Miglitol: Detailed Review of its Transformative R&D Success, Mechanism of Action, and Drug Target
Miglitol's R&D Progress
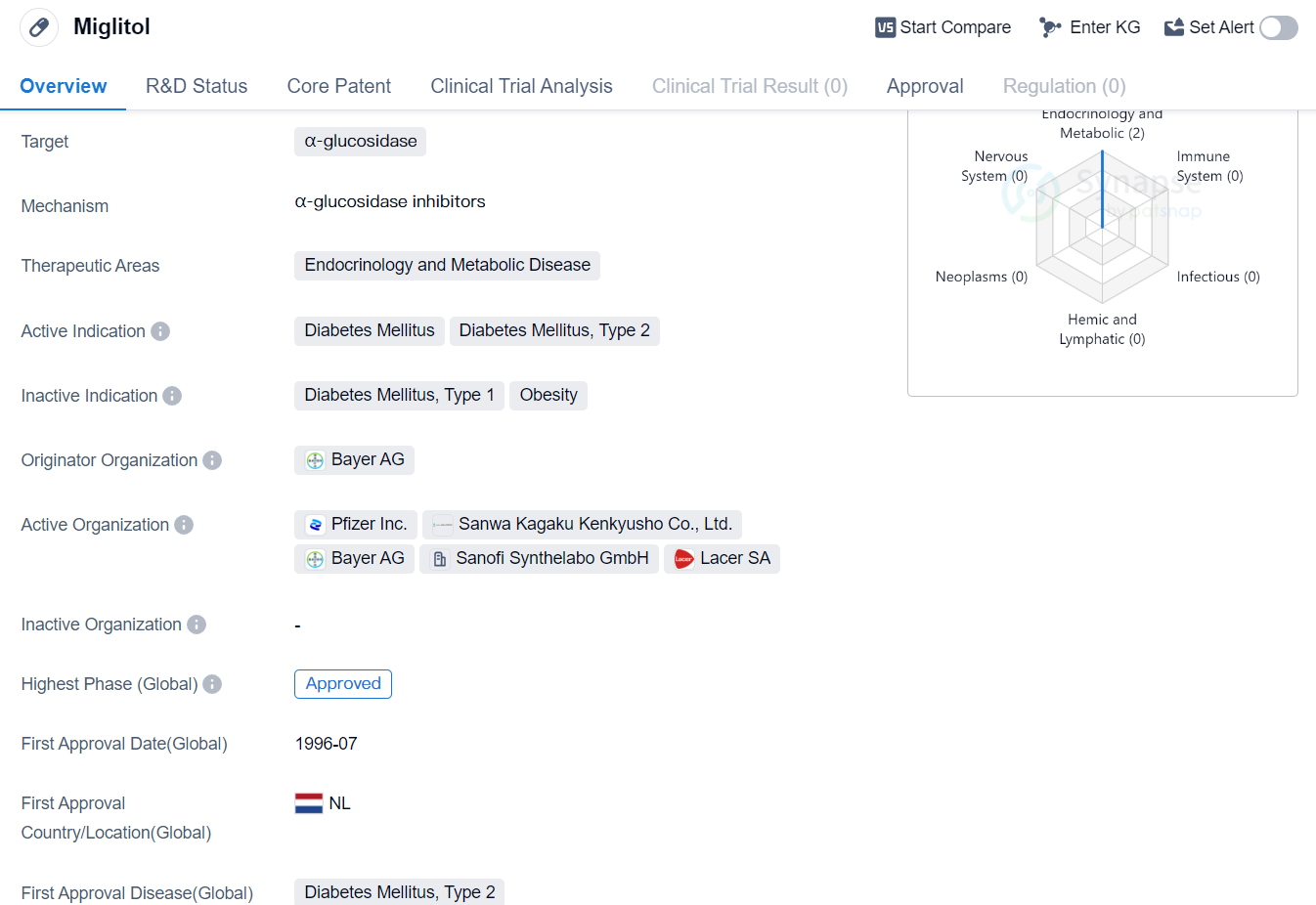
Miglitol is a small molecule drug that falls under the therapeutic areas of endocrinology and metabolic disease. It specifically targets α-glucosidase, an enzyme involved in the breakdown of carbohydrates. The drug is primarily indicated for the treatment of diabetes mellitus, specifically type 2 diabetes.
The originator organization of Miglitol is Bayer AG, a well-known pharmaceutical company. The drug has reached the highest phase of development which is approved globally. Miglitol received its first approval in the Netherlands in July 1996, making it a long-standing medication in the market.
As a small molecule drug, Miglitol is designed to inhibit α-glucosidase, an enzyme responsible for breaking down complex carbohydrates into simple sugars. By inhibiting this enzyme, Miglitol helps to slow down the digestion and absorption of carbohydrates in the small intestine. This mechanism of action ultimately leads to a reduction in postprandial blood glucose levels, making it an effective treatment option for individuals with type 2 diabetes.
The therapeutic areas of endocrinology and metabolic disease encompass a wide range of conditions related to hormone imbalances and metabolic disorders. Diabetes mellitus, particularly type 2 diabetes, is a prevalent condition characterized by high blood sugar levels due to insulin resistance or insufficient insulin production. Miglitol offers a targeted approach to managing this condition by specifically addressing the digestion and absorption of carbohydrates.
