Decoding Lacosamide: A Comprehensive Study of its R&D Trends and Mechanism on Drug Target
Lacosamide's R&D Progress
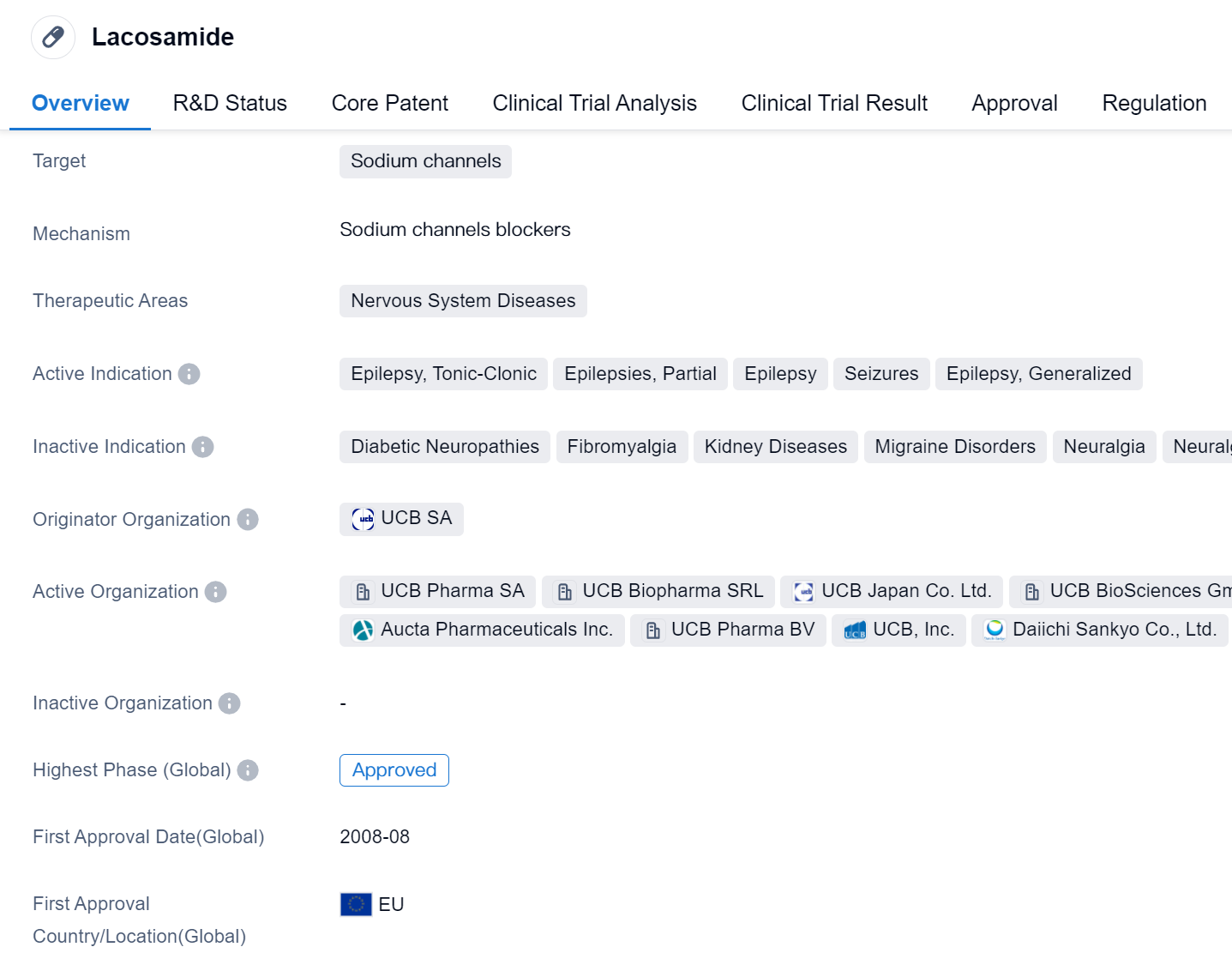
Lacosamide is a small molecule drug that targets sodium channels and is primarily used in the treatment of nervous system diseases. It has been approved for various indications related to epilepsy, including tonic-clonic seizures, partial epilepsies, generalized epilepsy, and seizures. The drug was first approved in the European Union in August 2008 and has since received approval in other countries.
Lacosamide is developed by UCB SA, a pharmaceutical organization that specializes in the research and development of drugs for various therapeutic areas. As a sodium channel blocker, lacosamide works by stabilizing the hyperexcitable neuronal membranes, thereby reducing the occurrence of seizures in patients with epilepsy.
The drug has undergone rigorous testing and evaluation, reaching the highest phase of development which is approved globally. The approval process for lacosamide may have been expedited due to its designation for priority review, which suggests that it addresses an unmet medical need or offers significant therapeutic benefits compared to existing treatments.
Lacosamide's approval for multiple indications related to epilepsy highlights its versatility in managing different types of seizures. This makes it a valuable treatment option for patients with various forms of epilepsy, providing them with a potentially effective and well-tolerated therapy.
