An In-depth Analysis of itopride hydrochloride's R&D Progress and Mechanism of Action on Drug Target
itopride hydrochloride's R&D Progress
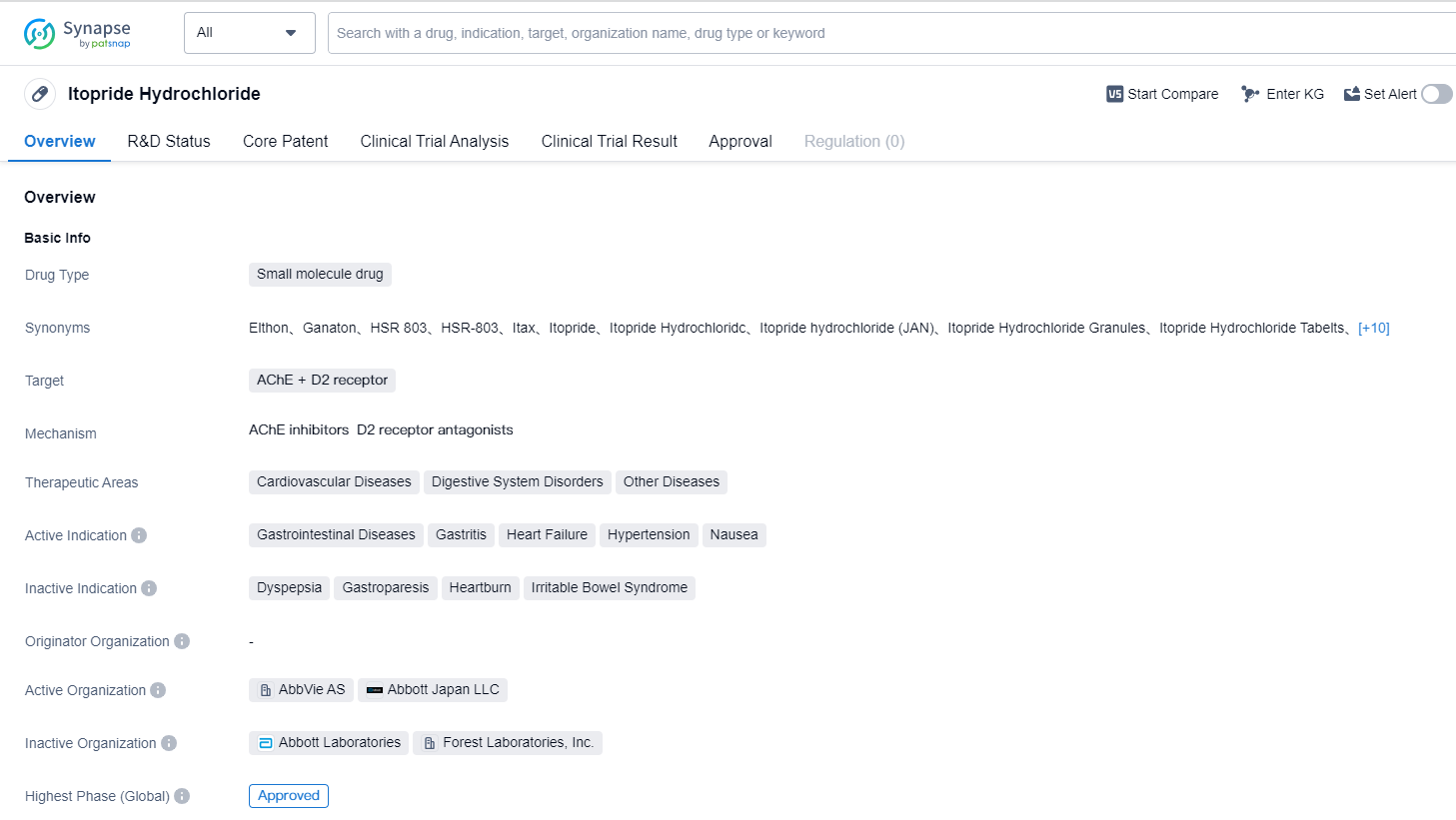
Itopride Hydrochloride is a small molecule drug that targets both the AChE (acetylcholinesterase) enzyme and the D2 receptor. It is primarily used in the treatment of various cardiovascular diseases, digestive system disorders, and other diseases. The drug has been approved for use in several therapeutic areas, including gastrointestinal diseases, gastritis, heart failure, hypertension, and nausea.
The highest phase of development for Itopride Hydrochloride is approved, indicating that it has successfully completed clinical trials and has been deemed safe and effective for use in patients. The highest R&D phase of this drug is approved.
Itopride Hydrochloride received its first approval in Japan in February 1996. This indicates that it has a long history of use and has been available to patients for over two decades. The drug's first approval country/location being Japan suggests that it may have been initially developed and tested in this region before expanding to other markets.
The drug's dual targeting of AChE and the D2 receptor suggests that it may have a multifaceted mechanism of action. AChE inhibitors are commonly used in the treatment of Alzheimer's disease and other neurological disorders, as they help increase the levels of acetylcholine in the brain. The D2 receptor is primarily associated with dopamine signaling and is targeted in the treatment of conditions such as Parkinson's disease and schizophrenia. Itopride Hydrochloride's targeting of both these pathways may indicate its potential to address a range of diseases and symptoms.
