Analysis on the Research Progress of Calcineurin Inhibitor
CaN, or Calcineurin, plays a crucial role in the human body as a calcium-dependent protein phosphatase. It is involved in various cellular processes, including immune response, neuronal development, and cardiac function. CaN regulates the activation of T-cells, a type of white blood cell, by dephosphorylating key proteins involved in immune signaling pathways. Additionally, it is essential for the development and maintenance of the central nervous system, as well as the proper functioning of the heart. Understanding the role of CaN is vital for the development of pharmaceutical interventions targeting immune disorders, neurological diseases, and cardiovascular conditions.
As an immunosuppressant, CaN inhibitors are divided into exogenous inhibitors and endogenous protein inhibitors. The exogenous inhibitors mainly include cyclosporine, tacrolimus, and others, while the endogenous protein inhibitors mainly include Cain, FKBP 38, and others.
CaN Competitive Landscape
According to the data provided by Patsnap Synapse-Global Drug Intelligence Database: the following figure shows that as of 3 Sep 2023, there are a total of 25 CaN drugs worldwide, from 65 organizations, covering 63 indications, and conducting 2331 clinical trials.
👇Please click on the picture link below for free registration or login directly if you have freemium accounts, you can browse the latest research progress on drugs , indications, organizations, clinical trials, clinical results, and drug patents related to this target.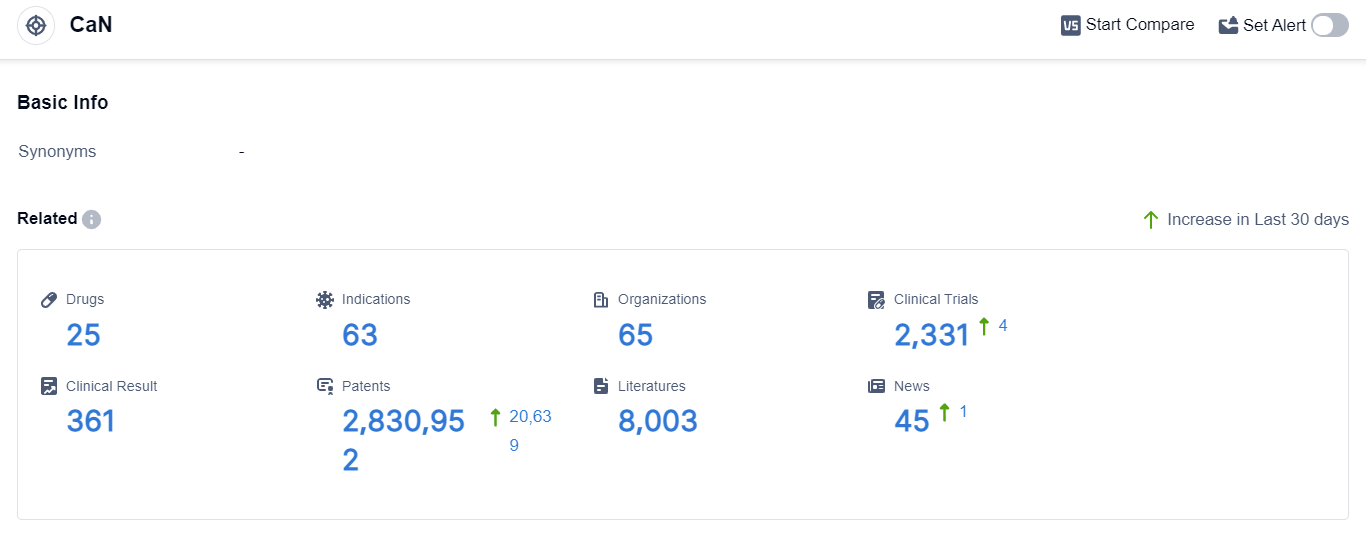
The analysis of the current competitive landscape for the target CaN reveals that Novartis AG, Astellas Pharma, Inc., Aurinia Pharmaceuticals, Inc., Huons Co., Ltd., and Santen Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. are the companies growing fastest in this field. These companies have made significant progress in the development of drugs for the target CaN, with Novartis AG having the highest number of approved drugs.
The indications with the highest number of approved drugs include dermatitis, atopic, graft rejection, xerophthalmia, lupus nephritis, conjunctivitis, allergic, and myasthenia gravis. Small molecule drugs and synthetic peptides are the drug types progressing most rapidly, indicating intense competition around innovative drugs.
