An In-depth Analysis of Glofitamab's R&D Progress and Mechanism of Action on Drug Target
Glofitamab's R&D Progress
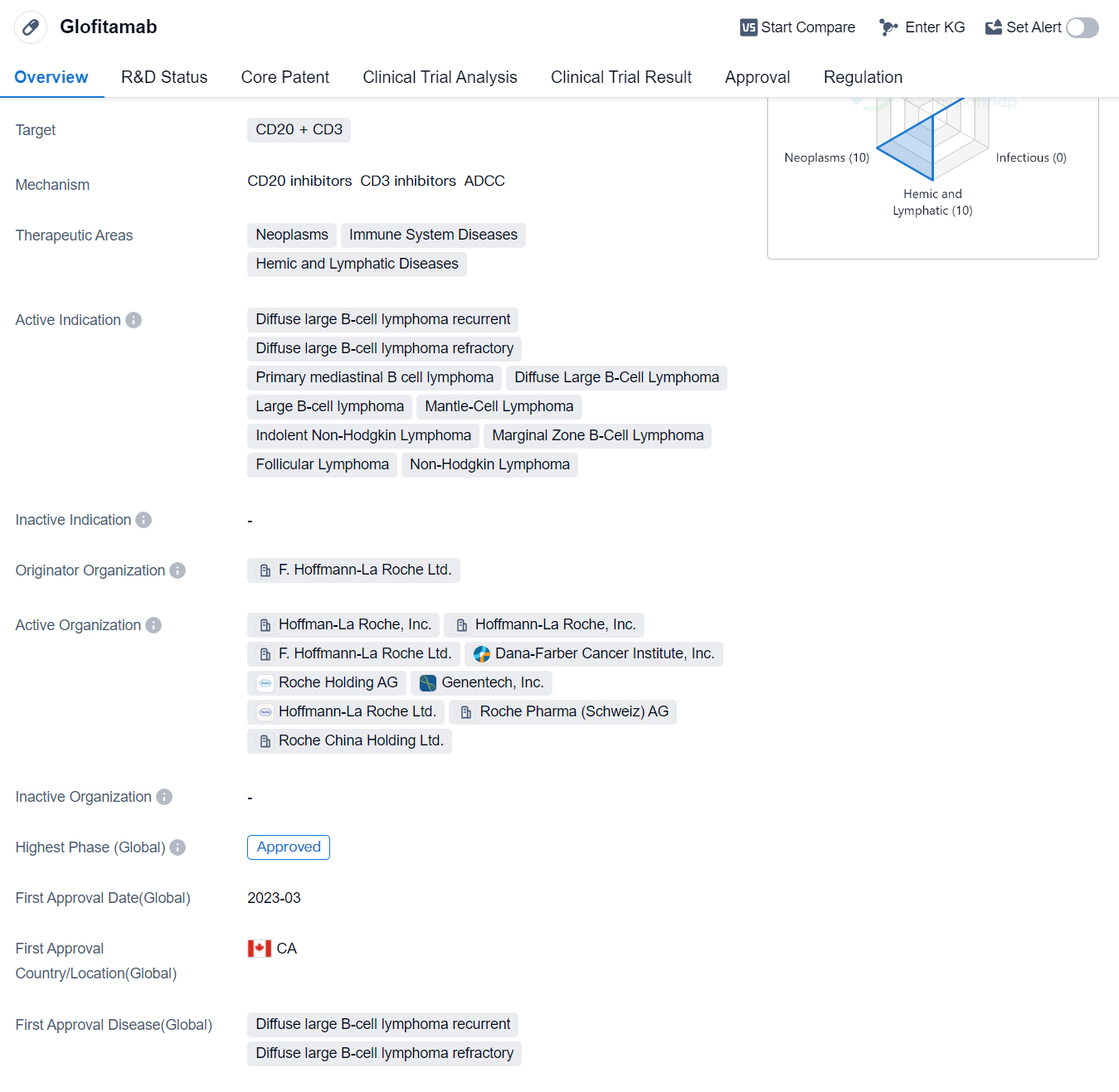
Glofitamab is a bispecific antibody drug that targets CD20 and CD3 proteins. It falls under the therapeutic areas of neoplasms, immune system diseases, and hemic and lymphatic diseases. The drug is indicated for various types of lymphomas, including diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL), primary mediastinal B-cell lymphoma, mantle-cell lymphoma, indolent non-Hodgkin lymphoma, marginal zone B-cell lymphoma, follicular lymphoma, and non-Hodgkin lymphoma.
The originator organization of Glofitamab is F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd., a renowned pharmaceutical company. The drug has reached the highest phase of development which is approved globally. In China, Glofitamab is currently in the NDA/BLA phase, which suggests that it is undergoing the process of seeking regulatory approval in the country.
Glofitamab received its first approval in Canada in March 2023, making it available for use in the Canadian market. The drug has been granted various regulatory designations, including priority review, conditional marketing approval, accelerated approval, breakthrough therapy, and orphan drug status. These designations highlight the potential significance of Glofitamab in addressing unmet medical needs and expediting its availability to patients.
As a bispecific antibody, Glofitamab offers a unique mechanism of action by simultaneously targeting CD20 and CD3 proteins. CD20 is expressed on the surface of B-cells, while CD3 is found on T-cells. By binding to both proteins, Glofitamab facilitates the engagement of T-cells with cancerous B-cells, leading to their destruction. This approach holds promise for the treatment of various lymphomas, particularly DLBCL, which is known for its aggressive nature and resistance to standard therapies.
