Decoding Risdiplam: A Comprehensive Study of its R&D Trends and Mechanism on Drug Target
Risdiplam's R&D Progress
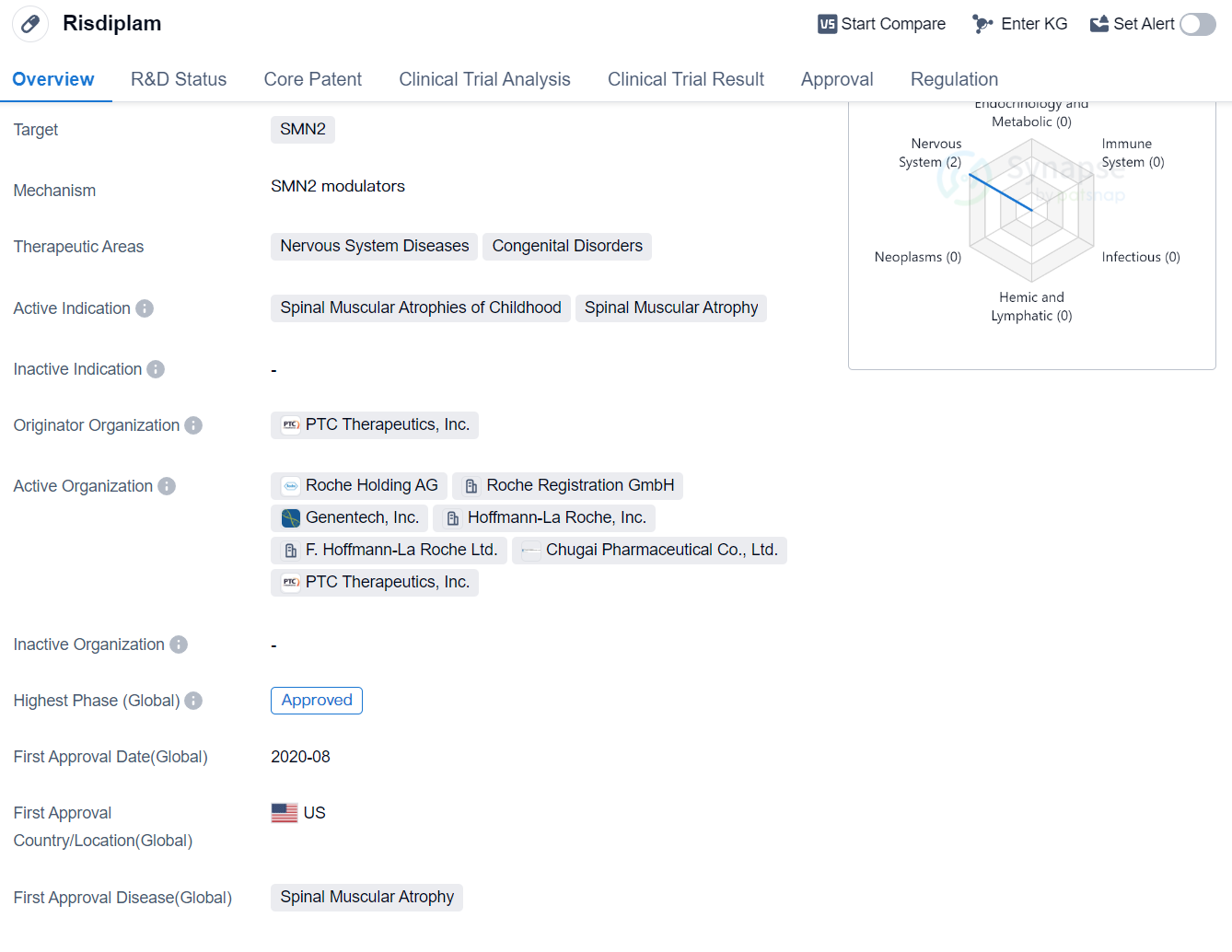
Risdiplam is a small molecule drug that targets SMN2, making it a potential treatment option for nervous system diseases and congenital disorders. Specifically, it has shown promise in treating Spinal Muscular Atrophies of Childhood and Spinal Muscular Atrophy.
The drug was developed by PTC Therapeutics, Inc., an originator organization in the pharmaceutical industry. It has successfully completed the highest phase of clinical trials which is approved globally.
Risdiplam received its first approval in the United States in August 2020, marking a significant milestone for the drug and its potential impact on patients suffering from the aforementioned conditions. The approval was granted based on the drug's efficacy and safety profile demonstrated during clinical trials.
In terms of regulatory status, Risdiplam has been designated as an orphan drug, indicating its potential to treat rare diseases. It has also received additional regulatory designations such as PRIME, Accelerated Assessment, Priority Review, Fast Track, and Special Review Project. These designations highlight the urgency and importance of bringing this drug to market quickly to address unmet medical needs.
👇Please click on the image below to directly access the latest data (R&D Status | Core Patent | Clinical Trial | Approval status in Global countries) of this drug.
Mechanism of Action for Risdiplam: SMN2 modulator
SMN2 modulators are a type of drugs or compounds that target the SMN2 gene. SMN2 stands for Survival Motor Neuron 2, which is a gene involved in the production of survival motor neuron (SMN) protein. SMN protein is essential for the proper functioning and survival of motor neurons, which are nerve cells responsible for controlling muscle movement.
