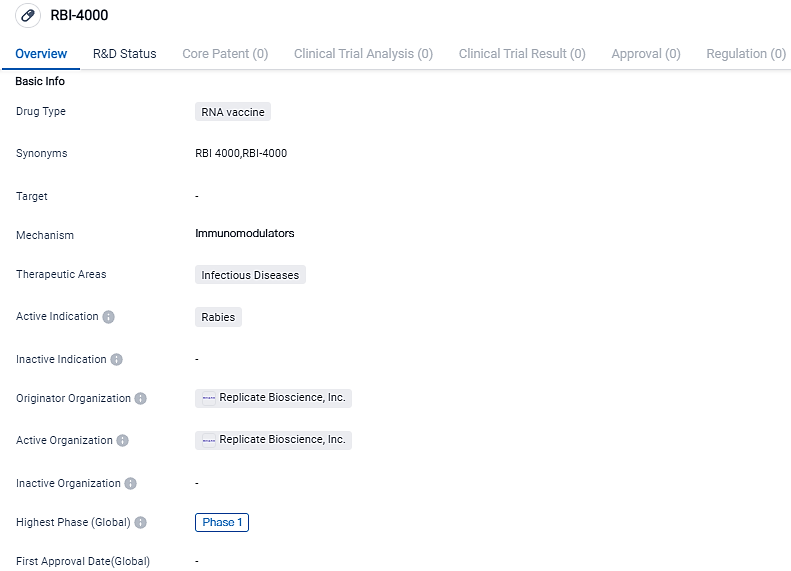
Bioscience Replication begins a Phase 1 Study for its upcoming srRNA Vaccine
Replicate Bioscience, an advanced-stage firm specializing in the innovative self-copying RNA technology to surpass the shortcomings of existing mRNA mechanisms and broaden the utilization of RNA therapies for infectious diseases, cancer and auto-immune conditions, announced the administration of the initial dosage to the first participant for its RBI-4000 vaccine, which is currently in Phase 1 trials and aims at preventing rabies.
👇Please click on the image below to directly access the latest data (R&D Status | Core Patent | Clinical Trial | Approval status in Global countries) of this drug.
The experiment, a first-of-its-kind human application of Replicate's preeminent srRNA technology, will act as a cornerstone for practical use in this particular and other challenging infectious diseases. It will also offer fundamental knowledge to guide subsequent clinical trials, predominantly in oncology and autoimmune disease.
"Working on Rabies gives us a fantastic conduit to rapidly verify our groundbreaking vaccine technology, given the ample unexposed population and the existing protective parallels outlined by the World Health Organization," said Nathaniel Wang, Ph.D., Replicate's founder, and CEO. "Administering our first dose is a significant milestone for our enterprise as we expand our srRNA technology in various disease areas."
"Our srRNA technology presents the possibility for stronger and longer-lasting immune responses, with enhanced tolerability at lower doses when juxtaposed with existing mRNA procedures," said Zelanna Goldberg, M.D., Replicate's CMO. "In infectious disease, our srRNA technology unlocks opportunities to effectively target more intricate infectious disease symptoms and permits us to swiftly manufacture vaccine solutions to cure or defend against sickness — a valuable asset for preparing for future pandemics."
The company's first vaccine release, the RBI-4000, is an srRNA vaccine designed to prod virus-neutralizing immune reactions to rabies for prevention. The Phase 1 experiment will examine the product's safety, tolerability, and immunogenicity in 84 test subjects in the U.S. In preclinical analyses, injecting RBI-4000 intramuscularly offered sustained defense against the rabies virus, summoning antibody generation and noticeable virus-specific T cells.
👇Please click on the picture link below for free registration or login directly if you have freemium accounts, you can browse the latest research progress on drugs, targets, organizations, clinical trials, clinical results, and drug patents related to this indication.
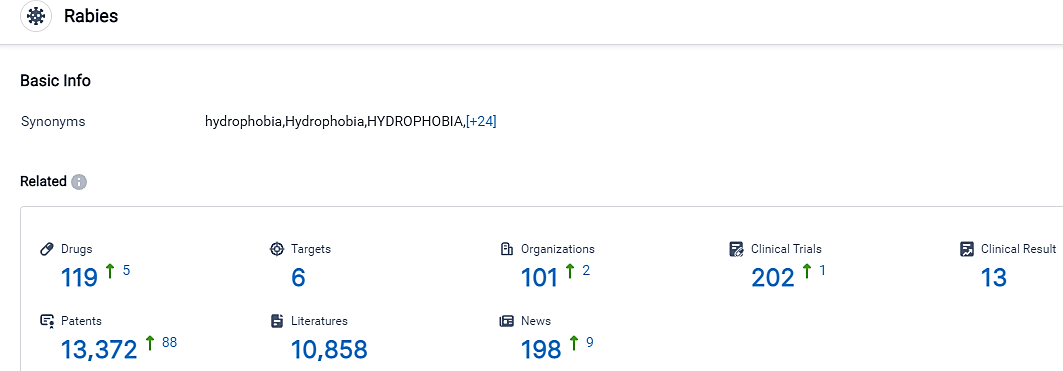
According to the data provided by the Synapse Database, As of September 17, 2023, there are 119 investigational drugs for the Rabies, including 6 targets, 101 R&D institutions involved, with related clinical trials reaching 202,and as many as 13372 patents.
Rabies remains a public health threat in several geographical regions and is designated an NIAID Priority Pathogen. The indication Rabies is highly competitive, with multiple companies, targets, drug types, and countries/locations involved in its development. China National Pharmaceutical Group Co., Ltd., Sanofi, AIM Vaccine Co., Ltd., and Poonawalla Group of Cos. are some of the companies growing fastest under this indication. The future development of the indication Rabies is promising, with ongoing research and development efforts focused on improving prevention and treatment options.