Decoding Axicabtagene Ciloleucel: a comprehensive study of its R&D trends and its clinical results in 2023 ASH
On 11 Dec 2023, The clinical data about Axicabtagene Ciloleucel from pivotal ZUMA-7 study will be updated in 2023 ASH.
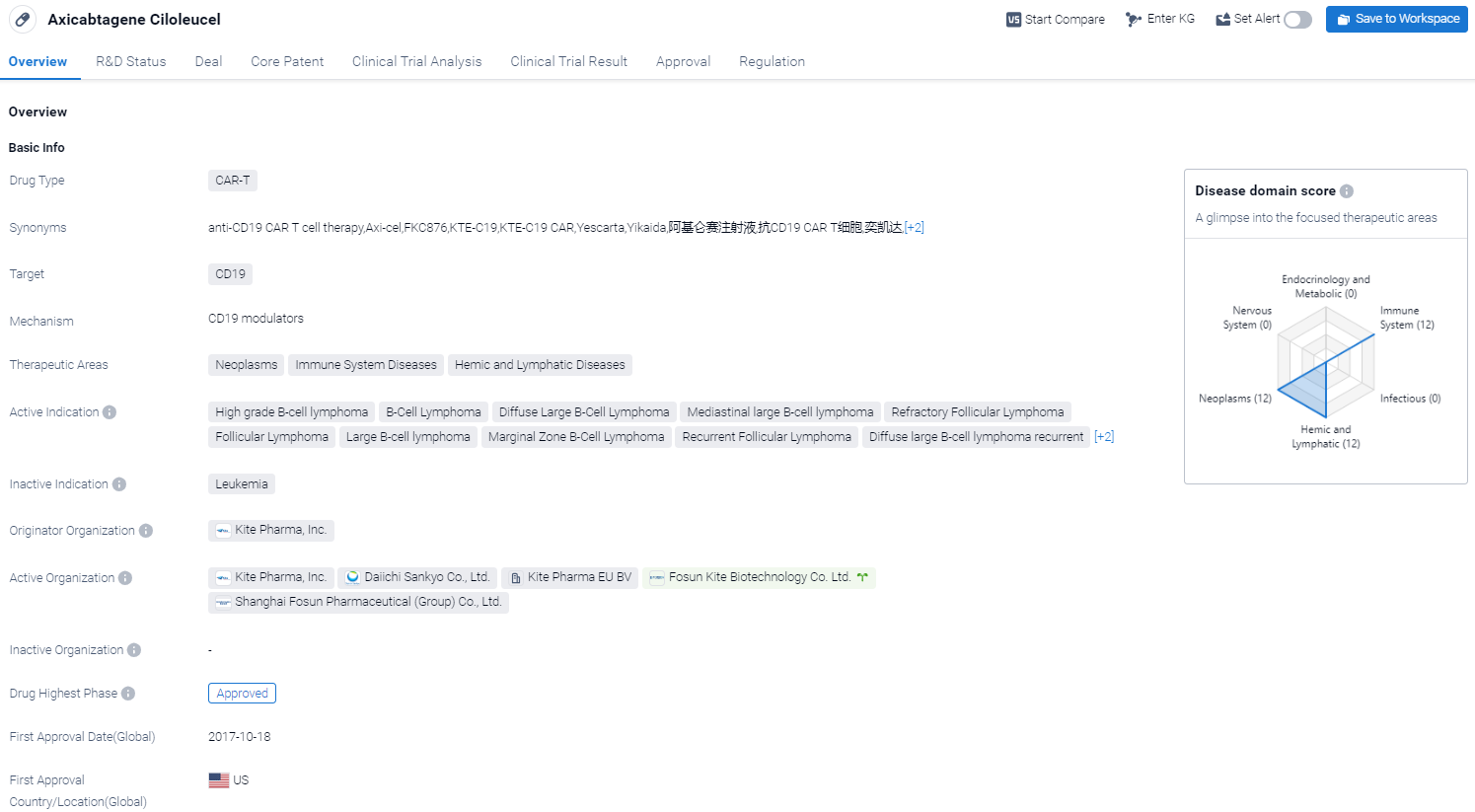
Axicabtagene Ciloleucel's R&D Progress
Axicabtagene ciloleucel is a CAR-T therapy drug developed by Kite Pharma, Inc. It falls under the category of chimeric antigen receptor T-cell (CAR-T) therapies, which are a type of immunotherapy that uses genetically modified T-cells to target specific proteins on cancer cells. In the case of axicabtagene ciloleucel, it targets CD19, a protein found on the surface of B-cells. The drug has been approved for use in the treatment of various neoplasms, immune system diseases, and hemic and lymphatic diseases.
