An In-depth Analysis of methsuximide's R&D Progress and Mechanism of Action on Drug Target
Methsuximide's R&D Progress
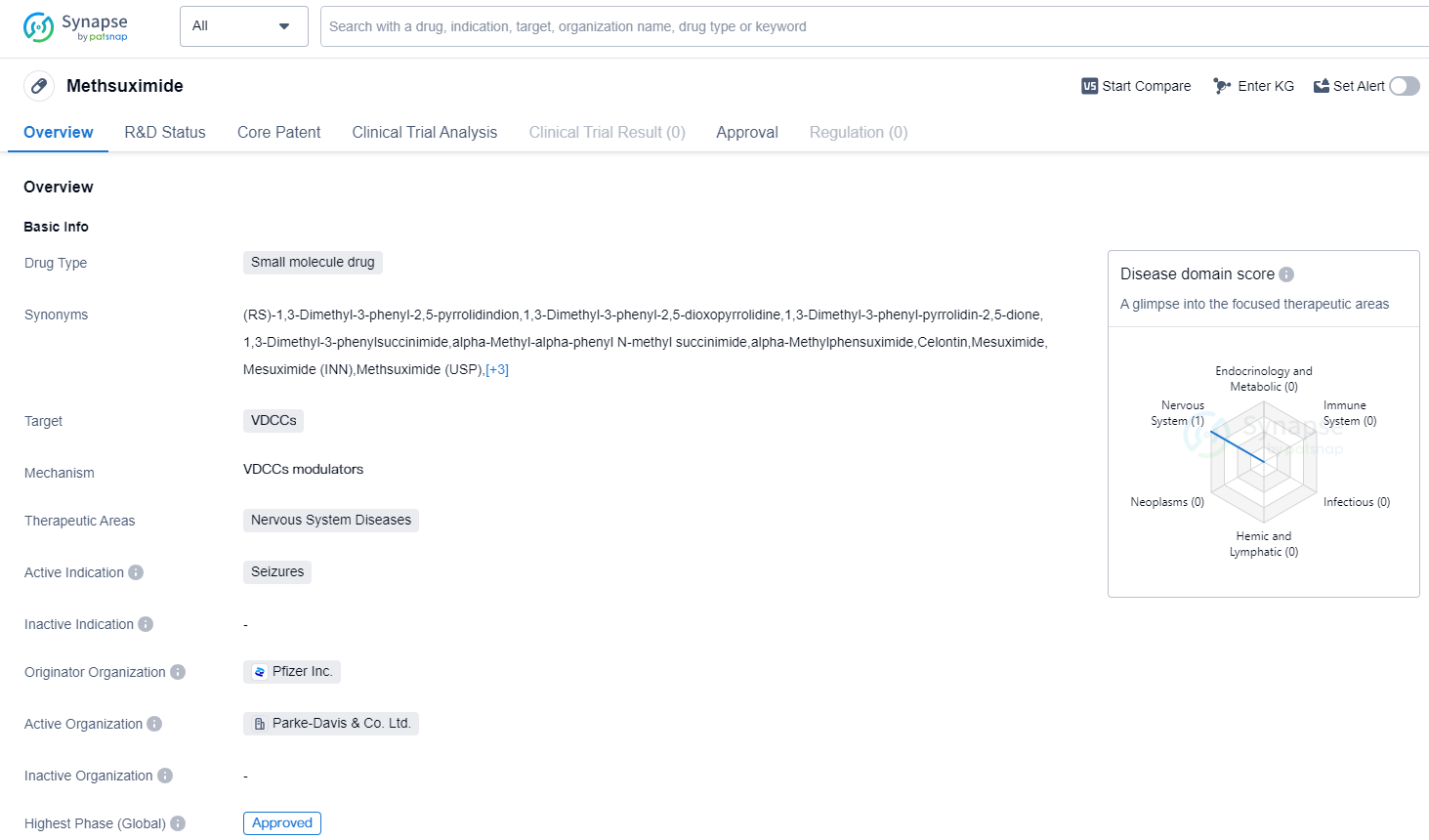
Methsuximide is a small molecule drug that falls under the therapeutic area of Nervous System Diseases. It is primarily used for the treatment of seizures. The drug targets VDCCs (Voltage-Dependent Calcium Channels) in order to achieve its therapeutic effects.
Methsuximide was first approved in the United States in February 1957, making it one of the older drugs in the pharmaceutical market. The drug was developed by Pfizer Inc., a renowned pharmaceutical company with a strong presence in the industry.
Being a small molecule drug, Methsuximide is characterized by its relatively low molecular weight and ability to penetrate cell membranes. This allows it to interact with its target, VDCCs, and modulate their activity. By doing so, Methsuximide aims to reduce the occurrence and severity of seizures in patients.
The fact that Methsuximide The highest R&D phase of this drug is approved. This milestone is a significant achievement for any drug, as it signifies that it has met the necessary regulatory requirements to be marketed and prescribed to patients.
Since its first approval in 1957, Methsuximide has likely undergone further studies and evaluations to ensure its continued safety and effectiveness. However, the provided information does not specify any subsequent approvals or updates regarding the drug.
👇Please click on the image below to directly access the latest data (R&D Status | Core Patent | Clinical Trial | Approval status in Global countries) of this drug.
Mechanism of Action for methsuximide: VDCCs modulators
VDCCs modulators refer to compounds or substances that can modulate or regulate the activity of voltage-dependent calcium channels (VDCCs). Voltage-dependent calcium channels are ion channels that allow the passage of calcium ions across cell membranes in response to changes in membrane potential. These channels play a crucial role in various physiological processes, including muscle contraction, neurotransmitter release, hormone secretion, and gene expression.
