Checkpoint announces latest clinical trial data for PD-L1 inhibitor cosibelimab
Recently, Checkpoint Therapeutics announced the long-term data obtained in its key study on the PD-L1 inhibitor cosibelimab for the treatment of locally advanced and metastatic cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma (cSCC). The latest results show that the degree of disease remission deepens over time, with a complete remission rate significantly higher than previous reports.
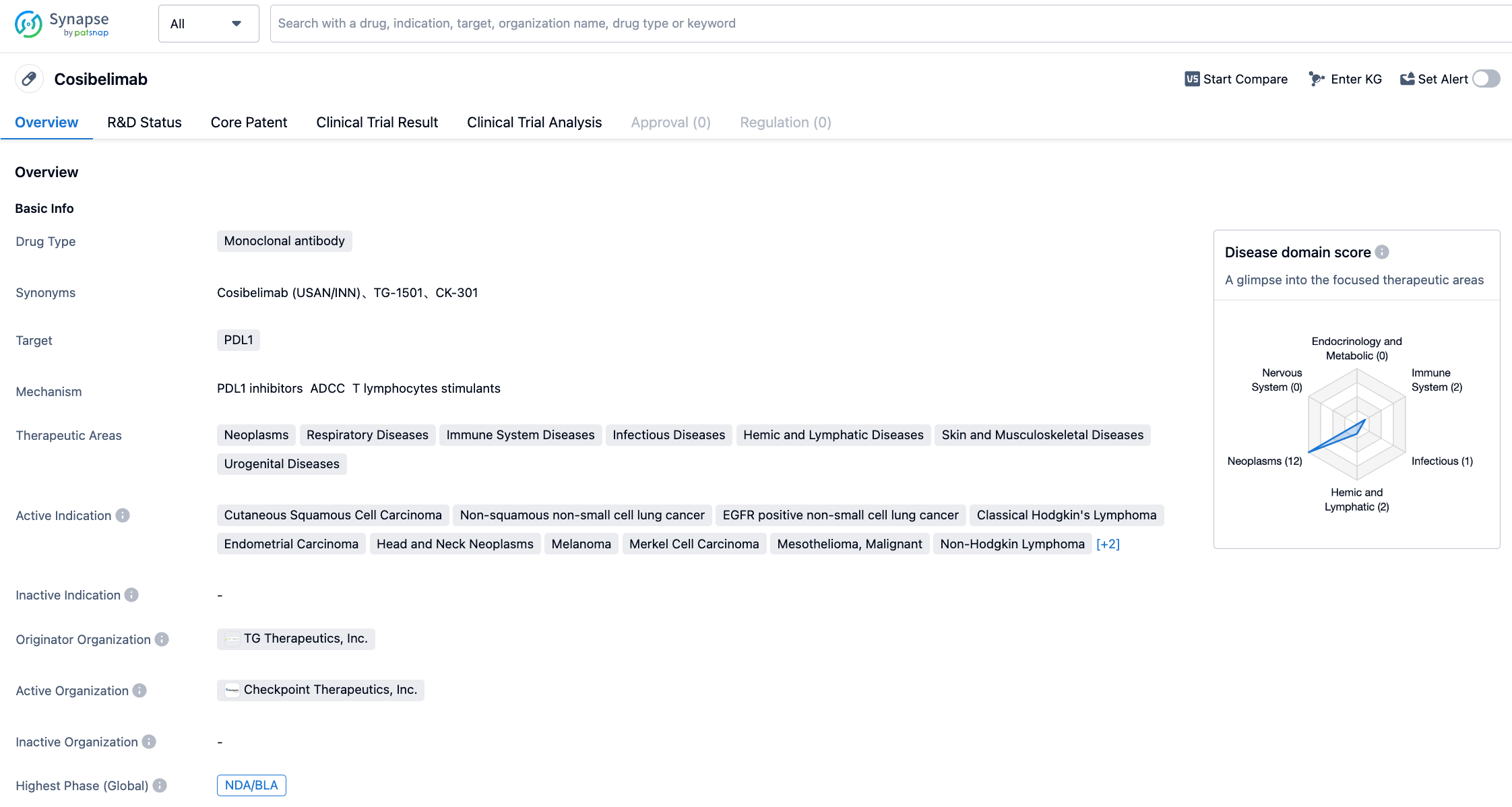
Cosibelimab is a high-affinity humanized IgG1 subtype monoclonal antibody developed by Checkpoint Therapeutics. It binds directly with PD-L1 and blocks the interaction of PD-L1 with PD-1 and B7.1 receptors. Its primary mode of action is based on inhibiting the interaction between PD-L1 and these receptors, thereby eliminating the inhibitory effect of PD-L1 on tumor-fighting CD9 positive T cells and restoring the cytotoxic T cell response. One potential difference between cosibelimab and currently available PD-1 and PD-L1 antibodies is its persistence, with over 99% tumor occupancy, which reactivates the anti-tumor immune response. Also, it has a functional Fc domain that can induce antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC), thereby exerting a more robust therapeutic effect in some types of tumors. On January 4, 