According to the Patsnap Synapse, Axicabtagene ciloleucel received its first approval in the United States in October 2017. It has also been approved in China. And the clinical trial areas for Axicabtagene Ciloleucel are primarily in the United States, China and United Kingdom. The key indication is Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma recurrent. 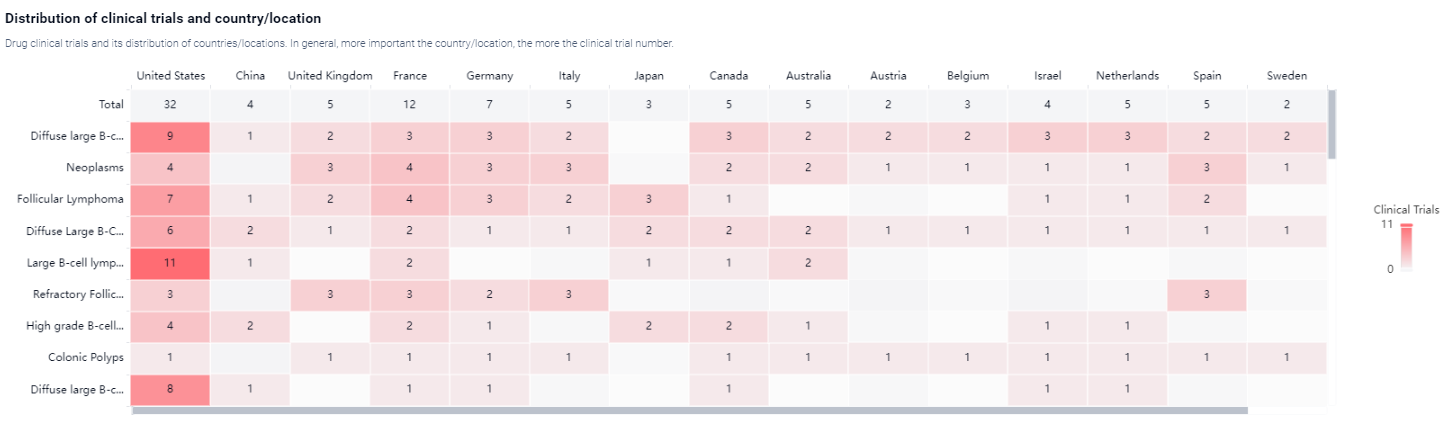
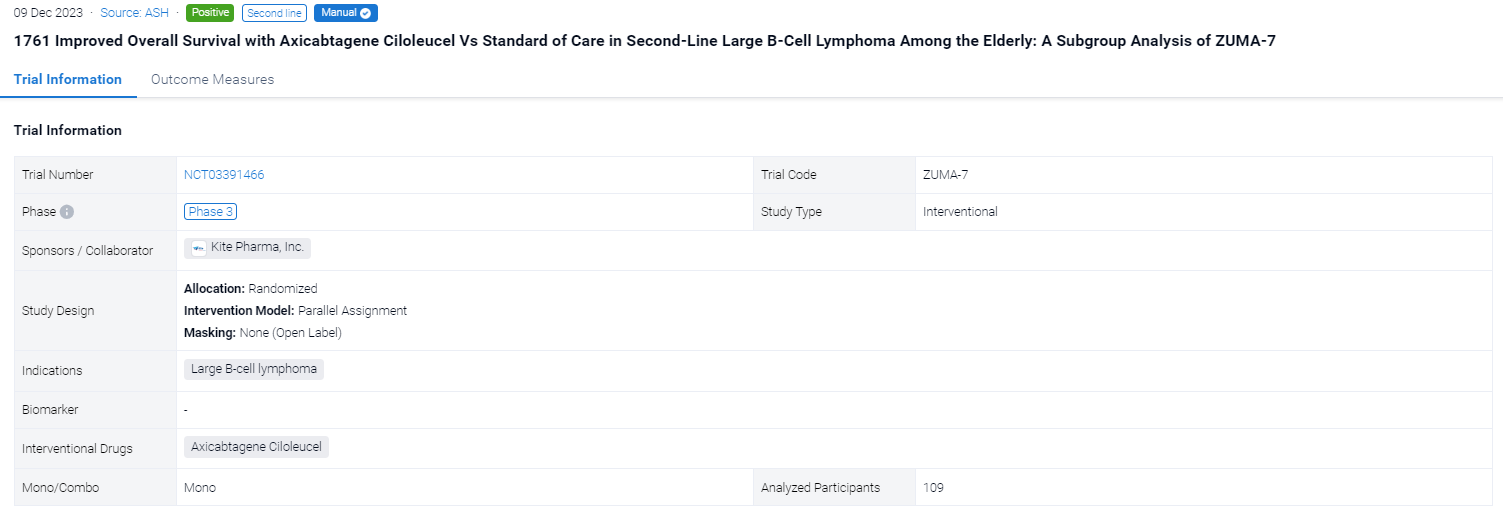
Detailed Clinical Result of Axicabtagene Ciloleucel
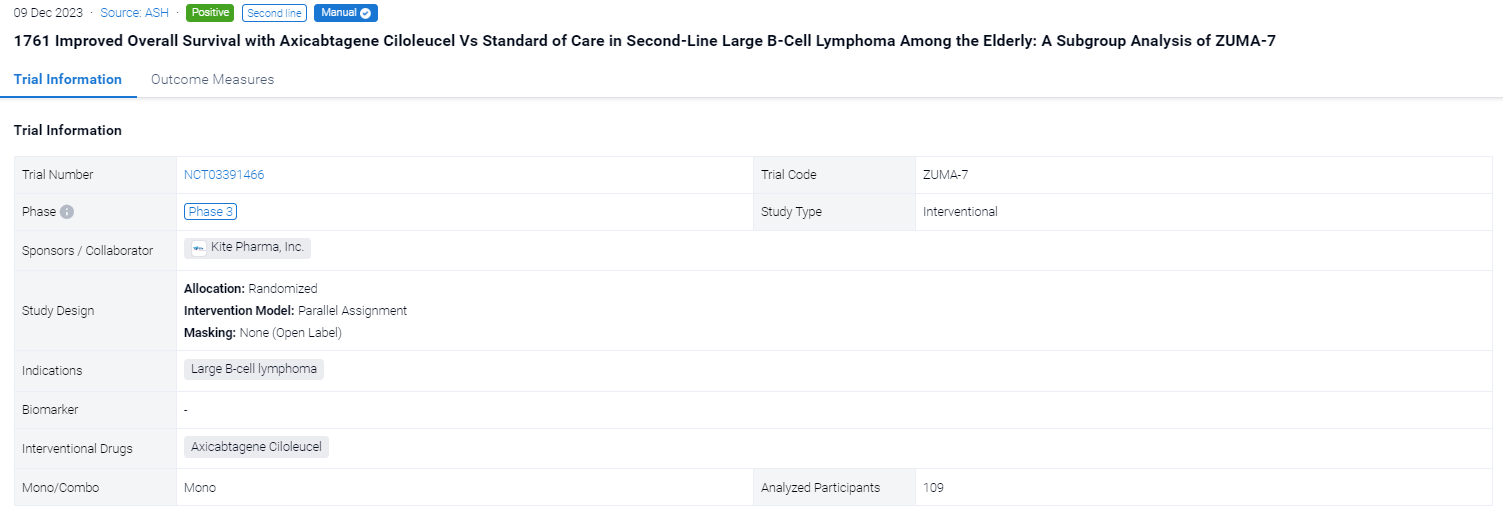
This randomized, parallel assignment, open-labeled clinical trial (NCT03391466) was aimed to investigate the safety and preliminary efficacy of Axicabtagene Ciloleucel in second-line large B-cell lymphoma among the elderly.
In this study, eligible pts were randomized 1:1 to axi-cel or SOC (2-3 cycles of platinum-based chemoimmunotherapy; responding pts proceeded to high-dose chemotherapy with ASCT). The primary OS analysis occurred 5 y after the first pt was randomized (01/25/2018) per protocol. Other endpoints included progression-free survival (PFS) per investigator assessment and safety. A planned subgroup analysis of pts aged ≥65 y was conducted in addition to an analysis for those ≥70 y. Multivariate analyses were performed to examine treatment efficacy with axi-cel compared with SOC after adjusting for multiple covariates, including sex, disease type, molecular subgroup, lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), tumor burden, and age; strata for these analyses included second-line age-adjusted International Prognostic Index (aaIPI), and relapsed vs refractory disease. Exploratory analyses were conducted to determine the association between OS and axi-cel product characteristics for pts aged ≥65 y.
