Analysis on the Research Progress of Neurokinin 1 Receptor Antagonist
Neurokinin is a type of central neurotransmitter, involved in various physiological activities in the human body. Neurokinin is a large family, encompassing a variety of substances such as Substance P, Neurokinin A, Neurokinin B, etc. Among them, Substance P is the most important neurotransmitter, widely distributed in the central nervous system and the gastrointestinal tract of the human body. Neurokinin needs to bind with the neurokinin receptors to function. The neurokinin receptors are divided into three types, namely Neurokinin-1 receptor (NK1 receptor), Neurokinin-2 receptor (NK2 receptor), and Neurokinin-3 receptor (NK3 receptor). The binding ability of Substance P and Neurokinin-1 receptor is the strongest. If the Neurokinin-1 receptor is excited, it can cause nausea and vomiting in humans. If the Neurokinin-1 receptor is inhibited, it can produce an antiemetic effect. This is the pharmacological mechanism of Neurokinin-1 receptor antagonists. Neurokinin-1 receptor antagonists can be used for acute vomiting caused by chemotherapy and are also effective for delayed vomiting. In addition, it also has anti-depressant and anti-anxiety effects.
Neurokinin-1 (NK1) receptor antagonists are used for prevention of acute and delayed nausea and vomiting. The NK1 receptor antagonist competitively binds to the NK1 receptor, which blocks the binding of substance P and prevents the emetic signal being transmitted. NK1 receptor antagonists can be used in conjunction with 5-HT3-receptor antagonists and corticosteroids to augment their antiemetic activity.
NK1 receptor, also known as the neurokinin-1 receptor, plays a crucial role in the human body. It is a type of receptor found in the central and peripheral nervous systems, particularly in areas associated with pain, inflammation, and mood regulation. Activation of the NK1 receptor by substance P, a neuropeptide, leads