Deep Scientific Insights on Isophane Insulin's R&D Progress, Mechanism of Action, and Drug Target
Isophane Insulin's R&D Progress
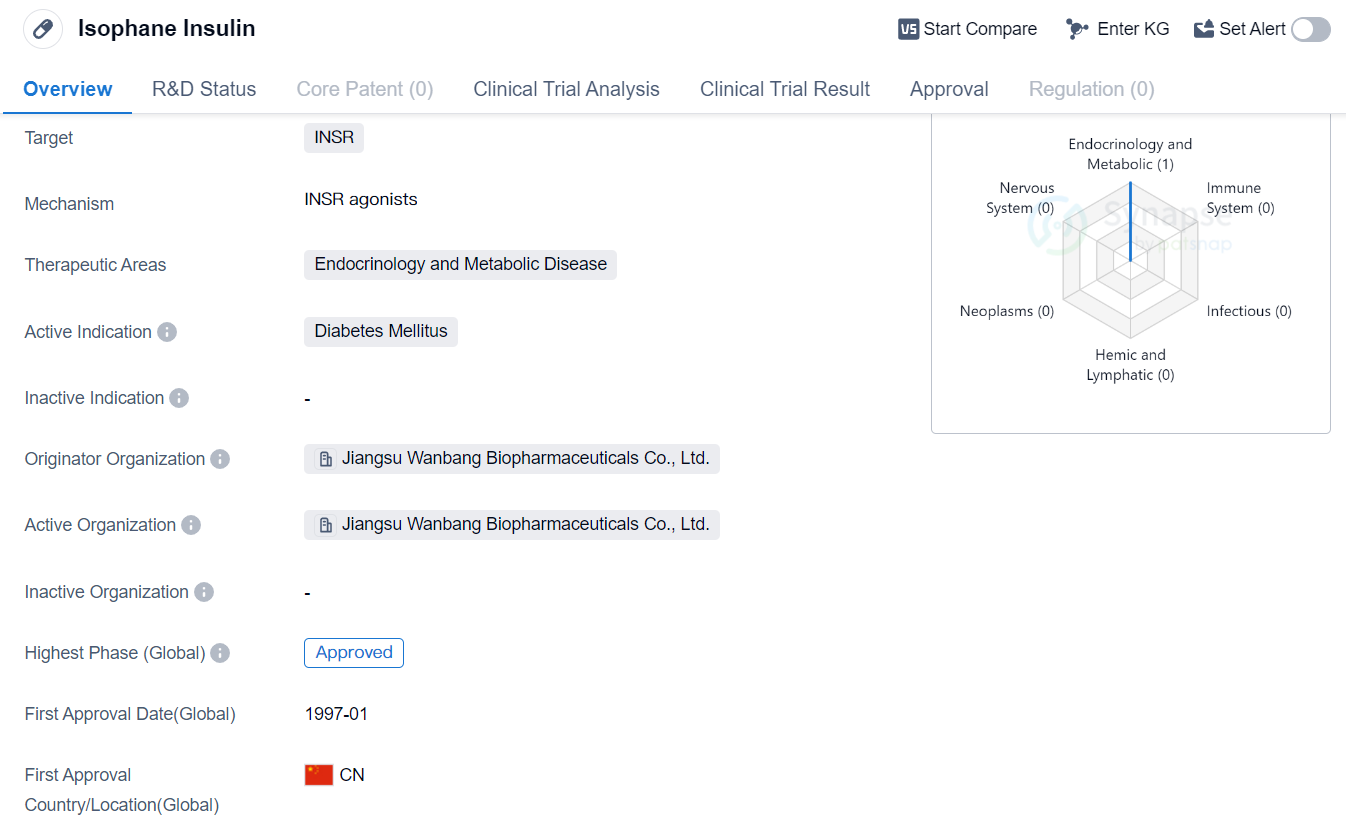
Isophane Insulin is a hormone drug that targets the INSR (insulin receptor) and is primarily used in the treatment of diabetes mellitus. It falls under the therapeutic areas of endocrinology and metabolic disease. The drug was first approved in China in January 1997 and is manufactured by Jiangsu Wanbang Biopharmaceuticals Co., Ltd.
Isophane Insulin is a type of insulin that is commonly used to manage diabetes. It works by replacing or supplementing the insulin that is naturally produced by the body. Insulin is a hormone that helps regulate blood sugar levels, and individuals with diabetes either do not produce enough insulin or are unable to effectively use the insulin they produce.
The drug is specifically designed to target the INSR, which is the receptor for insulin. By binding to this receptor, Isophane Insulin helps facilitate the uptake of glucose from the bloodstream into cells, thereby lowering blood sugar levels.
Isophane Insulin is primarily indicated for the treatment of diabetes mellitus, a chronic condition characterized by high blood sugar levels. It is commonly used in both type 1 and type 2 diabetes, although the dosing and administration may vary depending on the individual's specific needs.
Jiangsu Wanbang Biopharmaceuticals Co., Ltd. is the originator organization of Isophane Insulin. They are responsible for the development, manufacturing, and distribution of the drug. Isophane Insulin has reached the highest phase of development which is approved globally.
👇Please click on the image below to directly access the latest data (R&D Status | Core Patent | Clinical Trial | Approval status in Global countries) of this drug.