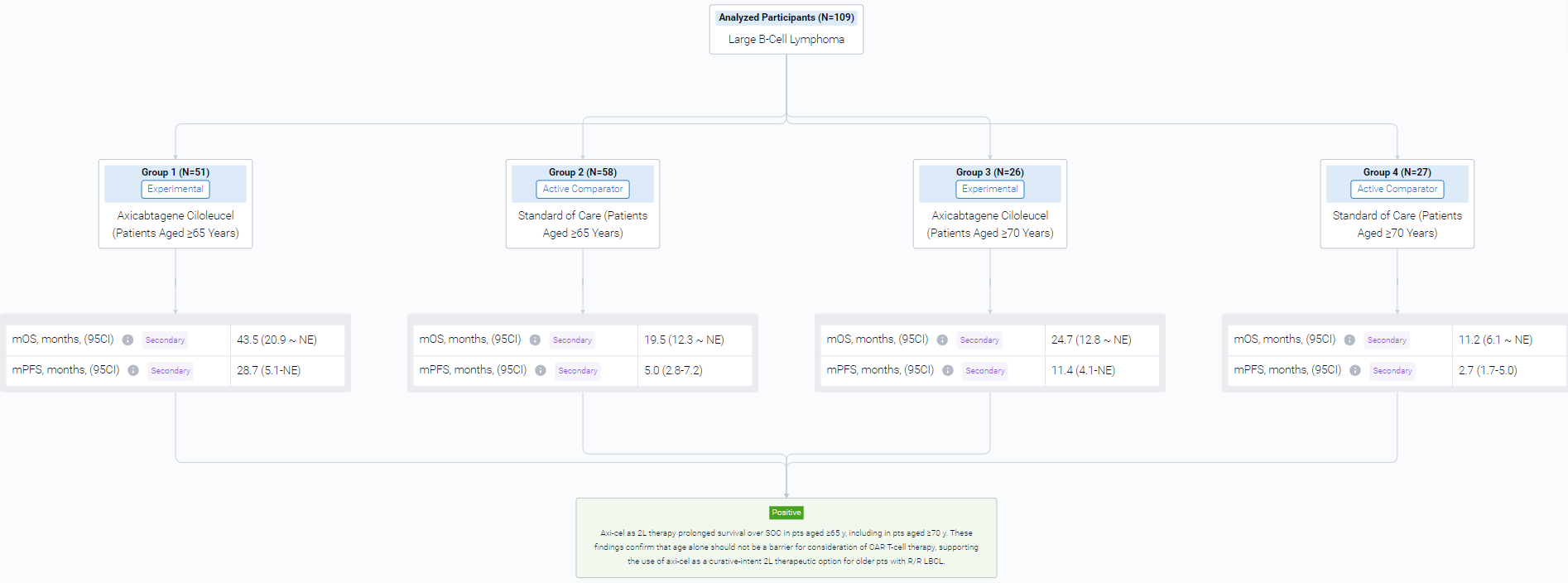
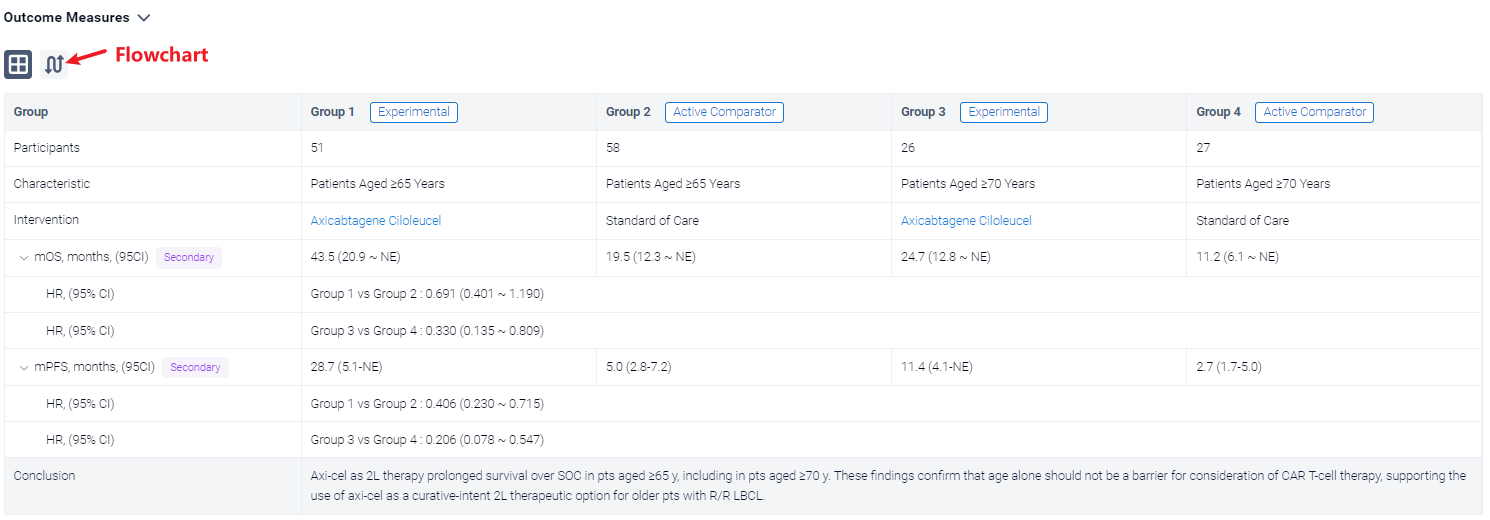
The result showed that a total of 109 pts were included in the analysis (axi-cel: 51 were ≥65 y, 26 of whom were ≥70 y, maximum age was 80 y; SOC: 58 were ≥65 y, 27 of whom were ≥70 y, maximum age was 81 y). Compared with SOC pts at baseline, more axi-cel pts had high-risk features, including aaIPI 2-3, elevated LDH, and high-grade B-cell lymphoma. At a median follow-up of 46.6 mo, OS was prolonged in the axicel vs SOC arm in pts aged ≥65 y (HR, 0.691; 95% CI, 0.401-1.190) and for those ≥70 y (HR, 0.330; 95% CI, 0.135-0.809). Similar results were observed using the piecewise Cox regression model. The median OS for axi-cel and SOC pts was 43.5 mo (95% CI, 20.9-not estimable [NE]) and 19.6 mo (95% CI, 12.3-NE), respectively, among those aged ≥65 y, and 24.7 mo (95% CI, 12.8-NE) and 11.2 mo (95% CI, 6.1-NE), respectively, among those aged ≥70 y. In the SOC arm, 57% and 52% of pts received subsequent cellular immunotherapy off protocol in pts aged ≥65 y and ≥70 y, respectively. Multivariate analyses demonstrated an even greater OS benefit with axi-cel over SOC when adjusting for differences in baseline characteristics in pts aged ≥65 y (HR, 0.526; 95% CI, 0.266-1.041) and in pts aged ≥70 y (HR, 0.184; 95% CI, 