to various physiological responses such as pain transmission, vasodilation, and immune cell activation. Due to its involvement in these processes, the NK1 receptor has become a target for pharmaceutical interventions, particularly in the development of drugs for pain management, anti-inflammatory treatments, and mental health disorders.
Neurokinin 1 Receptor Competitive Landscape
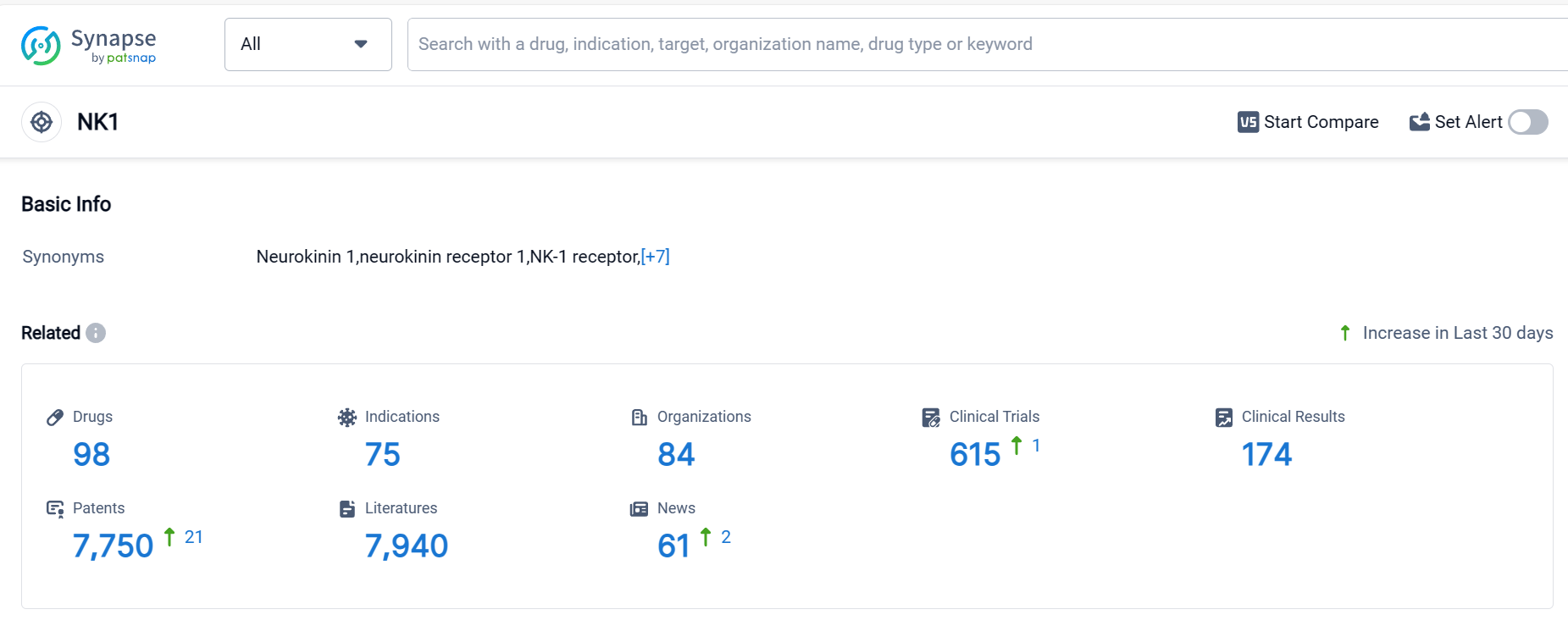
According to Patsnap Synapse, as of 5 Oct 2023, there are a total of 98 NK1 drugs worldwide, from 84 organizations, covering 75 indications, and conducting 615 clinical trials.
👇Please click on the picture link below for free registration or login directly if you have freemium accounts, you can browse the latest research progress on drugs , indications, organizations, clinical trials, clinical results, and drug patents related to this target.
The current competitive landscape of target NK1 is characterized by the presence of multiple companies with varying stages of development and drug counts. Merck & Co., Inc. is leading in terms of the highest stage of development, with 2 approved drugs. Indications such as chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting, nausea, vomiting, and postoperative nausea and vomiting have seen the most approvals. Small molecule drugs are progressing rapidly, indicating intense competition. The United States, European Union, Japan, and China are the countries/locations with the highest development activity. China has shown progress in the development of drugs under target NK1. Overall, the target NK1 presents opportunities for further development and competition in the pharmaceutical industry.
The first marketed neurokinin 1 receptor antagonist:Aprepitant
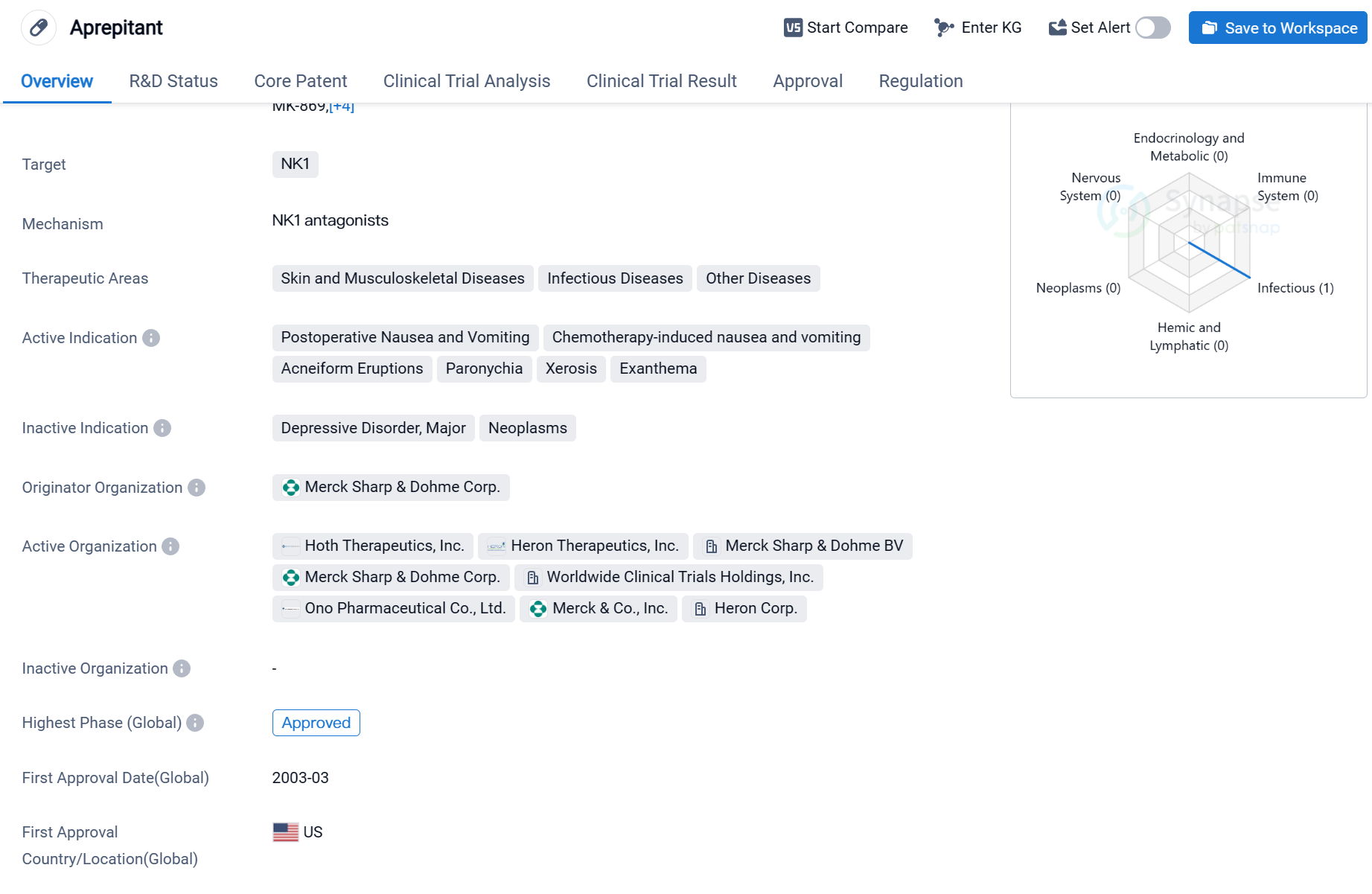
