Faricimab Unveiled: A Detailed Overview of its Revolutionary R&D Breakthroughs
Faricimab's R&D Progress
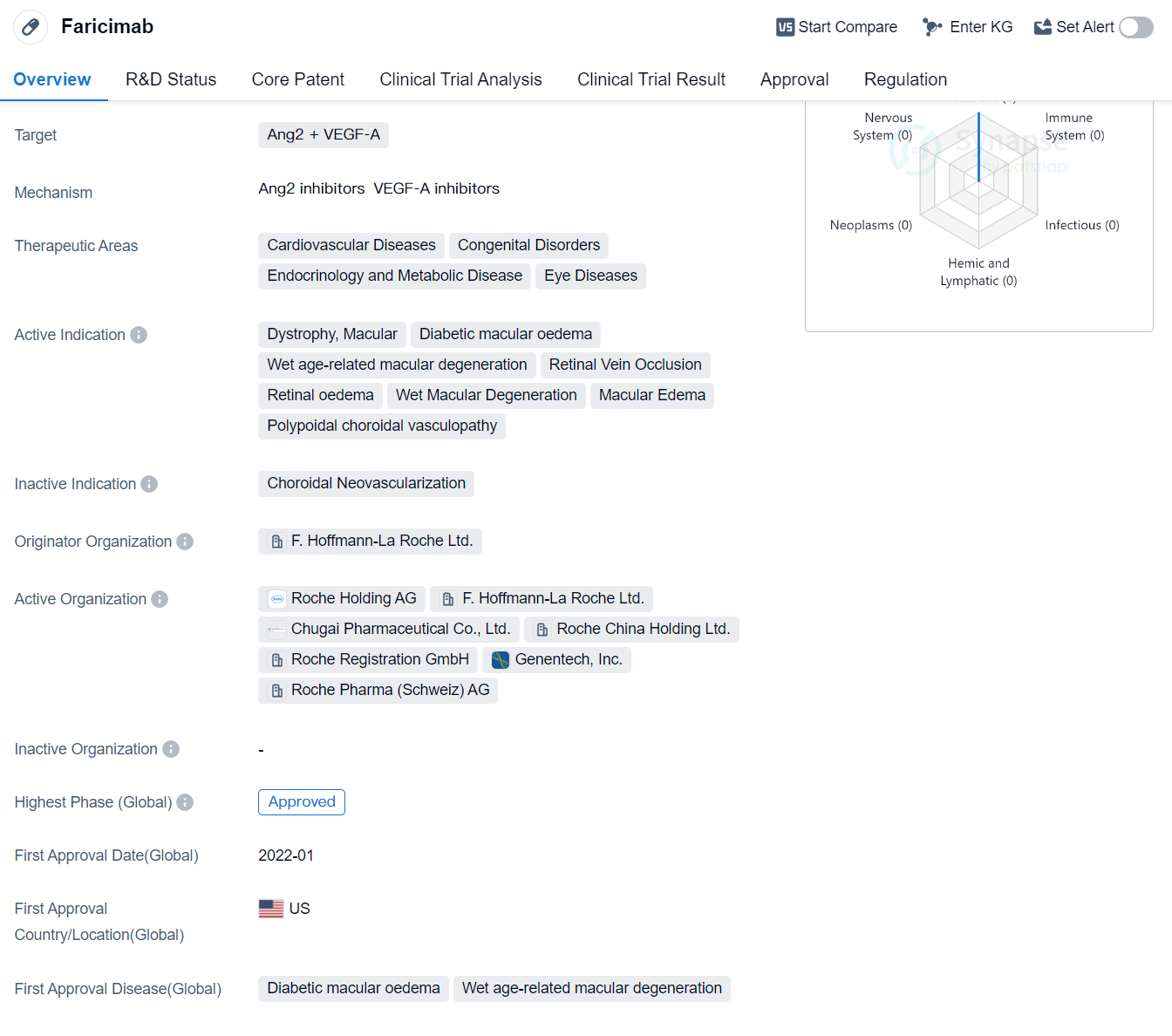
Faricimab is a bispecific antibody drug that targets Ang2 and VEGF-A. It falls under the therapeutic areas of cardiovascular diseases, congenital disorders, endocrinology and metabolic disease, and eye diseases. The drug is indicated for various conditions including dystrophy, macular, diabetic macular edema, wet age-related macular degeneration, retinal vein occlusion, retinal edema, wet macular degeneration, macular edema, and polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy.
The originator organization of Faricimab is F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd. The highest R&D phase of this drug is approved. The drug received its first approval in the United States in January 2022, making it available for use in patients in that country.
Faricimab has undergone priority review, which suggests that it addresses an unmet medical need or offers significant advantages over existing treatments. This regulatory designation expedites the review process, allowing the drug to reach patients more quickly.
As a bispecific antibody, Faricimab has the potential to simultaneously target two different molecules involved in disease processes, Ang2 and VEGF-A. Ang2 is associated with abnormal blood vessel growth and inflammation, while VEGF-A plays a crucial role in promoting the growth of new blood vessels. By targeting both of these molecules, Faricimab may offer a more comprehensive and effective treatment approach for the indicated conditions.