0.045-0.755). PFS assessed by investigator confirmed benefit of axi-cel over SOC in pts aged ≥65 y (HR, 0.406; 95% CI, 0.230-0.715) and in pts aged ≥70 y (HR, 0.206; 95% CI, 0.078-0.547). The median PFS for axi-cel and SOC pts was 28.7 mo (95% CI, 5.1-NE) and 5.0 mo (95% CI, 2.8-7.2), respectively, for those aged ≥65 y, and 11.4 mo (95% CI, 4.1-NE) and 2.7 mo (95% CI, 1.7-5.0), respectively, for those aged ≥70 y. No new treatment-related deaths occurred since the primary EFS analysis. There were no manufacturing failures for any pt who underwent leukapheresis. Similar associations between product characteristics and outcomes were observed among the elderly and overall populations, including improved OS associated with a greater (>median) proportion of juvenile or stem memory T-cell phenotype cells (CCR7+CD45RA+ T cells) in the axi-cel product among pts aged ≥65 y (HR, 0.369; 95% CI, 0.138-0.984).
It can be concluded that Axi-cel as 2L therapy prolonged survival over SOC in pts aged ≥65 y, including in pts aged ≥70 y. These findings confirm that age alone should not be a barrier for consideration of CAR T-cell therapy, supporting the use of axi-cel as a curative-intent 2L therapeutic option for older pts with R/R LBCL.
How to Easily View the Clinical Results Using Synapse Database?