👇Please click on the image below to directly access the latest data (R&D Status | Core Patent | Clinical Trial | Approval status in Global countries) of this drug.
Mechanism of Action for itopride hydrochloride: AChE inhibitors D2 receptor antagonists
AChE inhibitors are a type of medication that inhibit the activity of the enzyme acetylcholinesterase (AChE). Acetylcholinesterase is responsible for breaking down the neurotransmitter acetylcholine in the brain. By inhibiting this enzyme, AChE inhibitors increase the levels of acetylcholine in the brain, which can be beneficial in certain conditions such as Alzheimer's disease. This increase in acetylcholine can help improve cognitive function and memory.
D2 receptor antagonists, on the other hand, are a class of drugs that block the activity of dopamine D2 receptors in the brain. Dopamine is a neurotransmitter involved in various functions including movement, motivation, and pleasure. By antagonizing the D2 receptors, these drugs reduce the effects of dopamine in the brain. D2 receptor antagonists are commonly used in the treatment of psychiatric disorders such as schizophrenia, where excessive dopamine activity is believed to contribute to the symptoms of the condition.
In summary, AChE inhibitors inhibit the activity of the enzyme acetylcholinesterase, while D2 receptor antagonists block the activity of dopamine D2 receptors.
Drug Target R&D Trends for itopride hydrochloride
The acetylcholinesterase (AChE) enzyme and the D2 receptor play crucial roles in the human body. AChE is responsible for breaking down the neurotransmitter acetylcholine, which is involved in various functions such as muscle movement, cognition, and memory. Dysfunction of AChE can lead to conditions like Alzheimer's disease. On the other hand, the D2 receptor is a type of dopamine receptor found in the brain. It plays a role in regulating dopamine levels, which are important for mood, motivation, and movement. Dysregulation of D2 receptors has been implicated in psychiatric disorders like schizophrenia and addiction. Understanding the functions of AChE and D2 receptors is vital for developing treatments targeting these pathways.
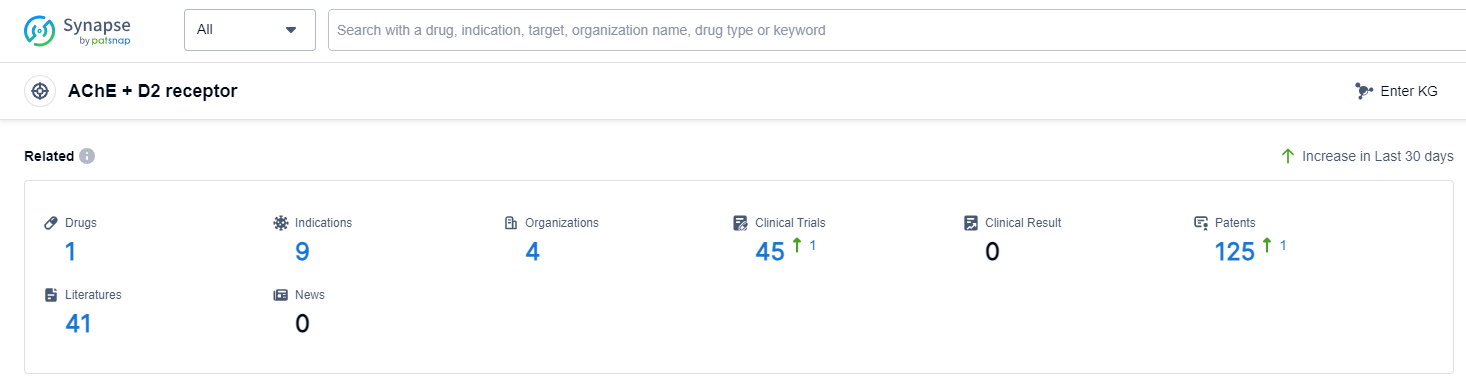
According to Patsnap Synapse, as of 7 Sep 2023, there are a total of 1 AChE + D2 receptor drugs worldwide, from 4 organizations, covering 9 indications, and conducting 45 clinical trials.
The analysis of the target AChE + D2 receptor reveals a competitive landscape with companies such as Abbott Laboratories and AbbVie, Inc. leading in terms of R&D progress. The approved drugs for indications such as nausea, heart failure, gastrointestinal diseases, hypertension, gastritis, and gastroparesis highlight the therapeutic potential of targeting this receptor. The dominance of small molecule drugs in the highest development phase suggests their effectiveness and potential as therapeutic agents. Furthermore, countries/locations such as Japan, Thailand, China, India, Philippines, European Union, Czechia, and Malaysia are actively developing drugs for the target AChE + D2 receptor, with China showing significant progress. Overall, the current competitive landscape indicates a promising future for the development of drugs targeting the AChE + D2 receptor.
👇Please click on the picture link below for free registration or log in directly if you have a freemium account, you can browse the latest research progress on drugs, indications, organizations, clinical trials, clinical results, and drug patents related to this target
Conclusion
In summary, Itopride Hydrochloride is a small molecule drug that targets AChE and the D2 receptor. It has been approved for use in various therapeutic areas, including cardiovascular diseases, digestive system disorders, and other diseases. The drug was first approved in Japan in 1996 and has since gained approval in worldwide. Its dual targeting mechanism suggests potential versatility in addressing different conditions.