Decoding Norepinephrine Bitartrate: A Comprehensive Study of its R&D Trends
Norepinephrine Bitartrate's R&D Progress
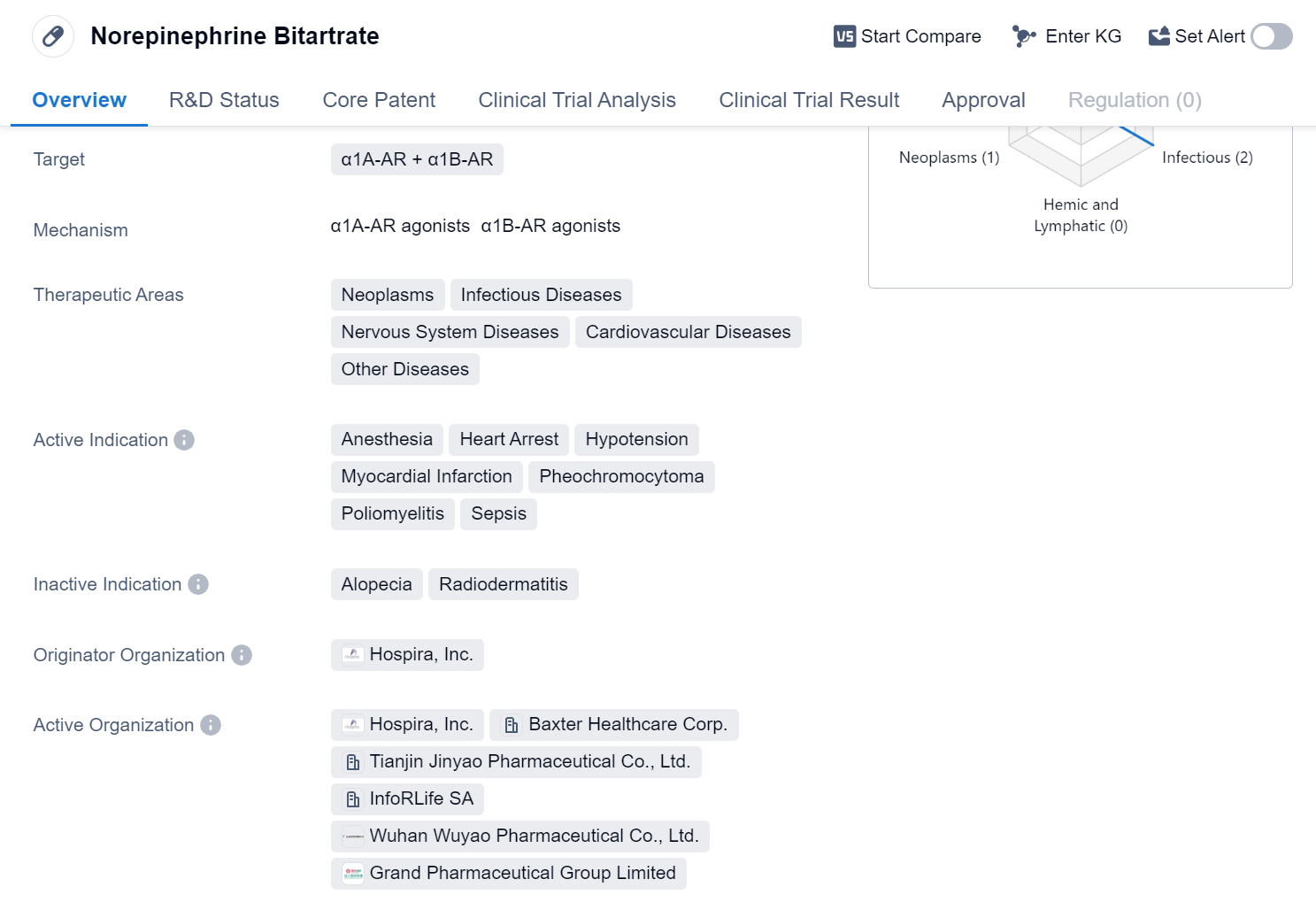
Norepinephrine Bitartrate is a small molecule drug that targets α1A-AR and α1B-AR receptors. It has been approved for use in various therapeutic areas including neoplasms, infectious diseases, nervous system diseases, cardiovascular diseases, and other diseases. The drug is indicated for anesthesia, heart arrest, hypotension, myocardial infarction, pheochromocytoma, poliomyelitis, and sepsis.