The United States, European Union, China, and Japan are the countries/locations developing fastest, with China showing notable progress.
Overall, the target CaN presents a competitive landscape with multiple companies, indications, drug types, and countries/locations involved in its development, indicating a promising future for the treatment of CaN-related conditions.
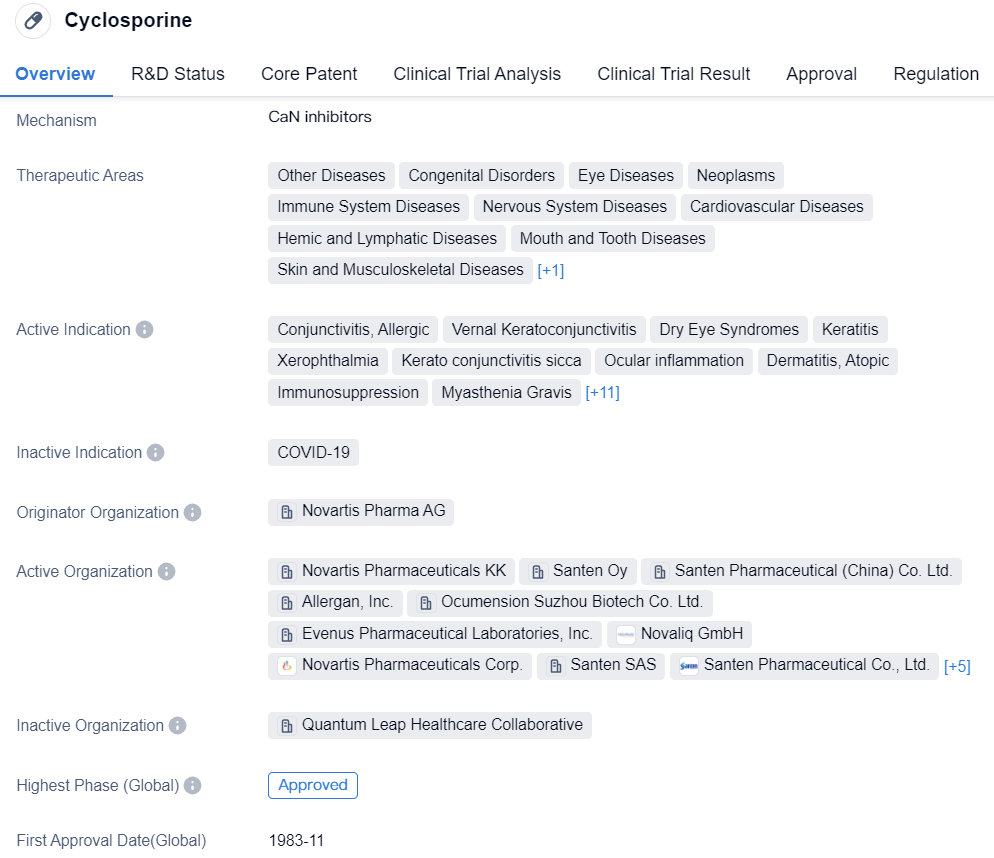
Key Drug: Cyclosporine
Cyclosporine is a synthetic peptide drug developed by Novartis Pharma AG. It primarily targets CaN and has been approved for various therapeutic areas, including a wide range of diseases affecting different body systems. Its active indications cover conditions such as eye diseases, immune system disorders, and transplant rejection.
👇Please click on the image below to directly access the latest data (R&D Status | Core Patent | Clinical Trial | Approval status in Global countries) of this drug.
Cyclosporine has achieved the highest phase of approval globally and in China, and it was first approved in the United States in 1983. The drug is regulated as an overseas new drug urgently needed in clinical settings and has orphan drug status.
