Acepromazine: Detailed Review of its Transformative R&D Success, Mechanism of Action, and Drug Target
Acepromazine's R&D Progress
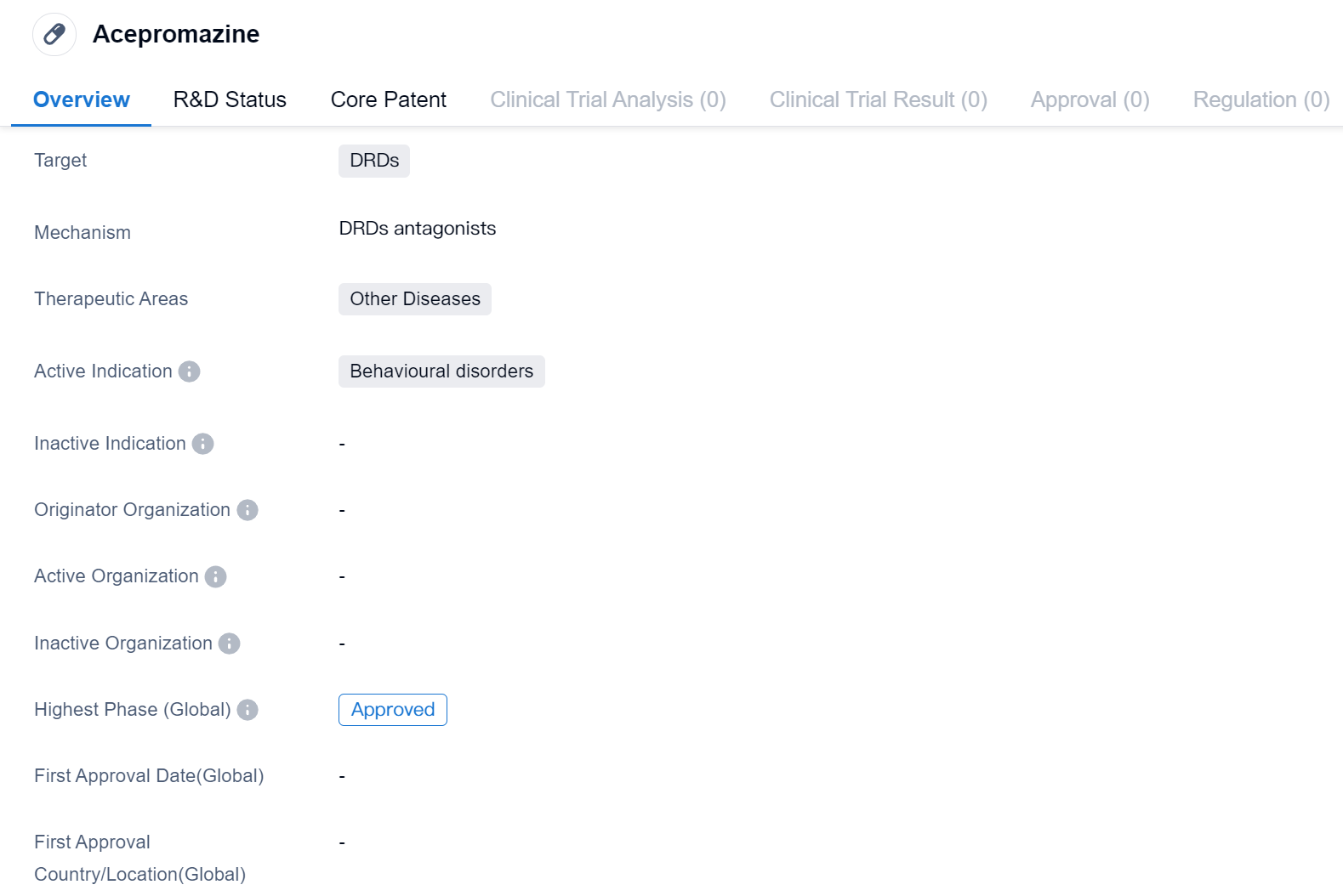
Acepromazine is a small molecule drug that targets dopamine receptors (DRDs) and is primarily used in the treatment of behavioural disorders. It falls under the therapeutic area of other diseases. Currently, Acepromazine has reached the highest phase of development.
As a small molecule drug, Acepromazine is composed of low molecular weight compounds that can easily penetrate cell membranes. This characteristic allows for efficient absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion within the body. Small molecule drugs are typically synthesized chemically and are known for their stability and ease of manufacturing.
Acepromazine specifically targets dopamine receptors (DRDs). Dopamine is a neurotransmitter that plays a crucial role in various physiological processes, including mood regulation, reward-motivated behavior, and movement control. By targeting DRDs, Acepromazine modulates dopamine signaling, which can help alleviate behavioural disorders.