With its long history of approval and widespread use, Miglitol has established itself as a reliable treatment option for individuals with type 2 diabetes. Its mechanism of action and therapeutic areas make it a valuable asset in the field of biomedicine, contributing to the management of endocrinological and metabolic diseases.
👇Please click on the image below to directly access the latest data (R&D Status | Core Patent | Clinical Trial | Approval status in Global countries) of this drug.
Mechanism of Action for Miglitol: α-glucosidase inhibitor
From a biomedical perspective, α-glucosidase inhibitors are a type of medication used in the treatment of diabetes mellitus. These inhibitors work by slowing down the digestion and absorption of carbohydrates in the small intestine. By inhibiting the enzyme α-glucosidase, which is responsible for breaking down complex carbohydrates into simple sugars, these medications help to control blood sugar levels after meals. By delaying the absorption of glucose, α-glucosidase inhibitors can help prevent rapid spikes in blood sugar levels and maintain more stable glucose levels throughout the day. This class of drugs is commonly prescribed alongside other diabetes medications, such as insulin or oral hypoglycemic agents, to achieve optimal glycemic control.
Drug Target R&D Trends for Miglitol
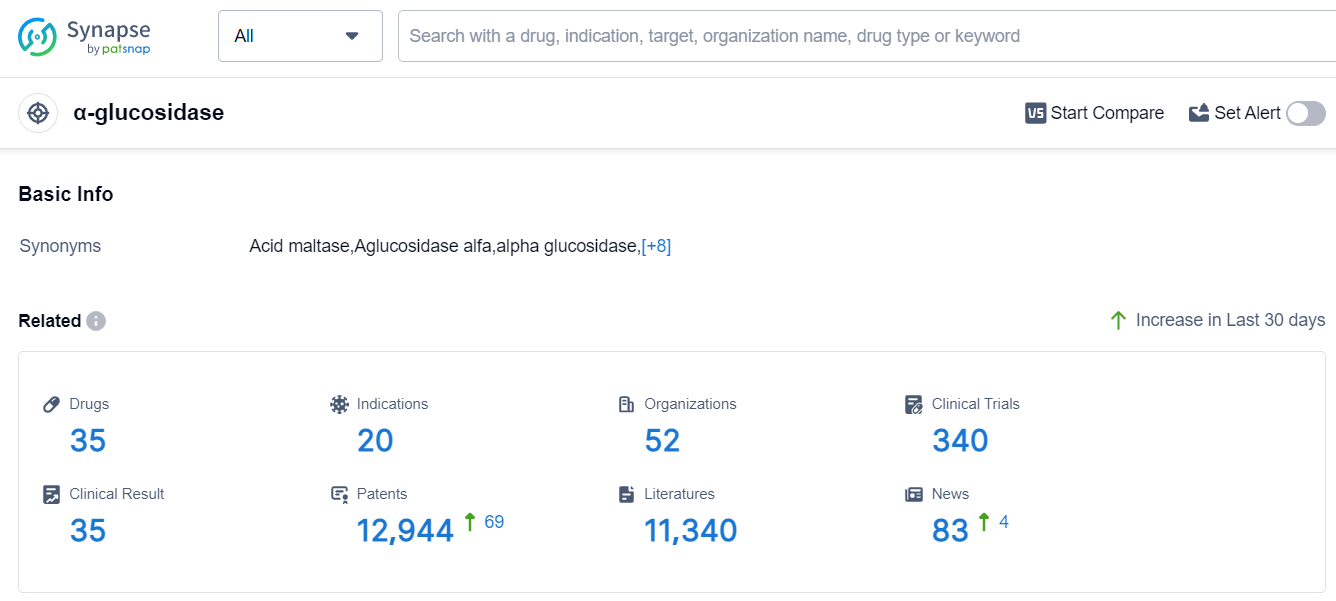
Based on the analysis of the provided data, the current competitive landscape of target α-glucosidase in the pharmaceutical industry is characterized by the presence of multiple companies with varying stages of development. Sanofi and Bayer AG are leading in terms of the highest stage of development and number of approved drugs. The indications with the highest number of approved drugs are Diabetes Mellitus, Type 2, and Glycogen Storage Disease Type II. Small molecule drugs, enzymes, and gene therapies are progressing rapidly, indicating potential areas of focus for future development. The United States, Japan, China, and the European Union are the countries/locations developing fastest, with China showing significant progress. Overall, the target α-glucosidase presents opportunities for further research and development, particularly in the areas of small molecule drugs, enzymes, and gene therapies, with a focus on indications such as Diabetes Mellitus, Type 2, and Glycogen Storage Disease Type II.
According to Patsnap Synapse, as of 12 Sep 2023, there are a total of 35 α-glucosidase drugs worldwide, from 52 organizations, covering 20 indications, and conducting 340 clinical trials.
Please click on the picture link below for free registration or log in directly if you have a freemium account, you can browse the latest research progress on drugs, indications, organizations, clinical trials, clinical results, and drug patents related to this target
Conclusion
In summary, Miglitol is a small molecule drug developed by Bayer AG that targets α-glucosidase and is primarily indicated for the treatment of diabetes mellitus, specifically type 2 diabetes. It received its first approval in the Netherlands in 1996 and has since gained global approval. With its mechanism of action and therapeutic areas, Miglitol plays a significant role in the field of biomedicine, particularly in endocrinology and metabolic disease management.