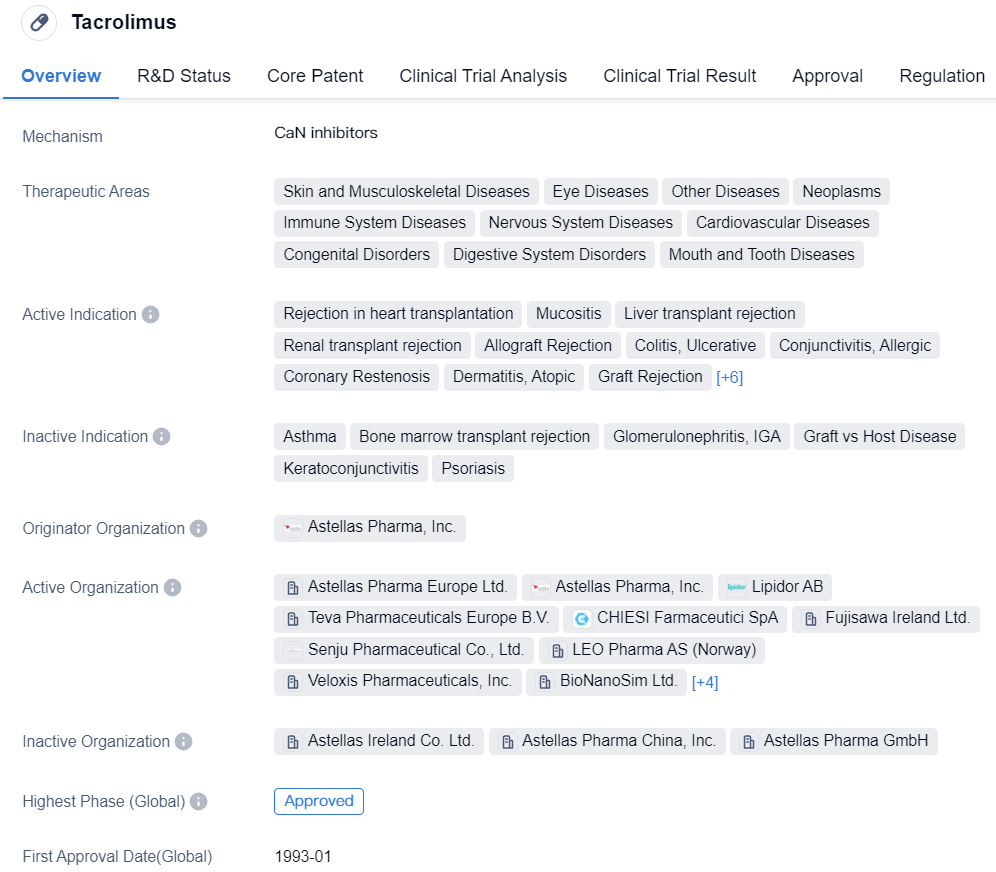
Tacrolimus
Tacrolimus is a small molecule drug that primarily targets CaN. It has been approved for various therapeutic areas including skin and musculoskeletal diseases, eye diseases, neoplasms, immune system diseases, nervous system diseases, cardiovascular diseases, congenital disorders, digestive system disorders, and mouth and tooth diseases. The drug has shown efficacy in treating rejection in heart transplantation, mucositis, liver transplant rejection, renal transplant rejection, allograft rejection, colitis, ulcerative, conjunctivitis, allergic, coronary restenosis, dermatitis, atopic, graft rejection, lupus nephritis, myasthenia gravis, rheumatoid arthritis, rejection of lung transplantation, and uveitis, anterior, eczema.
👇Please click on the image below to directly access the latest data (R&D Status | Core Patent | Clinical Trial | Approval status in Global countries) of this drug.
Tacrolimus was developed by Astellas Pharma, Inc., and it received its first approval in Japan in January 1993. It has since been approved in various countries globally. In terms of regulatory status, Tacrolimus has undergone priority review and has been designated as an orphan drug.
As a small molecule drug targeting CaN, Tacrolimus has demonstrated its effectiveness in multiple therapeutic areas. Its approval for various indications highlights its versatility and potential in treating a wide range of diseases.
The relationship between Cyclosporine and Tacrolimus
As a second-generation calcineurin inhibitor, Tacrolimus presents more advantages over Cyclosporine. The advantage of Tacrolimus is its lower side effects compared to Cyclosporine, especially less occurrence of side effects such as excess hair growth and gum swelling. Tacrolimus also tends to have a lower impact on kidney function, blood pressure, and blood potassium levels. As for the therapeutic effect, both are remarkably similar, as they are based on "equivalent doses". Naturally, individual responses to drugs vary. Some patients who do not respond well to Cyclosporine find increased effectiveness when switching to Tacrolimus; others who do not get good results from Tacrolimus may see their condition improve after switching to Cyclosporine.
Because Cyclosporine is significantly cheaper than Tacrolimus, if only a small dose is needed clinically, such as 100mg/d of Cyclosporine or 2mg/d of Tacrolimus, Cyclosporine is recommended, as its side effects are quite low at small doses. However, if a larger dose is needed, such as 200mg/d of Cyclosporine or 4mg/d of Tacrolimus, Tacrolimus is preferred because it will cause fewer side effects.