Mechanism of Action for Isophane Insulin: INSR agonist
INSR agonists refer to compounds or drugs that activate the insulin receptor (INSR). The INSR is a protein found on the surface of cells, particularly in tissues such as the liver, muscle, and adipose tissue. When insulin binds to the INSR, it triggers a cascade of signaling events that regulate glucose metabolism and other cellular processes.
INSR agonists mimic the action of insulin by binding to the INSR and activating its signaling pathway. This leads to increased uptake of glucose into cells, enhanced glycogen synthesis, and inhibition of glucose production in the liver. By activating the INSR, these agonists can help lower blood glucose levels and improve insulin sensitivity.
In a biomedical perspective, INSR agonists are of great interest in the field of diabetes research and treatment. They are being investigated as potential therapeutic agents for type 2 diabetes, where there is a deficiency in insulin action or insulin resistance. By directly targeting the INSR, agonists can bypass some of the defects in insulin signaling pathways and provide an alternative approach to managing blood glucose levels.
It is important to note that the development and use of INSR agonists require careful evaluation and consideration of their efficacy, safety, and potential side effects. Clinical trials and further research are needed to fully understand their therapeutic potential and optimize their use in the management of diabetes and other metabolic disorders.
Drug Target R&D Trends for Isophane Insulin
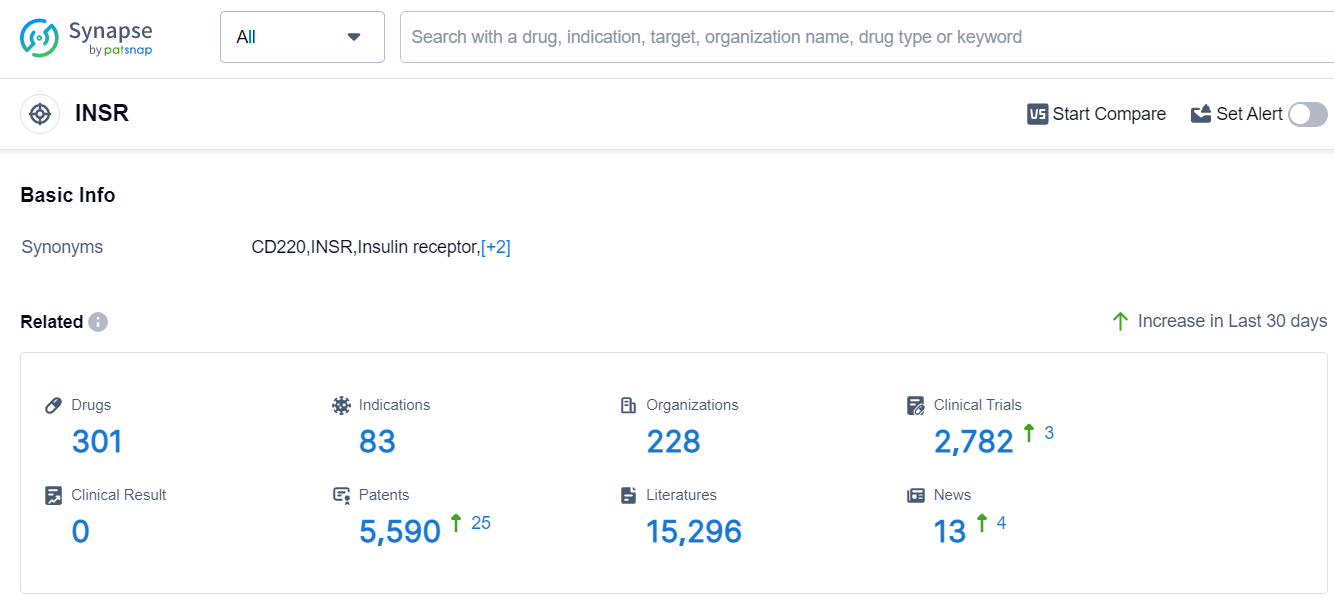
The analysis of the target INSR reveals a competitive landscape with multiple companies actively developing drugs. Novo Nordisk A/S, Sanofi, Gan & Lee Pharmaceuticals Co., Ltd., Eli Lilly & Co., and Shanghai Fosun High Technology (Group) Co., Ltd. are the companies growing fastest under this target. The focus is primarily on addressing diabetes-related indications, with a significant number of approved drugs for Diabetes Mellitus, Type 2, and Diabetes Mellitus, Type 1. Hormones and Biosimilars are the drug types progressing most rapidly, indicating intense competition. China, the European Union, the United States, and Japan are the countries/locations developing fastest under the target INSR, with China showing significant progress. Overall, the target INSR presents a promising area for future development in the pharmaceutical industry.
According to Patsnap Synapse, as of 14 Sep 2023, there are a total of 301 INSR drugs worldwide, from 228 organizations, covering 83 indications, and conducting 2782 clinical trials.
Please click on the picture link below for free registration or log in directly if you have a freemium account, you can browse the latest research progress on drugs, indications, organizations, clinical trials, clinical results, and drug patents related to this target
Conclusion
Overall, Isophane Insulin is an important medication in the field of biomedicine, specifically in the treatment of diabetes mellitus. Its approval in China in 1997 highlights its long-standing presence in the market, and its target of the INSR receptor demonstrates its mechanism of action in regulating blood sugar levels. As an expert in the pharmaceutical industry, it is crucial to stay updated on the latest developments and advancements in drugs like Isophane Insulin to ensure effective business development strategies.