Aprepitant is a small molecule drug that targets the NK1 receptor. It has been approved for use in various therapeutic areas, including skin and musculoskeletal diseases, infectious diseases, and other diseases. The drug has shown efficacy in treating postoperative nausea and vomiting, chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting, acneiform eruptions, paronychia, xerosis, and exanthema.
The originator organization of Aprepitant is Merck Sharp & Dohme Corp. It received its first approval in the United States in March 2003. The drug has also been approved in China, indicating its global reach and acceptance.
Aprepitant's highest phase of development is approved The drug's fast track designation indicates that it has been granted expedited review and approval by regulatory authorities due to its potential to address unmet medical needs.
Aprepitant's approval for postoperative nausea and vomiting and chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting highlights its effectiveness in managing these common side effects of surgical procedures and cancer treatments. Additionally, its approval for various skin conditions, such as acneiform eruptions, paronychia, xerosis, and exanthema, suggests its potential in addressing dermatological issues.
👇Please click on the image below to directly access the latest data (R&D Status | Core Patent | Clinical Trial | Approval status in Global countries) of this drug.
As a small molecule drug targeting the NK1 receptor, Aprepitant likely exerts its therapeutic effects by modulating the activity of this receptor, which is involved in various physiological processes. By targeting the NK1 receptor, Aprepitant may help alleviate symptoms associated with nausea, vomiting, and skin diseases.
Overall, Aprepitant's approval in multiple countries and its fast track designation indicate its potential as a valuable treatment option for various indications. Its efficacy in managing postoperative and chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting, as well as its potential in addressing skin conditions, make it a promising drug in the field of biomedicine.