2023, Checkpoint Therapeutics announced the submission of the Biologics License Application (BLA) for Cosibelimab for metastatic cSCC or locally advanced cSCC patients who are not suitable for curative surgery or radiotherapy to the FDA. In March 2023, the FDA accepted this BLA application with a PDUFA target date set for January 3, 2024.
In January 2022, Checkpoint Therapeutics announced positive results from a registration clinical trial evaluating cosibelimab (fixed dose 800mg, once every two weeks) for the treatment of metastatic CSCC. Using Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors 1.1 (RECISTv1.1), an independent center review of 78 patients enrolled in the metastatic CSCC cohort found an ORR of 47.4% for Cosibelimab treatment. At the data cut-off time, 76% of remissions were still ongoing, and median remission duration (DOR) was not yet reached. Based on these positive results, Checkpoint Therapeutics submitted a marketing application for cosibelimab.
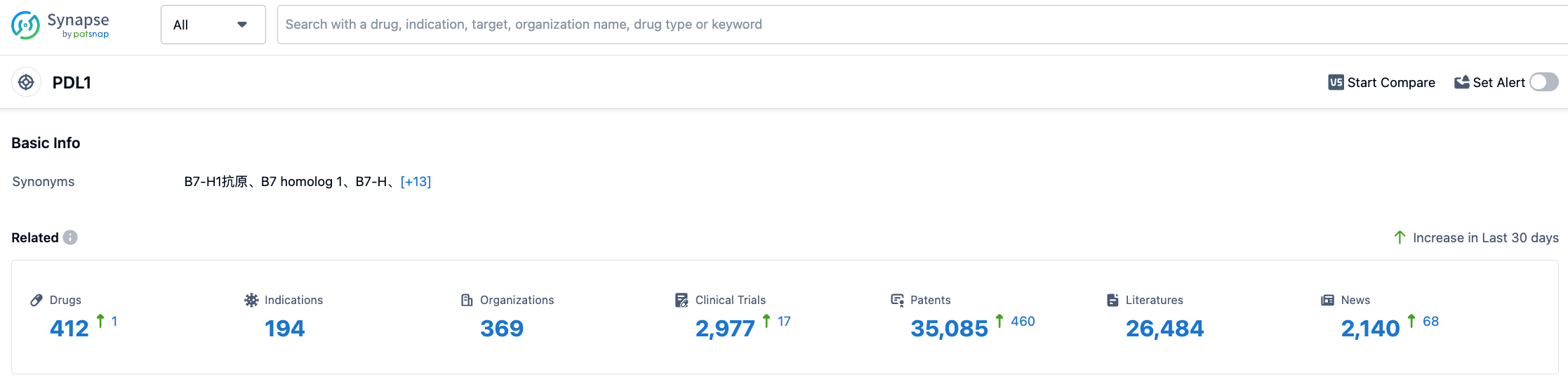
According to information disclosed by Synapse, as of August 1, 2023, there are a total of 412 drugs under development targeting PDL1, with 194 indications, 369 R&D institutions, 2,971 related clinical trials, and as many as 35,128 patents. It is hoped that cosibelimab can be launched soon to provide new treatment options for patients.