The therapeutic area of Acepromazine is classified as other diseases, indicating that it is primarily used for conditions outside of the commonly recognized disease categories. While the specific behavioural disorders that Acepromazine targets are not mentioned, it can be inferred that the drug is used to manage conditions characterized by abnormal or disruptive behaviours.
Acepromazine has successfully completed all phases of clinical development and has received approval for use. Approval indicates that regulatory authorities have reviewed the data and determined that the benefits of the drug outweigh its potential risks.
👇Please click on the image below to directly access the latest data (R&D Status | Core Patent | Clinical Trial | Approval status in Global countries) of this drug.
Mechanism of Action for Acepromazine: DRDs antagonists
DRDs antagonists refers to dopamine receptor D2 (DRD2) antagonists. Dopamine is a neurotransmitter that plays a crucial role in various physiological processes, including movement, motivation, reward, and mood regulation. DRD2 is a specific type of dopamine receptor found in the brain.
DRD2 antagonists are medications that block the activity of DRD2 receptors. By doing so, they reduce the binding of dopamine to these receptors, leading to a decrease in dopamine signaling in the brain. This can have several effects, depending on the specific condition being treated.
In the field of biomedicine, DRD2 antagonists are primarily used in the treatment of psychiatric disorders such as schizophrenia. Schizophrenia is a chronic mental disorder characterized by symptoms like hallucinations, delusions, disorganized thinking, and abnormal behavior. DRD2 antagonists help alleviate these symptoms by modulating dopamine transmission in the brain.
Additionally, DRD2 antagonists may also be used in the management of other conditions such as bipolar disorder, substance use disorders, and certain movement disorders like tardive dyskinesia. However, it's important to note that the use of DRD2 antagonists should be carefully monitored and prescribed by healthcare professionals due to potential side effects and individual variations in response.
Drug Target R&D Trends for Acepromazine
DRDs, or dopamine receptors, play a crucial role in the human body. These receptors are found in the brain and are responsible for receiving signals from dopamine, a neurotransmitter involved in various physiological processes. DRDs are involved in regulating mood, motivation, reward, and movement. They are also implicated in several neurological disorders, including Parkinson's disease, schizophrenia, and addiction. Understanding the function and regulation of DRDs is essential for developing targeted therapies that can modulate dopamine signaling and potentially treat these disorders.
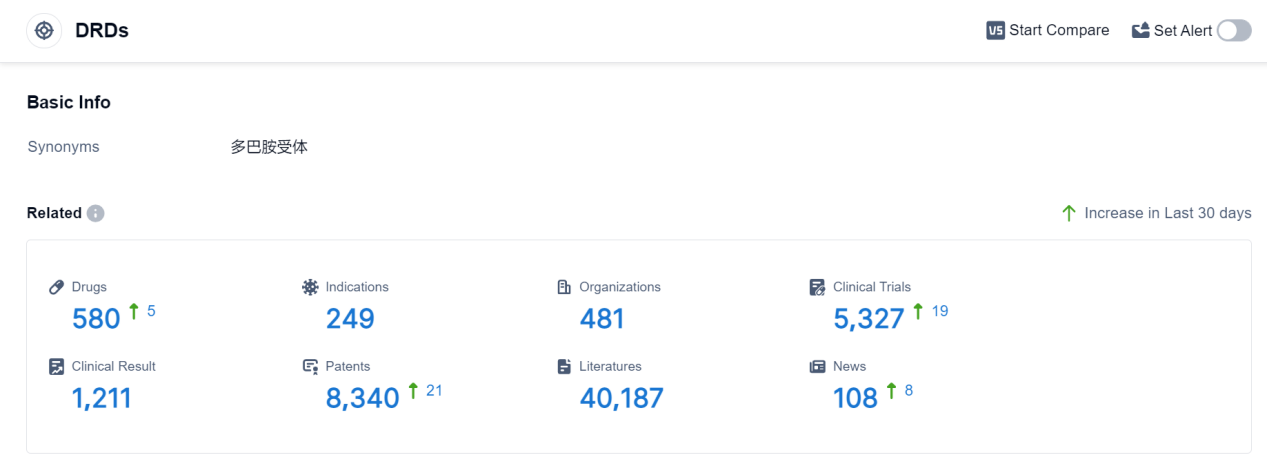
According to Patsnap Synapse, as of 7 Sep 2023, there are a total of 580 DRDs drugs worldwide, from 481 organizations, covering 249 indications, and conducting 5327 clinical trials.
👇Please click on the picture link below for free registration or log in directly if you have a freemium account, you can browse the latest research progress on drugs, indications, organizations, clinical trials, clinical results, and drug patents related to this target
Conclusion
In summary, Acepromazine is a small molecule drug that targets dopamine receptors (DRDs) and is used in the treatment of behavioural disorders. It falls under the therapeutic area of other diseases and has reached the highest phase of development. The drug's approval signifies that it has undergone extensive testing and has been deemed safe and effective for its intended use.