Decoding Hydrochlorothiazide/Lisinopril: A Comprehensive Study of its R&D Trends and Mechanism on Drug Target
Hydrochlorothiazide/Lisinopril's R&D Progress
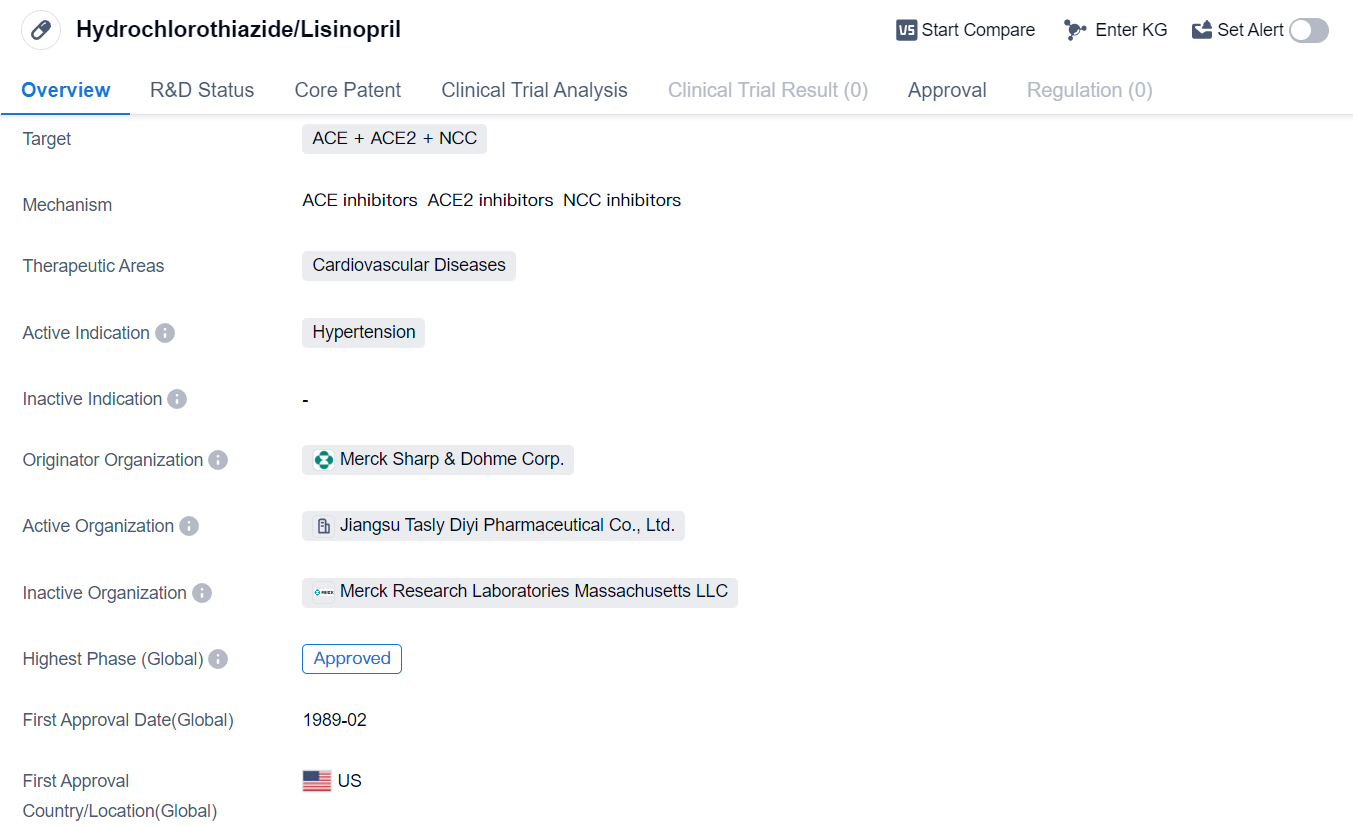
Hydrochlorothiazide/Lisinopril is a small molecule drug used in the treatment of hypertension, a condition characterized by high blood pressure. It is classified as a combination drug, as it contains two active ingredients: hydrochlorothiazide and lisinopril.
The drug targets three key components involved in blood pressure regulation: angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE), angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2), and the sodium-chloride cotransporter (NCC). By inhibiting ACE, which is responsible for the production of angiotensin II, a hormone that constricts blood vessels, hydrochlorothiazide/lisinopril helps to relax and widen the blood vessels, reducing blood pressure. ACE2 is involved in the breakdown of angiotensin II, further contributing to the blood pressure-lowering effects. NCC is responsible for reabsorbing sodium in the kidneys, and inhibiting its activity helps to reduce fluid volume and lower blood pressure.
The therapeutic area of hydrochlorothiazide/lisinopril is cardiovascular diseases, with its primary indication being hypertension. It is commonly prescribed to patients with high blood pressure to help manage and control their condition.
The drug was developed by Merck Sharp & Dohme Corp., a pharmaceutical company known for its expertise in the field of biomedicine. Hydrochlorothiazide/lisinopril has received approval for use in multiple countries, including the United States, where it was first approved in February 1989. It has also obtained approval in China, indicating its global reach and recognition.
As a small molecule drug, hydrochlorothiazide/lisinopril is likely available in oral dosage forms, such as tablets or capsules, making it convenient for patients to take. Its approval in multiple countries and its long history of use since 1989 suggest that it has been well-studied and proven to be effective in managing hypertension.
