribed for anxiety disorders, insomnia, epilepsy, muscle spasms, etc. By enhancing the inhibitory effects of GABA, these drugs help to restore the balance of neuronal activity and reduce symptoms associated with excessive excitability.
It is important to note that GABAA receptor agonists can have sedative and hypnotic effects, and their use should be carefully monitored by healthcare professionals to avoid potential side effects and interactions with other medications.
Drug Target R&D Trends for Ganaxolone
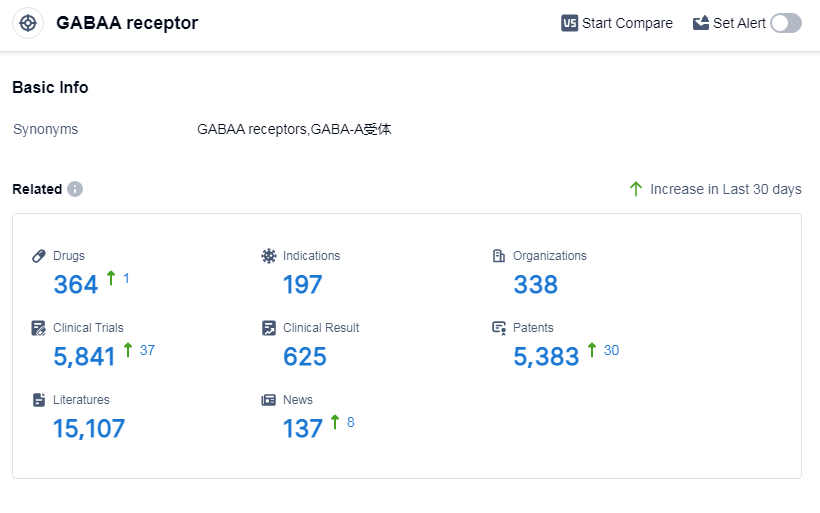
According to Patsnap Synapse, as of 10 Sep 2023, there are a total of 364 GABAA receptor drugs worldwide, from 338 organizations, covering 197 indications, and conducting 5841 clinical trials.
The analysis of the target GABAA receptor reveals a competitive landscape with multiple companies actively involved in research and development. Pfizer Inc., Sumitomo Chemical Co., Ltd., Teva Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd., and Jiangsu Nhwa Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. are among the companies with the highest stage of development on this target. Sleep initiation and maintenance disorders, anesthesia, and anxiety are the most common indications for approved drugs. Small molecule drugs are progressing rapidly, indicating intense competition and innovation. China, the United States, and Japan are the countries/locations with the fastest development under the target GABAA receptor. Overall, the target GABAA receptor shows promising potential for future development in the pharmaceutical industry.
👇Please click on the picture link below for free registration or log in directly if you have a freemium account, you can browse the latest research progress on drugs, indications, organizations, clinical trials, clinical results, and drug patents related to this target
Conclusion
In summary, Ganaxolone is a small molecule drug that targets the GABAA receptor and has been approved for use globally. It has shown efficacy in treating various nervous system diseases, congenital disorders, urogenital diseases, skin and musculoskeletal diseases, and other diseases. The drug has received its first approval in the United States and is currently in phase 3 of development in China. It is regulated under priority review, rare pediatric disease, and orphan drug designations.