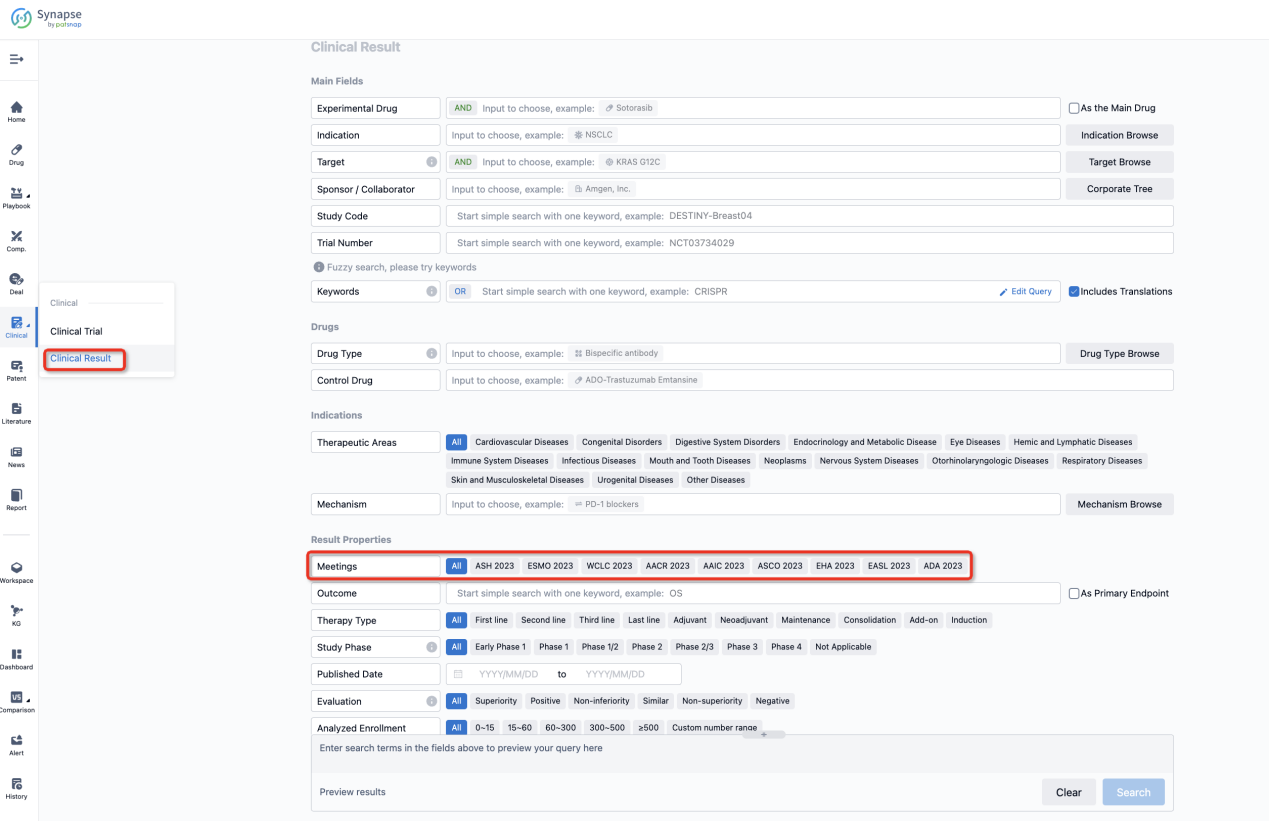
If you want to know the other clinical results of popular conferences, please lick on the “Clinical Results” on the homepage of Patsnap Synapse, which provides multi-dimensional screening and filtering of drugs, indications, targets, companies, result evaluation, release date, popular conferences, etc. to help you quickly locate the data you need.
Select the clinical meeting you are interested in, such as ESMO. In the results, you can quickly locate the data you want to view by indication, phase and drug name.