👇Please click on the image below to directly access the latest data (R&D Status | Core Patent | Clinical Trial | Approval status in Global countries) of this drug.
Mechanism of Action for Faricimab: Ang2 inhibitor and VEGF-A inhibitor
Ang2 inhibitors and VEGF-A inhibitors are both types of drugs used in biomedicine.
Ang2 inhibitors are medications that specifically target and inhibit the activity of angiopoietin-2 (Ang2), a protein involved in blood vessel formation and remodeling. Ang2 plays a role in promoting inflammation and vascular leakage, which are associated with various diseases such as cancer, diabetic retinopathy, and age-related macular degeneration. By inhibiting Ang2, these drugs aim to reduce inflammation and prevent abnormal blood vessel growth, thereby potentially improving the outcomes of these diseases.
VEGF-A inhibitors, on the other hand, target vascular endothelial growth factor A (VEGF-A), a protein that stimulates the growth of new blood vessels. In certain diseases like cancer, diabetic retinopathy, and wet age-related macular degeneration, excessive VEGF-A production can lead to the formation of abnormal and leaky blood vessels. VEGF-A inhibitors work by blocking the action of VEGF-A, thereby inhibiting the growth of these abnormal blood vessels and reducing vascular leakage.
Both Ang2 inhibitors and VEGF-A inhibitors are used as therapeutic approaches to manage diseases involving abnormal blood vessel growth and inflammation. They are often administered through injections or infusions and may be used alone or in combination with other treatments, such as chemotherapy or laser therapy, depending on the specific disease being treated. These drugs have shown promising results in clinical trials and have been approved for use in certain conditions.
Drug Target R&D Trends for Faricimab
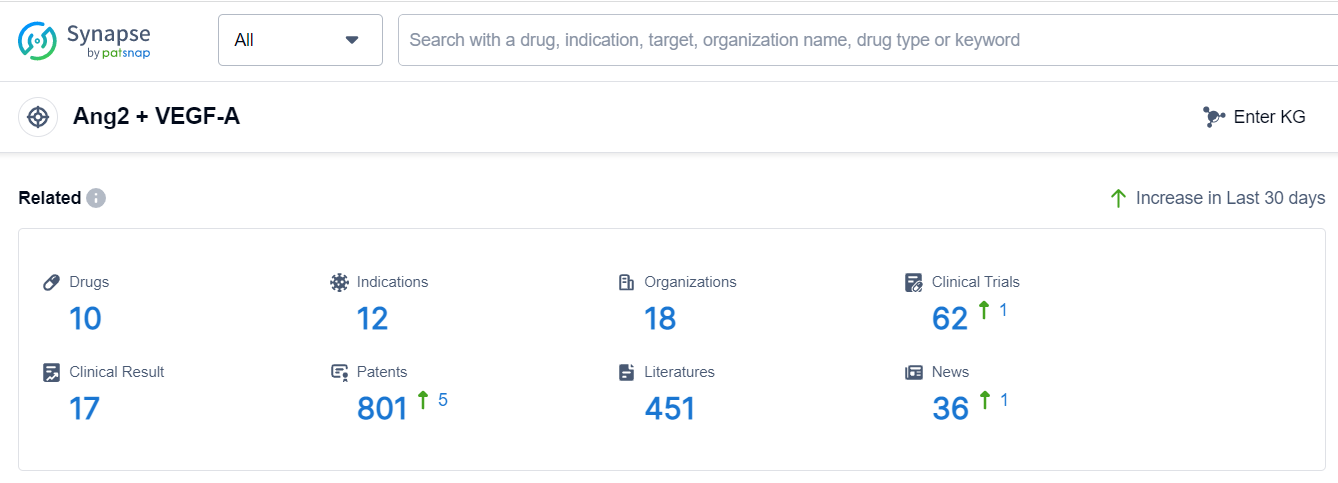
Based on the analysis of the provided data, the target Ang2 + VEGF-A has attracted the attention of several companies in the pharmaceutical industry. Roche Holding AG is the company with the highest phase of development, followed by Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc., Bayer AG, and other companies. The indications for drugs under this target range from ophthalmic conditions to cancer, indicating a wide range of potential applications. Bispecific antibodies are the most prominent drug type, suggesting intense competition. The development of drugs targeting Ang2 + VEGF-A is a global effort, with companies and institutions from various countries/locations involved in the R&D process. Overall, the target Ang2 + VEGF-A shows a competitive landscape and promising future development in the pharmaceutical industry.
According to Patsnap Synapse, as of 5 Sep 2023, there are a total of 10 Ang2 + VEGF-A drugs worldwide, from 18 organizations, covering 12 indications, and conducting 62 clinical trials.
Please click on the picture link below for free registration or log in directly if you have a freemium account, you can browse the latest research progress on drugs, indications, organizations, clinical trials, clinical results, and drug patents related to this target
Conclusion
The approval of Faricimab represents a significant advancement in the field of biomedicine, particularly in the treatment of eye diseases. Its approval in the United States and ongoing regulatory processes in China indicate the potential for global availability and impact. Further research and real-world evidence will be crucial in assessing the long-term safety and efficacy of Faricimab in diverse patient populations.