Deep Scientific Insights on Erythromycin Ethylsuccinate's R&D Progress, Mechanism of Action, and Drug Target
Erythromycin Ethylsuccinate's R&D Progress
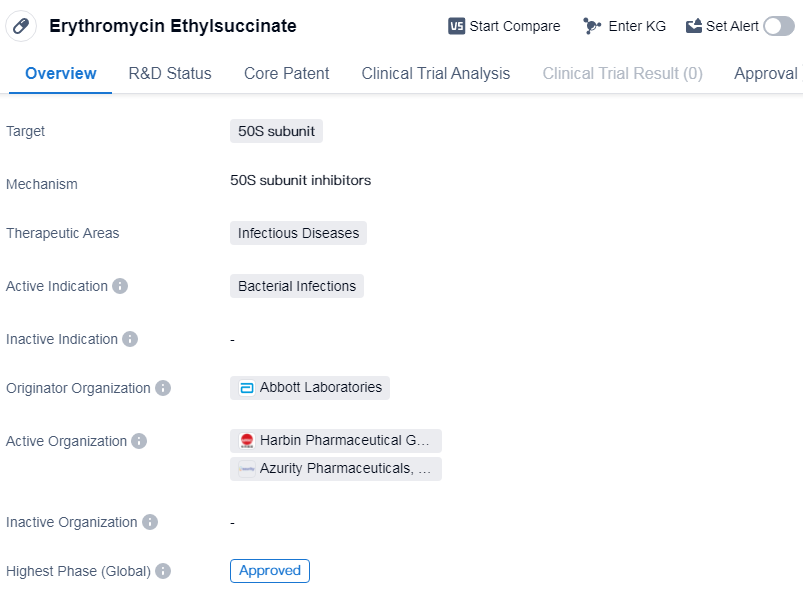
Erythromycin Ethylsuccinate is a small molecule drug that falls under the therapeutic area of infectious diseases. It specifically targets the 50S subunit, making it effective against bacterial infections. The drug was first approved in the United States in April 1965 and has since gained approval in other countries as well.
The originator organization of Erythromycin Ethylsuccinate is Abbott Laboratories, a renowned pharmaceutical company. This drug has reached the highest phase of approval globally, indicating its successful development and evaluation.
Erythromycin Ethylsuccinate is primarily used to treat bacterial infections, making it a valuable asset in the field of biomedicine. Its mechanism of action involves targeting the 50S subunit, which is essential for bacterial protein synthesis. By inhibiting this subunit, the drug effectively prevents the growth and spread of bacteria, ultimately leading to the resolution of infections.
Since its initial approval in 1965, Erythromycin Ethylsuccinate has been widely used in clinical practice. Its efficacy and safety profile have been well-established over the years, contributing to its continued use in the treatment of various bacterial infections.
👇Please click on the image below to directly access the latest data (R&D Status | Core Patent | Clinical Trial | Approval status in Global countries) of this drug.
Mechanism of Action for Erythromycin Ethylsuccinate: 50S subunit inhibitors
From a biomedical perspective, 50S subunit inhibitors refer to a class of drugs that specifically target the 50S subunit of bacterial ribosomes. Ribosomes are essential cellular structures responsible for protein synthesis. Bacterial ribosomes consist of two subunits, the 30S and 50S subunits. The 50S subunit is involved in the binding of transfer RNA (tRNA) and the formation of peptide bonds during protein synthesis.
Inhibitors of the 50S subunit, such as certain antibiotics, work by binding to specific regions of the subunit and interfering with its function. By doing so, they prevent the proper assembly of new proteins in bacterial cells, leading to inhibition of bacterial growth and ultimately bacterial cell death.
These inhibitors are commonly used in the treatment of bacterial infections. They can effectively target a wide range of bacteria, including gram-positive and some gram-negative bacteria. Examples of 50S subunit inhibitors include macrolide antibiotics like erythromycin, azithromycin, and clarithromycin.
It is important to note that 50S subunit inhibitors are specific to bacterial ribosomes and do not have the same effect on human ribosomes. This selective targeting allows these drugs to effectively treat bacterial infections while minimizing harm to human cells.
Drug Target R&D Trends for Erythromycin Ethylsuccinate
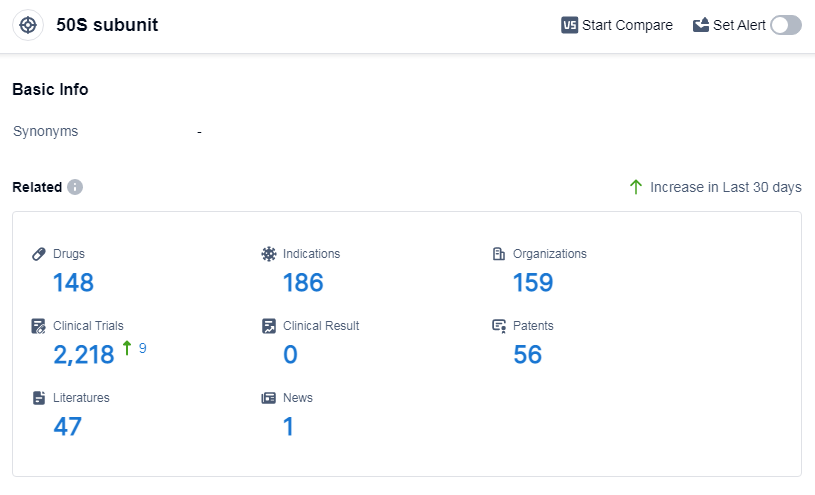
According to Patsnap Synapse, as of 10 Sep 2023, there are a total of 148 50S subunit drugs worldwide, from 159 organizations, covering 186 indications, and conducting 2218 clinical trials.
The analysis of the target 50S subunit reveals a competitive landscape with multiple companies actively involved in research and development. Pfizer Inc. leads in terms of the highest stage of development, with 9 approved drugs. Bacterial infections have the highest number of approved drugs. Small molecule drugs are progressing rapidly, with synthetic peptides also showing potential. China, the United States, and Japan are the leading countries in terms of drug development. The future development of the target 50S subunit is promising, with opportunities for innovation and competition in the pharmaceutical industry.
👇Please click on the picture link below for free registration or log in directly if you have a freemium account, you can browse the latest research progress on drugs, indications, organizations, clinical trials, clinical results, and drug patents related to this target
Conclusion
In conclusion, Erythromycin Ethylsuccinate is a small molecule drug developed by Abbott Laboratories. It targets the 50S subunit and is primarily used to treat bacterial infections. With its highest phase of approval achieved globally, this drug has proven its effectiveness and safety. Since its first approval in 1965, Erythromycin Ethylsuccinate has been widely utilized in clinical practice, making it a valuable asset in the field of biomedicine.