VDCCs modulators can either enhance or inhibit the activity of these calcium channels. Enhancers, also known as agonists, increase the opening of VDCCs, leading to an influx of calcium ions into the cell. This can have various effects depending on the specific cell type and context. For example, in cardiac muscle cells, VDCC enhancers can promote stronger and more coordinated contractions. In neurons, they can enhance neurotransmitter release and facilitate synaptic transmission.
On the other hand, VDCCs modulators can also act as inhibitors or blockers. These compounds reduce the opening or activity of VDCCs, thereby decreasing the influx of calcium ions into the cell. Blockers can have therapeutic applications in conditions where excessive calcium influx is detrimental. For instance, certain types of VDCC blockers are used in the treatment of hypertension, arrhythmias, and neuropathic pain.
Overall, VDCCs modulators are important pharmacological tools that can selectively regulate calcium signaling by targeting voltage-dependent calcium channels. By modulating the activity of these channels, researchers and clinicians can gain insights into cellular processes and develop therapeutic strategies for various diseases and disorders.
Drug Target R&D Trends for methsuximide
Voltage-dependent calcium channels (VDCCs) play a crucial role in various physiological processes within the human body. These channels are responsible for regulating the influx of calcium ions into cells in response to changes in membrane potential. VDCCs are found in excitable cells such as neurons, muscle cells, and endocrine cells, where they control neurotransmitter release, muscle contraction, and hormone secretion. Additionally, VDCCs are involved in modulating gene expression, cell proliferation, and differentiation. Due to their significance in cellular function, VDCCs have become attractive targets for pharmaceutical interventions, with drugs designed to selectively modulate their activity being explored for the treatment of various diseases and disorders.
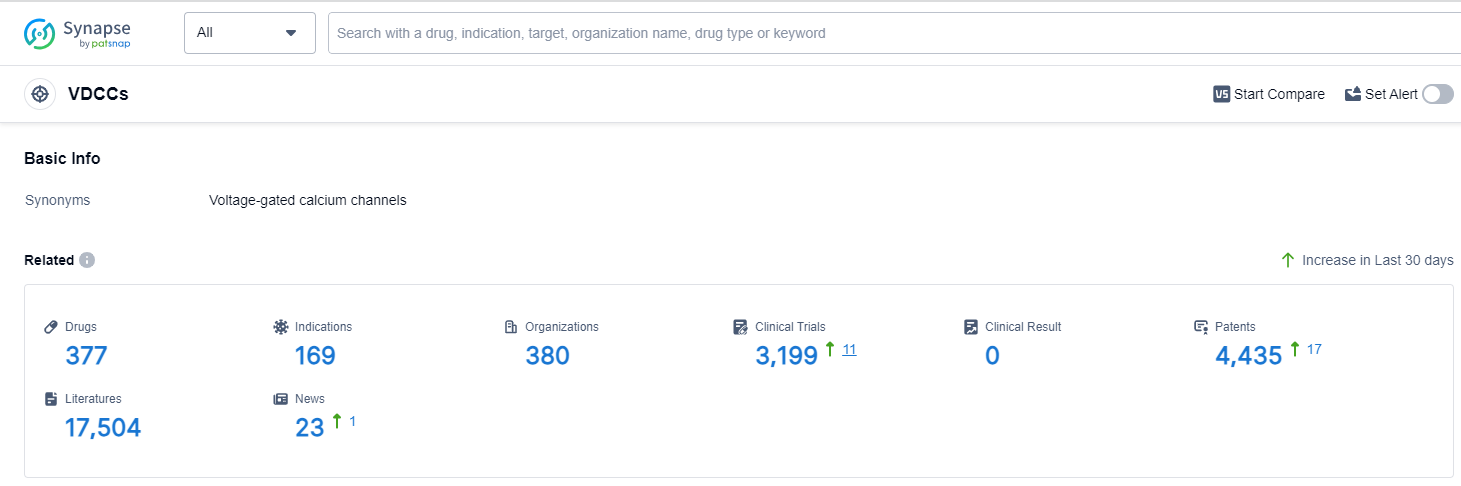
According to Patsnap Synapse, as of 14 Sep 2023, there are a total of 377 VDCCs drugs worldwide, from 380 organizations, covering 169 indications, and conducting 3199 clinical trials.
The analysis of target VDCCs from various perspectives provides valuable insights into the current competitive landscape and future development. Pfizer Inc., Hanmi Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., and Eisai Co., Ltd. are the companies with the highest number of approved drugs, indicating their strong R&D progress. Hypertension, Angina Pectoris, and Essential Hypertension are the most common approved indications, suggesting a focus on cardiovascular diseases. Small molecule drugs dominate the development phase, indicating their significance in VDCC-targeting drug development. China, Japan, and the United States are the leading countries in terms of drug development, with China showing significant progress. Overall, the analysis highlights the potential for further research and development in target VDCCs and provides insights into the competitive landscape and future prospects in this field.
👇Please click on the picture link below for free registration or log in directly if you have a freemium account, you can browse the latest research progress on drugs, indications, organizations, clinical trials, clinical results, and drug patents related to this target
Conclusion
In summary, Methsuximide is a small molecule drug developed by Pfizer Inc. It targets VDCCs and is primarily used for the treatment of seizures. The drug received its first approval in the United States in February 1957 and has reached the highest phase of development, indicating its approval for use in patients.