Pharmaceutical Insights: Gabapentin Enacarbil's R&D Progress and its Mechanism of Action on Drug Target
Gabapentin Enacarbil's R&D Progress
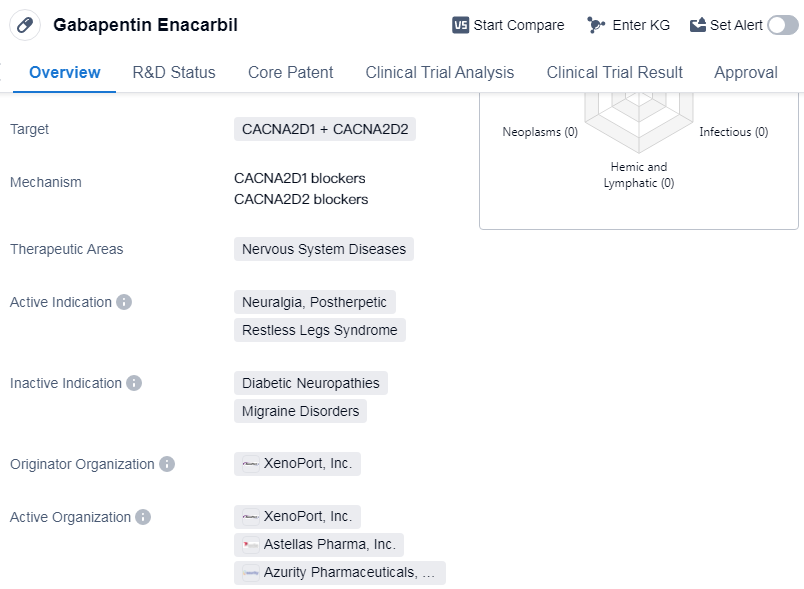
Gabapentin Enacarbil is a small molecule drug that falls under the therapeutic area of nervous system diseases. It targets two proteins including CACNA2D1 and CACNA2D2, which are involved in the regulation of calcium channels in the nervous system.
The drug was developed by XenoPort, Inc., an organization organized an originator specializing in the pharmaceutical industry. The regulatory status of Gabapentin Enacarbil is classified as an orphan drug, indicating that it is intended to provide a valuable therapeutic option for patients suffering from these rare conditions.
Gabapentin Enacarbil has reached the highest phase of development, which is the approved stage. This means that it has successfully undergone rigorous testing and clinical trials to demonstrate its safety and efficacy. The drug has been granted approval for use in the treatment of postherpetic neuralgia (PHN) and restless legs syndrome.
PHN is a condition characterized by severe pain that persists after a shingles infection. Restless legs syndrome is a neurological disorder that causes an uncontrollable urge to move the legs, often accompanied by uncomfortable sensations. Gabapentin Enacarbil has shown effectiveness in alleviating the symptoms associated with these conditions.
Gabapentin Enacarbil received its first approval in the United States in April 2011, this marked a significant milestone in the treatment of PHN and restless legs syndrome.
👇Please click on the image below to directly access the latest data (R&D Status | Core Patent | Clinical Trial | Approval status in Global countries) of this drug.
Mechanism of Action for Gabapentin Enacarbil: CACNA2D1 blockers and CACNA2D2 blockers
CACNA2D1 blockers and CACNA2D2 blockers are terms that refer to drugs or compounds that specifically target and block the activity of the CACNA2D1 and CACNA2D2 proteins, respectively.
From a biomedical perspective, CACNA2D1 and CACNA2D2 are subunits of voltage-gated calcium channels, which are essential for the regulation of calcium influx into cells. These calcium channels play crucial roles in various physiological processes, including neuronal signaling, muscle contraction, and hormone release.
CACNA2D1 blockers are drugs or compounds that inhibit the activity of the CACNA2D1 subunit, leading to a decrease in calcium channel function mediated by this subunit. By blocking CACNA2D1, these blockers can modulate calcium signaling pathways and potentially have therapeutic effects in conditions such as epilepsy, chronic pain, and neurological disorders.
Similarly, CACNA2D2 blockers specifically target and inhibit the CACNA2D2 subunit, resulting in the modulation of calcium channel activity associated with this subunit. The use of CACNA2D2 blockers may have potential applications in the treatment of neurological disorders, psychiatric conditions, and pain management.
It is important to note that the specific mechanisms and clinical applications of CACNA2D1 and CACNA2D2 blockers may vary depending on the specific drug or compound being used. Further research and development are necessary to fully understand the therapeutic potential of these blockers and their implications in biomedicine.
Drug Target R&D Trends for Gabapentin Enacarbil
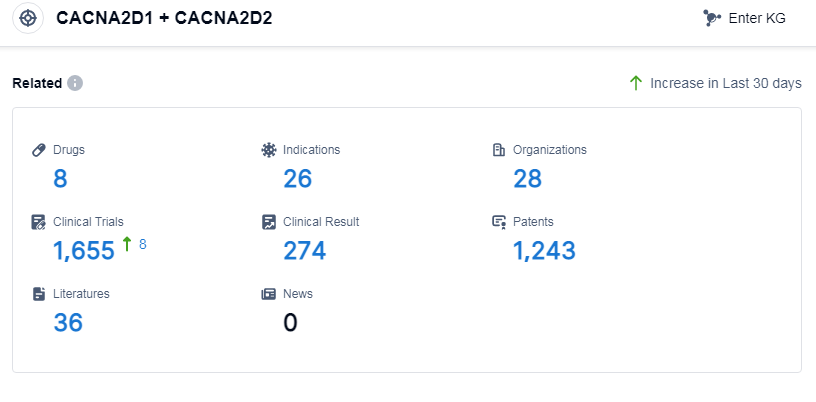
According to Patsnap Synapse, as of 8 Sep 2023, there are a total of 8 CACNA2D1 and CACNA2D2 drugs worldwide, from 28 organizations, covering 26 indications, and conducting 1655 clinical trials.
The analysis of the target CACNA2D1 and CACNA2D2 reveals a competitive landscape with multiple companies involved in its development. Pfizer Inc. stands out with the highest stage of development and multiple approved drugs. The indications for the drugs under this target cover a wide range of neurological and pain-related conditions. Small molecule drugs are progressing rapidly, indicating potential advancements in this area. The countries/locations with the highest development include Japan, United States, and China. The progress in China is noteworthy, although specific details are not provided. Overall, the target CACNA2D1 and CACNA2D2 shows promise in the pharmaceutical industry, with ongoing research and development efforts by various companies and countries.
👇Please click on the picture link below for free registration or log in directly if you have a freemium account, you can browse the latest research progress on drugs, indications, organizations, clinical trials, clinical results, and drug patents related to this target
Conclusion
In conclusion, Gabapentin Enacarbil is a small molecule drug developed by XenoPort, Inc. It has been approved for the treatment of PHN and restless legs syndrome. Its regulatory status as an orphan drug emphasizes its significance in addressing rare conditions. The drug's approval in the United States in 2011 represents a significant advancement in the field of biomedicine and offers new possibilities for patients suffering from these specific neurological disorders.