The originator organization of Norepinephrine Bitartrate is Hospira, Inc. It received its first approval in the United States in July 1950. The drug has also obtained approvals in other countries, making it a globally recognized medication.
Norepinephrine Bitartrate is primarily used in the treatment of conditions related to the cardiovascular system and the nervous system. It is commonly administered in emergency situations such as heart arrest and hypotension, where it helps to increase blood pressure and maintain organ perfusion. The drug is also used during anesthesia to stabilize blood pressure and prevent hypotension.
Additionally, Norepinephrine Bitartrate is indicated for the treatment of myocardial infarction, a condition characterized by reduced blood flow to the heart. By increasing blood pressure, the drug helps to improve blood flow and prevent further damage to the heart muscle.
Another important indication for Norepinephrine Bitartrate is pheochromocytoma, a rare tumor that affects the adrenal glands. The drug is used to control blood pressure in patients with this condition, as it helps to reduce the release of catecholamines, which are responsible for the symptoms associated with pheochromocytoma.
Furthermore, Norepinephrine Bitartrate is utilized in the treatment of poliomyelitis, a viral infection that affects the nervous system. The drug helps to maintain blood pressure and prevent complications associated with the disease.
Lastly, Norepinephrine Bitartrate is indicated for sepsis, a life-threatening condition caused by a severe infection. By increasing blood pressure, the drug helps to improve organ perfusion and prevent organ failure.
👇Please click on the image below to directly access the latest data (R&D Status | Core Patent | Clinical Trial | Approval status in Global countries) of this drug.
Mechanism of Action for Norepinephrine Bitartrate: α1A-AR agonists & α1B-AR agonists
α1A-AR agonists and α1B-AR agonists are terms related to biomedicine, specifically to pharmacology and drug development.
From a biomedical perspective, α1A-AR and α1B-AR refer to subtypes of alpha-1 adrenergic receptors. Adrenergic receptors are proteins found on the surface of cells that bind to the neurotransmitter norepinephrine (also known as noradrenaline) and trigger a physiological response. The alpha-1 adrenergic receptors are further divided into subtypes, including α1A-AR and α1B-AR.
α1A-AR agonists are drugs or compounds that specifically bind to and activate the α1A-AR subtype. By activating α1A-AR, these agonists can elicit various physiological responses, such as vasoconstriction (narrowing of blood vessels), smooth muscle contraction, and increased blood pressure. These agonists are used in the treatment of conditions like benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), a non-cancerous enlargement of the prostate gland.
Similarly, α1B-AR agonists are drugs or compounds that selectively bind to and activate the α1B-AR subtype. Activation of α1B-AR can lead to similar physiological effects as α1A-AR agonists, including vasoconstriction. These agonists may have potential applications in the treatment of conditions such as hypertension (high blood pressure) or other cardiovascular disorders.
In summary, α1A-AR agonists and α1B-AR agonists are drugs or compounds that target specific subtypes of alpha-1 adrenergic receptors, which play a role in regulating various physiological processes. These agonists can be used to elicit specific therapeutic effects in the treatment of certain medical conditions.