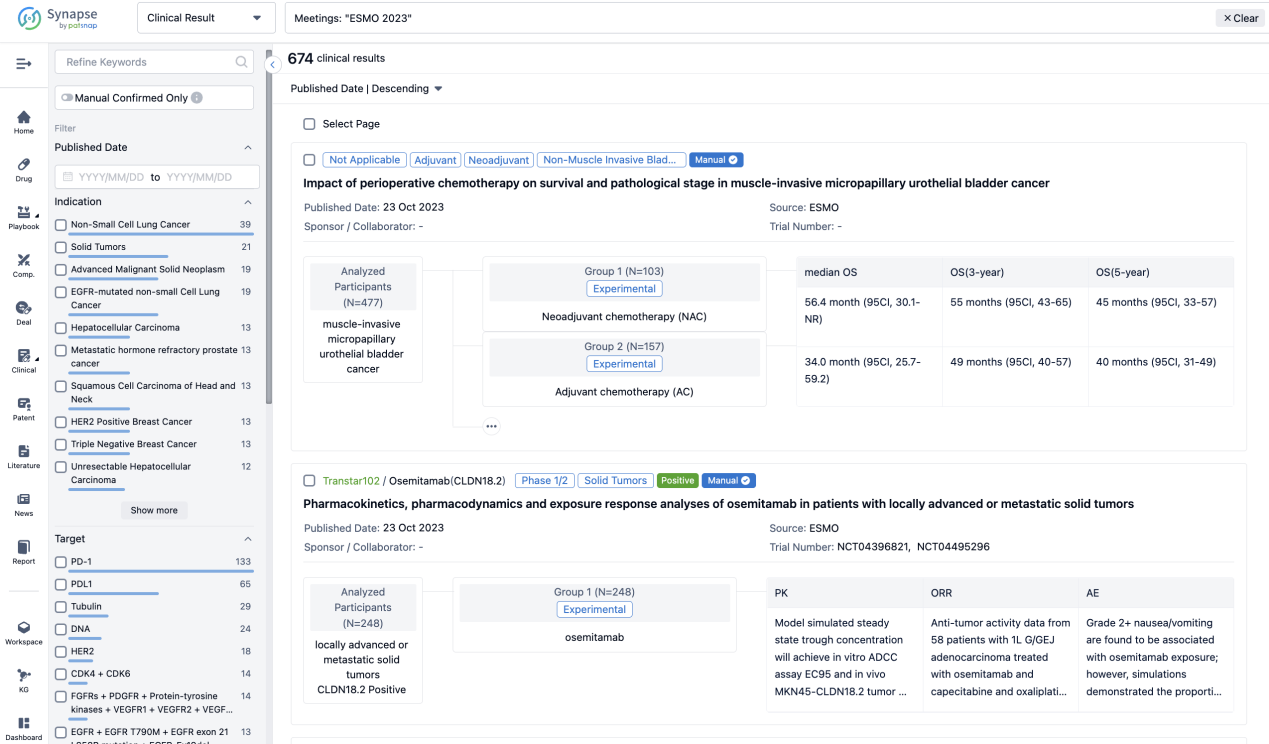
A single result clearly shows important information such as registration number, phase, indication, Sponsor/Collaborator, biomarker, Trial number, dosing regimen and more.
If you would like to view more information about this result, you can go to the result detail page by clicking on the title.
Above the headings, we provide the original source of the outcome data. The basic information is supplemented with more information beyond the list, such as company, study. design, etc.