👇Please click on the image below to directly access the latest data (R&D Status | Core Patent | Clinical Trial | Approval status in Global countries) of this drug.
Mechanism of Action for Hydrochlorothiazide/Lisinopril: ACE inhibitor and ACE2 inhibitor and NCC inhibitor
ACE inhibitors are a class of drugs that work by inhibiting the action of the enzyme angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE). This enzyme plays a role in the production of a hormone called angiotensin II, which causes blood vessels to narrow and promotes the release of another hormone called aldosterone, leading to increased blood pressure. By blocking the action of ACE, ACE inhibitors help to relax and widen blood vessels, reducing blood pressure and improving blood flow.
ACE2 inhibitors, on the other hand, target the enzyme angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2). ACE2 is involved in the breakdown of angiotensin II, and its inhibition can have various effects on the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system. ACE2 inhibitors may have potential therapeutic applications in conditions such as cardiovascular diseases, kidney disorders, and respiratory illnesses.
NCC inhibitors refer to inhibitors of the sodium-chloride cotransporter (NCC), a protein responsible for the reabsorption of sodium and chloride ions in the kidneys. By blocking NCC, these inhibitors reduce the reabsorption of sodium and chloride, leading to increased excretion of these ions in urine. This mechanism helps to lower blood pressure by reducing the overall volume of fluid in the body.
From a biomedical perspective, ACE inhibitors, ACE2 inhibitors, and NCC inhibitors are all relevant in the context of cardiovascular health and blood pressure regulation. They represent different targets for therapeutic intervention and can be used to manage conditions such as hypertension and heart failure.
Drug Target R&D Trends for Hydrochlorothiazide/Lisinopril
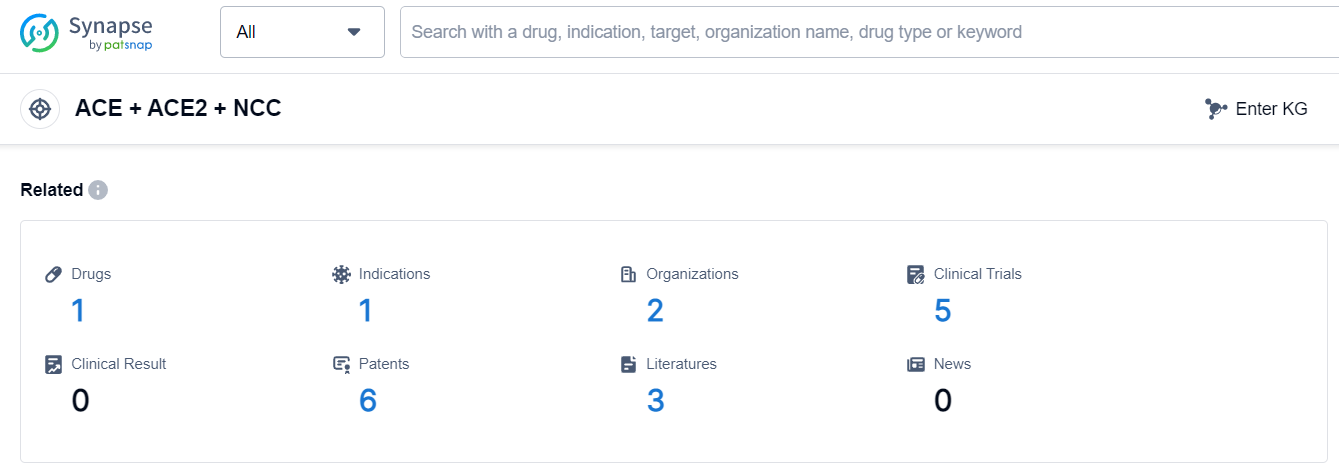
The analysis of the current competitive landscape and future development of target ACE + ACE2 + NCC reveals that Tianjin Fuhuade Science & Technology Development Co., Ltd. and Merck & Co., Inc. are the leading companies in terms of growth. Tianjin Fuhuade Science & Technology Development Co., Ltd. has achieved an approved drug, indicating their successful R&D progress. The indication analysis shows that drugs targeting ACE + ACE2 + NCC have been approved for hypertension, highlighting their potential in treating this condition. Small molecule drugs have shown the most rapid progress, indicating their effectiveness in targeting ACE + ACE2 + NCC. China has made significant progress in the development of drugs for this target, while the United States has shown slower progress. Overall, the analysis suggests a promising future for the development of drugs targeting ACE + ACE2 + NCC, with potential for further advancements and competition in the pharmaceutical industry.
According to Patsnap Synapse, as of 16 Sep 2023, there are a total of 1 ACE + ACE2 + NCC drugs worldwide, from 2 organizations, covering 1 indications, and conducting 5 clinical trials.
Please click on the picture link below for free registration or log in directly if you have a freemium account, you can browse the latest research progress on drugs, indications, organizations, clinical trials, clinical results, and drug patents related to this target
Conclusion
In summary, hydrochlorothiazide/lisinopril is a combination drug used for the treatment of hypertension. It targets ACE, ACE2, and NCC to help lower blood pressure and widen blood vessels. Developed by Merck Sharp & Dohme Corp., it has obtained approval in both the United States and China. With its long history of use, it is a well-established and widely recognized medication for managing hypertension.