Drug Target R&D Trends for Norepinephrine Bitartrate
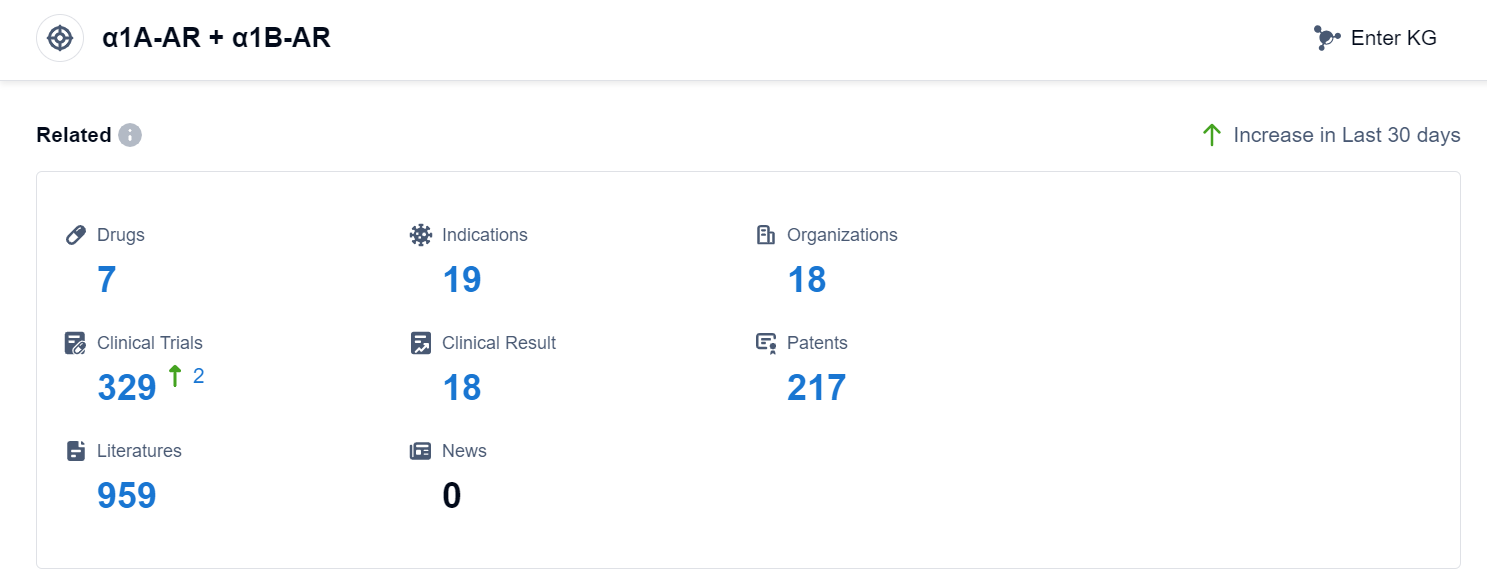
According to Pasnap Synapse, as of 10 Sep 2023, there are a total of 7 α1A-AR + α1B-AR drugs worldwide, from 18 organizations, covering 19 indications, and conducting 329 clinical trials.
In conclusion, the analysis of the target α1A-AR + α1B-AR reveals that companies such as Baxter International, Inc., InfoRLife SA, Grand Pharmaceutical Group Ltd., Shanghai Liuliguang Pharmaceutical Development Co., Ltd., and Pfizer Inc. are growing fastest under this target. Drugs targeting α1A-AR + α1B-AR have been approved for indications such as hypotension, anesthesia, heart arrest, pheochromocytoma, poliomyelitis, myocardial infarction, and sepsis. The development of small molecule drugs is progressing rapidly, with two approved drugs and one in the preclinical stage. The United States and China are leading in the development of drugs targeting α1A-AR + α1B-AR, with other countries also contributing to the research and development efforts. Overall, the target α1A-AR + α1B-AR shows promise in addressing various medical conditions, and further research and development are expected in the future.
👇Please click on the picture link below for free registration or log in directly if you have a freemium account, you can browse the latest research progress on drugs, indications, organizations, clinical trials, clinical results, and drug patents related to this target
Conclusion
In summary, Norepinephrine Bitartrate is a small molecule drug that targets α1A-AR and α1B-AR receptors. It has been approved for use in various therapeutic areas and is indicated for anesthesia, heart arrest, hypotension, myocardial infarction, pheochromocytoma, poliomyelitis, and sepsis. The drug was first approved in the United States in 1950 and is widely used globally for its cardiovascular and nervous system benefits.