In the important Outcome Measures section, we provide both list and flowchart forms, which are convenient for you to overview the comparison group information and core indicator data.
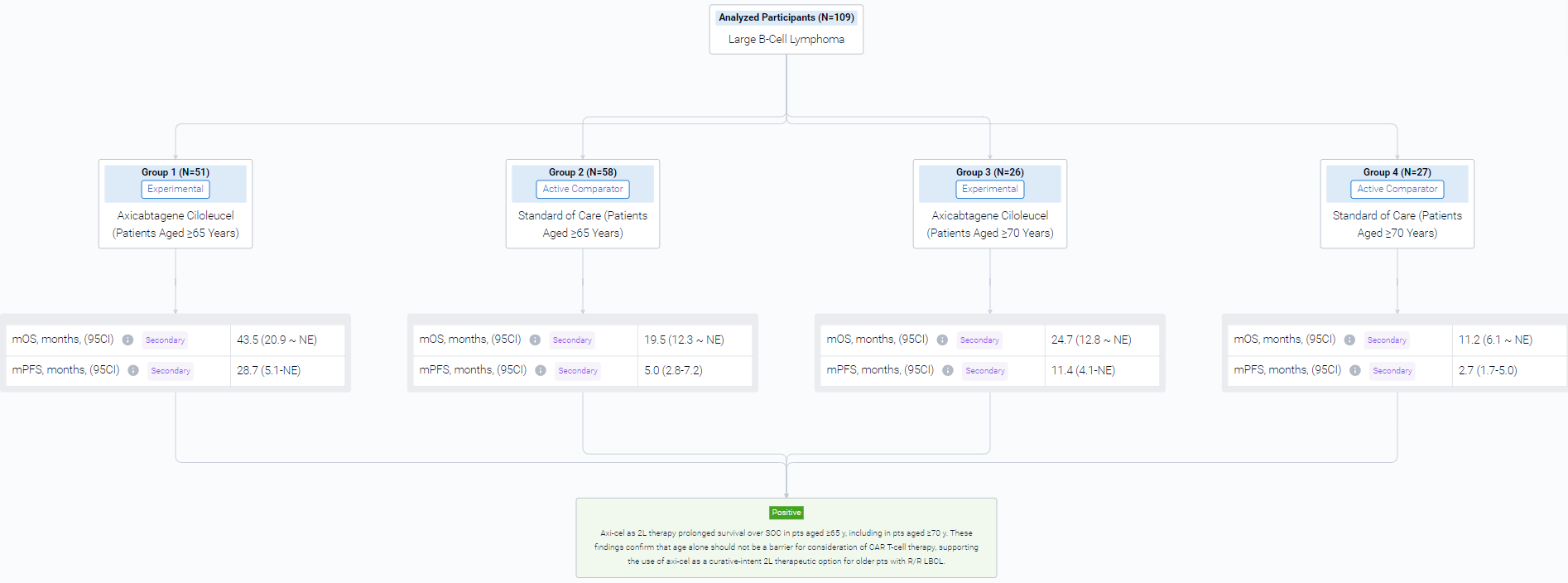
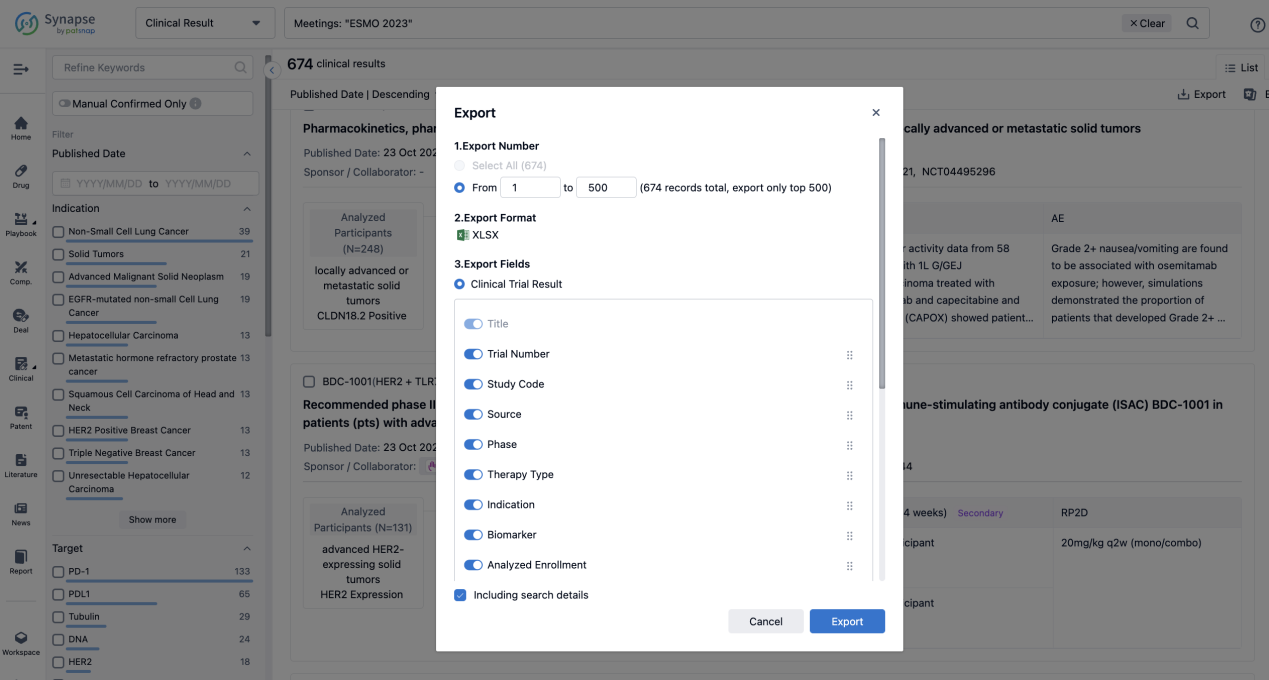
Finally, if you need to download these results, you can conveniently check the check boxes on the left side of the list, or directly click the "Export" button to download the data for personalized analysis and file sharing.
Click on the image below to embark on a brand new journey of drug discovery!