As a small molecule drug, lacosamide is likely to have advantages such as ease of formulation, administration, and manufacturing. These characteristics contribute to its potential for widespread use and accessibility in the pharmaceutical market.
👇Please click on the image below to directly access the latest data (R&D Status | Core Patent | Clinical Trial | Approval status in Global countries) of this drug.
Mechanism of Action for Lacosamide: Sodium channel blockers
Sodium channel blockers are a class of drugs that work by inhibiting the activity of sodium channels in the body. Sodium channels are proteins that are responsible for the movement of sodium ions across cell membranes. By blocking these channels, sodium channel blockers can prevent the influx of sodium ions into cells, which can have various effects depending on the specific drug and its target.
From a biomedical perspective, sodium channel blockers are commonly used in the treatment of various conditions, particularly those involving abnormal electrical activity in the body. For example, they are often prescribed to treat certain types of cardiac arrhythmias, where the abnormal electrical signals in the heart can be suppressed by blocking sodium channels. Sodium channel blockers can also be used as local anesthetics, as they can block the transmission of pain signals by inhibiting sodium channels in nerve cells.
It's important to note that sodium channel blockers can have side effects, and their use should be carefully monitored by healthcare professionals. Common side effects may include dizziness, nausea, and changes in heart rhythm. Additionally, certain individuals may be more susceptible to adverse reactions, so it's crucial to consider individual patient factors when prescribing sodium channel blockers.
Drug Target R&D Trends for Lacosamide
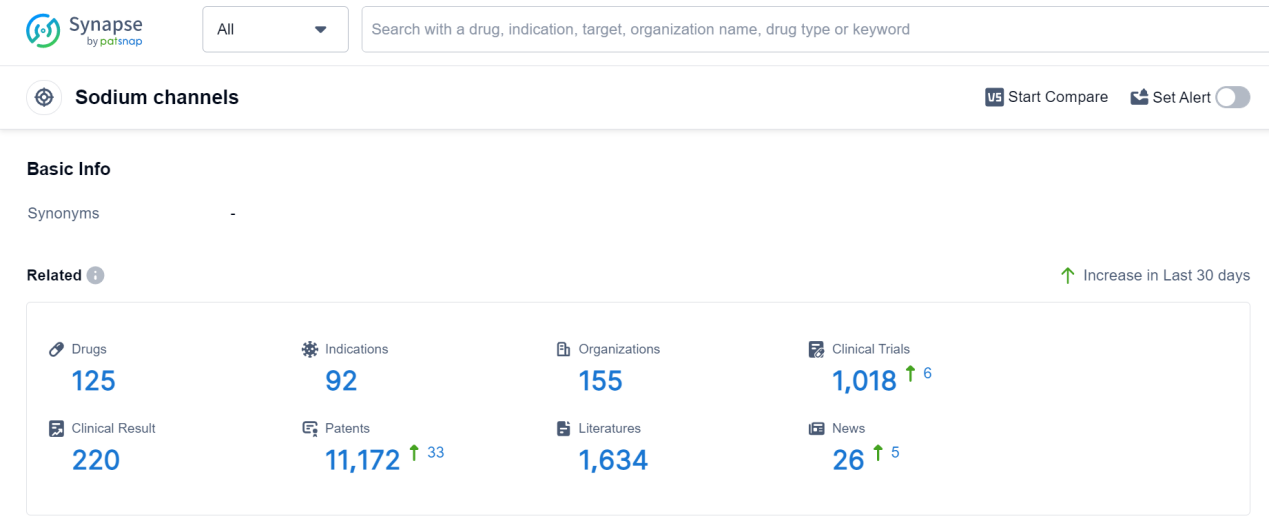
Sodium channels play a crucial role in the human body by facilitating the movement of sodium ions across cell membranes. These channels are integral to the generation and propagation of electrical signals in nerve cells, allowing for the transmission of information throughout the nervous system. They are also involved in muscle contraction, regulating the excitability and function of cardiac, skeletal, and smooth muscles. Dysfunction or dysregulation of sodium channels can lead to various disorders, including epilepsy, cardiac arrhythmias, and pain syndromes. Understanding the role of sodium channels is essential for the development of targeted therapies and drugs that modulate their activity for the treatment of these conditions.
According to Patsnap Synapse, as of 7 Sep 2023, there are a total of 125 Sodium channels drugs worldwide, from 155 organizations, covering 92 indications, and conducting 1018 clinical trials.
👇Please click on the picture link below for free registration or log in directly if you have a freemium account, you can browse the latest research progress on drugs, indications, organizations, clinical trials, clinical results, and drug patents related to this target
Conclusion
In summary, lacosamide is a small molecule drug developed by UCB SA that targets sodium channels and is approved for the treatment of various forms of epilepsy. Its approval in multiple countries, including the European Union and China, demonstrates its global recognition and potential for widespread use. With its ability to stabilize hyperexcitable neuronal membranes, lacosamide offers a valuable treatment option for patients with epilepsy, providing them with the potential for improved seizure control and quality of life.