In the context of biomedicine, SMN2 modulators are specifically designed to modify the splicing of the SMN2 gene. The SMN2 gene produces a shorter and less functional form of the SMN protein compared to another gene called SMN1. People with spinal muscular atrophy (SMA), a genetic disorder characterized by the degeneration of motor neurons, often have mutations in the SMN1 gene. However, they still have the SMN2 gene, which can produce some functional SMN protein.
SMN2 modulators aim to increase the production of functional SMN protein from the SMN2 gene by promoting the inclusion of exon 7 during the splicing process. Exon 7 is a critical part of the SMN protein that is often skipped in the splicing of the SMN2 gene, leading to the production of a less functional protein. By modulating the splicing of SMN2, these drugs can enhance the production of full-length SMN protein, which can help improve motor neuron function and potentially slow down the progression of SMA.
Overall, SMN2 modulators are a promising therapeutic approach for the treatment of spinal muscular atrophy, aiming to increase the production of functional SMN protein from the SMN2 gene and improve motor neuron function.
Drug Target R&D Trends for Risdiplam
The analysis of the current competitive landscape and future development of target SMN2 reveals several key findings. Roche Holding AG, Biogen, Inc., Ionis Pharmaceuticals, Inc., PTC Therapeutics, Inc., and Novartis AG are the companies growing fastest under the current target, with Roche Holding AG having the highest stage of development. The main indication for drugs targeting SMN2 is Spinal Muscular Atrophy, with some drugs also targeting other neuromuscular diseases. Small molecule drugs and Antisense oligonucleotides are the drug types progressing most rapidly, indicating potential competition around innovative drugs. The United States, European Union, and China are among the countries developing fastest under the target SMN2, with China showing significant progress. Overall, the analysis suggests a dynamic and competitive landscape in the pharmaceutical industry for target SMN2, with opportunities for further research, development, and collaboration.
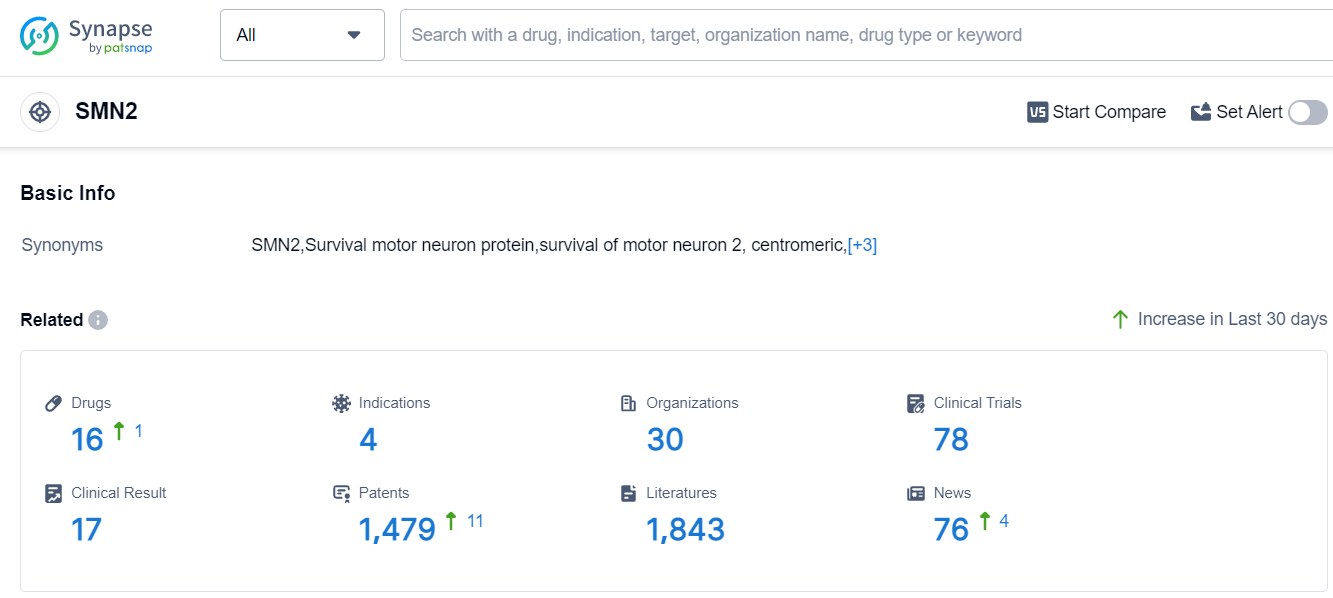
According to Patsnap Synapse, as of 11 Sep 2023, there are a total of 16 SMN2 drugs worldwide, from 30 organizations, covering 4 indications, and conducting 78 clinical trials.
Please click on the picture link below for free registration or log in directly if you have a freemium account, you can browse the latest research progress on drugs, indications, organizations, clinical trials, clinical results, and drug patents related to this target
Conclusion
Overall, Risdiplam represents a significant advancement in the field of biomedicine, particularly in the treatment of nervous system diseases and congenital disorders. Its small molecule structure and targeting of SMN2 make it a promising therapeutic option. With its successful completion of clinical trials and approvals in both the United States and China, Risdiplam has the potential to improve the lives of patients suffering from Spinal Muscular Atrophies of Childhood and Spinal Muscular Atrophy. The regulatory designations it has received further emphasize the importance of this drug and the need for expedited access for patients in need.