👇Please click on the image below to directly access the latest data (R&D Status | Core Patent | Clinical Trial | Approval status in Global countries) of this drug.
Mechanism of Action for Glofitamab: CD20 inhibitor and CD3 inhibitor ADCC
CD20 inhibitors are a type of medication that specifically target and inhibit the CD20 protein found on the surface of B cells. B cells are a type of white blood cell involved in the immune response. By inhibiting CD20, these inhibitors can effectively suppress the activity of B cells. This is particularly useful in conditions where B cells are overactive or malfunctioning, such as certain autoimmune diseases and B-cell lymphomas.
CD3 inhibitors, on the other hand, target the CD3 protein found on the surface of T cells. T cells are another type of white blood cell that play a crucial role in coordinating the immune response. By inhibiting CD3, these inhibitors can modulate the activity of T cells. This can be beneficial in conditions where T cells are hyperactive, such as certain autoimmune diseases and organ transplant rejection.
ADCC stands for Antibody-Dependent Cell-Mediated Cytotoxicity. It is a mechanism by which certain immune cells, such as natural killer (NK) cells, recognize and destroy target cells that have been marked by antibodies. The antibodies bind to specific antigens on the target cells, and the NK cells recognize these antibodies and subsequently release toxic substances to kill the target cells. ADCC plays a crucial role in the immune response against infected or cancerous cells.
In summary, CD20 inhibitors and CD3 inhibitors are types of medications that target specific proteins on B cells and T cells, respectively, to modulate their activity. ADCC is a mechanism by which immune cells can recognize and destroy target cells that have been marked by antibodies.
Drug Target R&D Trends for Glofitamab
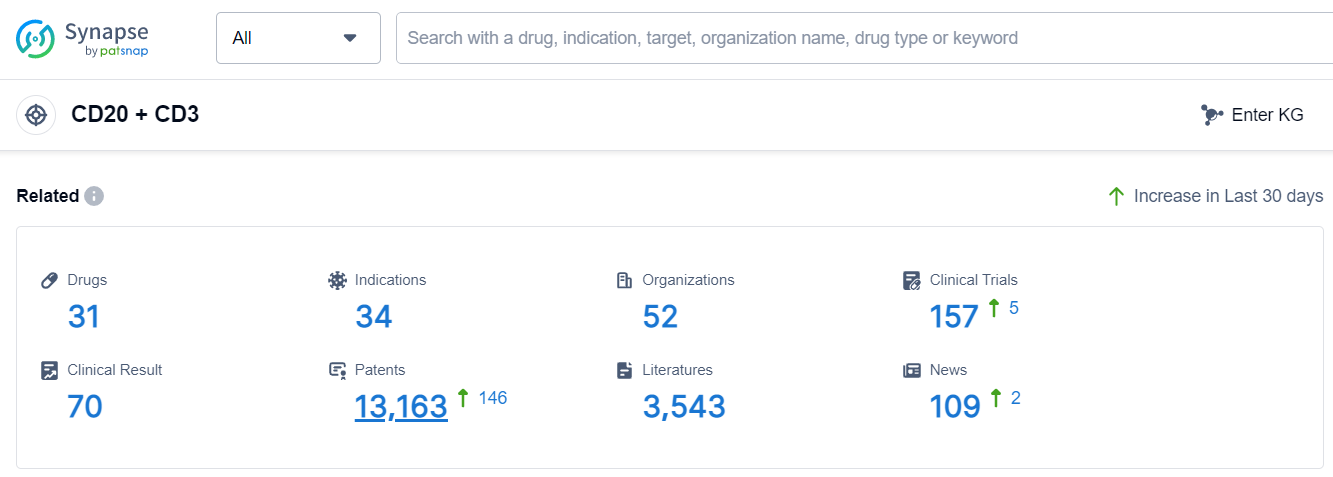
The current competitive landscape of target CD20 + CD3 is characterized by the presence of multiple companies actively involved in research and development. Roche Holding AG and Genmab A/S are the leading companies in terms of R&D progress, with drugs in various stages of development. The indications for drugs under this target include various types of lymphomas, leukemia, and other hematologic neoplasms. Bispecific antibodies and monoclonal antibodies are the most rapidly progressing drug types, indicating intense competition. The development of biosimilars by different research and development institutions further adds to the competitive landscape. The United States, European Union, and other countries/locations mentioned are actively developing drugs under this target, with China also making progress. Overall, the future development of target CD20 + CD3 holds promise in the field of oncology and hematologic diseases.
According to Patsnap Synapse, as of 6 Sep 2023, there are a total of 31 CD20 + CD3 drugs worldwide, from 52 organizations, covering 34 indications, and conducting 157 clinical trials.
Please click on the picture link below for free registration or log in directly if you have a freemium account, you can browse the latest research progress on drugs, indications, organizations, clinical trials, clinical results, and drug patents related to this target
Conclusion
In summary, Glofitamab is a bispecific antibody drug developed by F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd. It targets CD20 and CD3 proteins and has received approval for the treatment of several types of lymphomas. The drug has reached the highest phase of approval globally and is currently undergoing regulatory processes in China. Glofitamab's unique mechanism of action and its regulatory designations highlight its potential as a therapeutic option for patients with lymphomas, particularly those with DLBCL.